Are the new gridded DSM/DTMs of the Piemonte Region (Italy) proper for forestry? A fast and simple approach for a posteriori metric assessment
Enrico Borgogno Mondino, Vanina Fissore , Andrea Lessio, Renzo Motta
iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry, Volume 9, Issue 6, Pages 901-909 (2016)
doi: https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor1992-009
Published: Aug 29, 2016 - Copyright © 2016 SISEF
Research Articles
Abstract
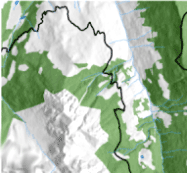
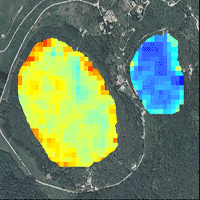
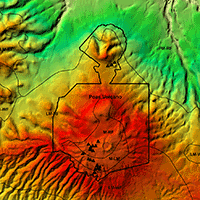
Aerial LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) derived data are widely adopted for the study and characterization of forests. In particular, LiDAR derived-CHM (Canopy Height Model) has proved essential in identifying tree height variability and estimating many forest features such as biomass and wood volume. However, CHM quality may be affected by internal limits and anomalies caused by raw data (point cloud) processing (i.e., vertical errors), which are quite often disregarded by users, thus generating potentially erroneous results in their applications. In this work, an auto-consistent procedure for the fast evaluation of CHM accuracy has been developed based on the assessment of internal anomalies affecting CHM data obtained by differencing gridded DSM (Digital Surface Model) and DTM (Digital Terrain Model). To this purpose, a CHM was generated using the gridded DTMs and DSMs provided by the Cartographic Office of the Piemonte Region (north-western Italy). We estimated the local potential CHM error over the whole region, and demonstrated its strictly dependence on the terrain morphometry, particularly slope. The relationship between potential CHM error and slope was modeled separately for mountain, hill and flat terrain contexts, and used to produce a potential error map over the whole region. Our results showed that approximately 20% of the regional territory suffers from CHM uncertainty (in particular high elevation areas, including the treeline), though the majority of regional forest categories was affected by negligible CHM error. The potential consequences of CHM error in forest applications were evaluated, concluding that the tested LiDAR dataset provide a reliable basis for forest applications in most of the regional territory.
Keywords
ALS, LiDAR, CHM, Data Quality, Vertical Errors, Slope Effect, Forest Applications
Authors’ Info
Authors’ address
Vanina Fissore
Andrea Lessio
Renzo Motta
DISAFA, University of Torino, l.go Paolo Braccini 2, I-10095, Grugliasco, TO (Italy)
Corresponding author
Paper Info
Citation
Borgogno Mondino E, Fissore V, Lessio A, Motta R (2016). Are the new gridded DSM/DTMs of the Piemonte Region (Italy) proper for forestry? A fast and simple approach for a posteriori metric assessment. iForest 9: 901-909. - doi: 10.3832/ifor1992-009
Academic Editor
Matteo Garbarino
Paper history
Received: Jan 21, 2016
Accepted: May 13, 2016
First online: Aug 29, 2016
Publication Date: Dec 14, 2016
Publication Time: 3.60 months
Copyright Information
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2016
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Web Metrics
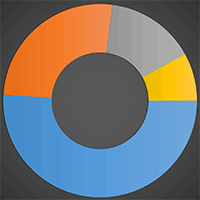
Breakdown by View Type
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 48379
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 40560
Abstract Page Views: 2782
PDF Downloads: 3757
Citation/Reference Downloads: 48
XML Downloads: 1232
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 3484
Overall contacts: 48379
Avg. contacts per week: 97.20
Citation Metrics
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2016): 11
Average cites per year: 1.10
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
References
Data reduction and error analysis for the physical sciences. McGraw-Hill, New York, USA, pp. 336.
Gscholar
Tipi forestali del Piemonte, Regione Piemonte [Forest types of Piemonte Region, Piemonte Region]. Blu edizioni, Torino, Italy, pp. 204. [in Italian]
Gscholar
Factors affecting the quality of DTM generation in forested areas. In: Proceedings of ISPRS Workshop “Laser scanning 2005”. Enschede (Netherlands) 12-14 Sep 2005. International Archives of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, pp. 85-90.
Online | Gscholar
Leica ALS50-II airborne laser scanner product specification. Leica Geosystems AG, Heerbrugg, Switzerland, pp. 12.
Gscholar
Individual tree segmentation over large areas using airborne LiDAR point cloud and very high resolution optical imagery. In: Proceedings of “IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS)”. Québec City (Canada) 13-18 Jul 2014, pp. 800-803.
CrossRef | Gscholar
Produzione di supporti topografici per la pianificazione a livello locale nella Regione Piemonte (IT), Relazione MDE Blocco 03 [Production of topographic products for local planning in Piemonte Region, MDE block 3 relation]. Regione Piemonte, Turin, Italy, pp. 23. [in Italian]
Gscholar