Estimating machine impact on strip roads via close-range photogrammetry and soil parameters: a case study in central Italy
iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry, Volume 11, Issue 1, Pages 148-154 (2018)
doi: https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor2590-010
Published: Feb 07, 2018 - Copyright © 2018 SISEF
Research Articles
Abstract
Several studies have been carried out to investigate soil compaction and rutting after logging vehicle traffic, based on time consuming and punctual field measurements. The objective of this study was to measure soil disturbances with two methods: (i) a new, image-based models derived by a structure-from-motion (SfM) photogrammetry approach; and (ii) a traditional soil sampling (bulk density and shear strength). Two trails were selected in a logging area (central Italy), one trafficked by a forwarder (FT) and one trafficked by a skidder (ST). Data collection was conducted before, during and after timber extraction. Image-based models derived by SfM photogrammetry was used to highlight the differences in the shape and distribution of the disturbances along ST and FT. Results showed that the physical parameters of soil significantly changed due to both FT and ST traffic. Machine passes increased bulk density (111% and 31% for FT and ST, respectively), penetration resistance (29% and 24% for FT and ST, respectively) and shear resistance (14% and 6% for FT and ST, respectively), whereas porosity decreased (46% and 9% for FT and ST, respectively). Significant differences between FT and ST were found when comparing ruts removal and bulges with SfM photogrammetry. After logging, FT clearly showed ruts and bulges, whereas in ST ruts and bulges were not visible, but soil displacement in the direction of extraction was evident and measurable. Nevertheless, although our result shows a larger soil disturbance caused by forwarders than skidders, it is not possible to draw any general conclusions about differences between the two machines. Data about the machine passes, or the wood volumes transported over each trial area were not available; therefore, any general conclusion is misleading. SfM photogrammetry give information not available via traditional methods, thus improving impact assessment.
Keywords
Forest Operation, Soil Impacts, Soil Displacement, Close Range Photogrammetry, Digital Terrain Model
Introduction
Forest operations are recognized as sources of soil disturbance and erosion and have been the subject of much research since the 1950s ([9]). In particular, machine trafficking causes soil compaction ([25]) and rutting, and is one of the major sources of human-induced forest soil degradation ([18], [6]). The pressure exerted by loaded vehicles moving through the forest is a major factor causing compaction and rut formation ([36], [4], [40], [16]). In the last decades, the weights of forestry machines have increased, thus raising new concern over forest soil degradation ([47]). Skid trails are forest areas prone to soil compaction and rutting because the road bed is not naturally compacted and do not have constructed drainage, leading to a reduction in soil porosity, water infiltration and gas exchange, as well as increasing soil erosion, water logging and mudflows ([26], [34], [13]).
Most studies concerning soil degradation due to forest operations have examined the physical parameters of soil, such as bulk density, total porosity, macro and micro porosity, shear and penetration resistances, and infiltration capacity ([4], [5], [29], [33]). The physical parameters of soil are usually determined by means of soil sample collection and analysis, or measured using specific instruments, such as penetrometers and scissometers ([41], [52]), or by means of manual measurements of cross-sectional and longitudinal profiles on skid trails ([31]). Although these methods have been improved over time ([29]), they are time consuming and costly. Moreover, these methods may affect the study area when repeatedly applied.
Recently, the field methods used for the analysis of geomorphological processes and quantification of soil impacts have changed, passing from traditional methods ([32], [6], [31]) to the use of remote sensing and proximal sensing techniques ([15], [49]) in order to analyse the spatial distribution of soil disturbances ([31], [17]). In recent decades, techniques allowing rapid acquisition of high-density topographic data have proliferated ([38]). These techniques include terrestrial laser scanners (TLS - [54], [11]) and photogrammetry techniques ([11], [30]), which are used, for example, for the analysis of soil erosion ([37], [38]). Such techniques make it possible to generate digital elevation models that accurately reproduce topographic surfaces ([54], [42], [43], [38]). Various methods have been proposed to measure soil surface microtopography ([21]), and their relative strengths and weaknesses have been discussed in recent comparative studies ([28], [2]). Although the use of close-range photogrammetry in mapping soil surface structure was demonstrated more than 20 years ago ([57]), the advent of structure-from-motion (SfM) photogrammetry ([24]) has generated an improvement in topographic methods, due to its better accessibility to a wider variety of users, low cost, and increased automatization of routines and workflow ([38]). The advantages introduced by SfM in geosciences have been demonstrated by James & Robson ([24]), and the reconstruction of high-resolution surface models ([50]) has opened new possibilities of application in geoscience analysis ([11]), forestry ([42], [43]) and agriculture ([39]).
The objective of this study was to investigate the usefulness of SfM photogrammetry in association with traditional methods for assessing soil disturbance in forest operations. The effects of forest operations on soil were considered for two types of forest machines, forwarder and skidder. The specific objectives of the study were: (i) to evaluate multitemporal analysis based on the use of image-based high-resolution ground surface models generated through the use of SfM photogrammetry workflow as an instrument to determine rutting and bulges caused by forest operations along all trail surfaces; (ii) to assess soil compaction with traditional techniques.
Materials and methods
Study area
The study was conducted in central Italy, in the Biogenetic reserve of Vallombrosa, which is in the municipality of Reggello (Florence Province). The study area covers 5.78 ha between 920 and 980 m a.s.l. and is characterised by moderate steep terrain (mean slope = 30%). The forest is characterised by an even-aged silver fir (Abies alba Mill.) plantation that was completely destroyed by a windstorm on the 5th of March, 2015 ([45], [12]). The climate is temperate-humid with Mediterranean-type rainfall (summer minimum) and a mean annual temperature of 9.7 °C. From 2009-2013, the mean annual precipitation was 1337 mm, with an average of 71.2 mm in June-August ([7]). Soil developed on sedimentary rocks of the boulder formation of Chianti, which are comprised of sandstone with thin layers of siltstone and rarely marl. Soil can be classified as Umbrepts and Umbric Dytrochrepts, based on the USDA Soil Taxonomy ([51]). This study was carried out during salvage harvesting of damaged trees.
Forest machines
Two forestry machines were used in our study. The first was a forwarder John Deere JD1110 D with an empty mass of 17.5 tons (121 kW), which was equipped with 8-wheel Nokian Forest Rider 700/50 × 26.5 tires inflated at 51 kPa. The second machine was a skidder John Deere 548H with an empty mass of 11 tons (96 kW), equipped with 4-wheel Nokian Forest Rider 622/32 × 24.5 tires with chains, inflated to 68 kPa.
Experimental design
Before logging, two 25 × 3.5 m plots were randomly selected in the study area along the trails designed for timber extraction; the first plot in the trail designated to be trafficked by the forwarder (henceforth: FT, forwarder trail), and the second in the trail to be trafficked by the skidder (ST, skidder trail). The mean slopes of the FT and ST plots were 25% and 20%, respectively.
Data collection was carried out at three time points: before forest logging (Time 1), considered as control data; seven working days after the beginning of logging (Time 2); and 13 working days after the beginning of logging (i.e., the day after the end of wood extraction - Time 3). The collected data were compared, taking into account the difference between: (i) periods 1 and 2 (Δ12); (ii) periods 2 and 3 (Δ23); and (iii) periods 1 and 3 (Δ13). The forwarder transported logs up to 6 m in length and the skidder transported whole un-delimbed trees. Extraction was carried out in uphill direction for both machines.
Data collection
Photogrammetry data
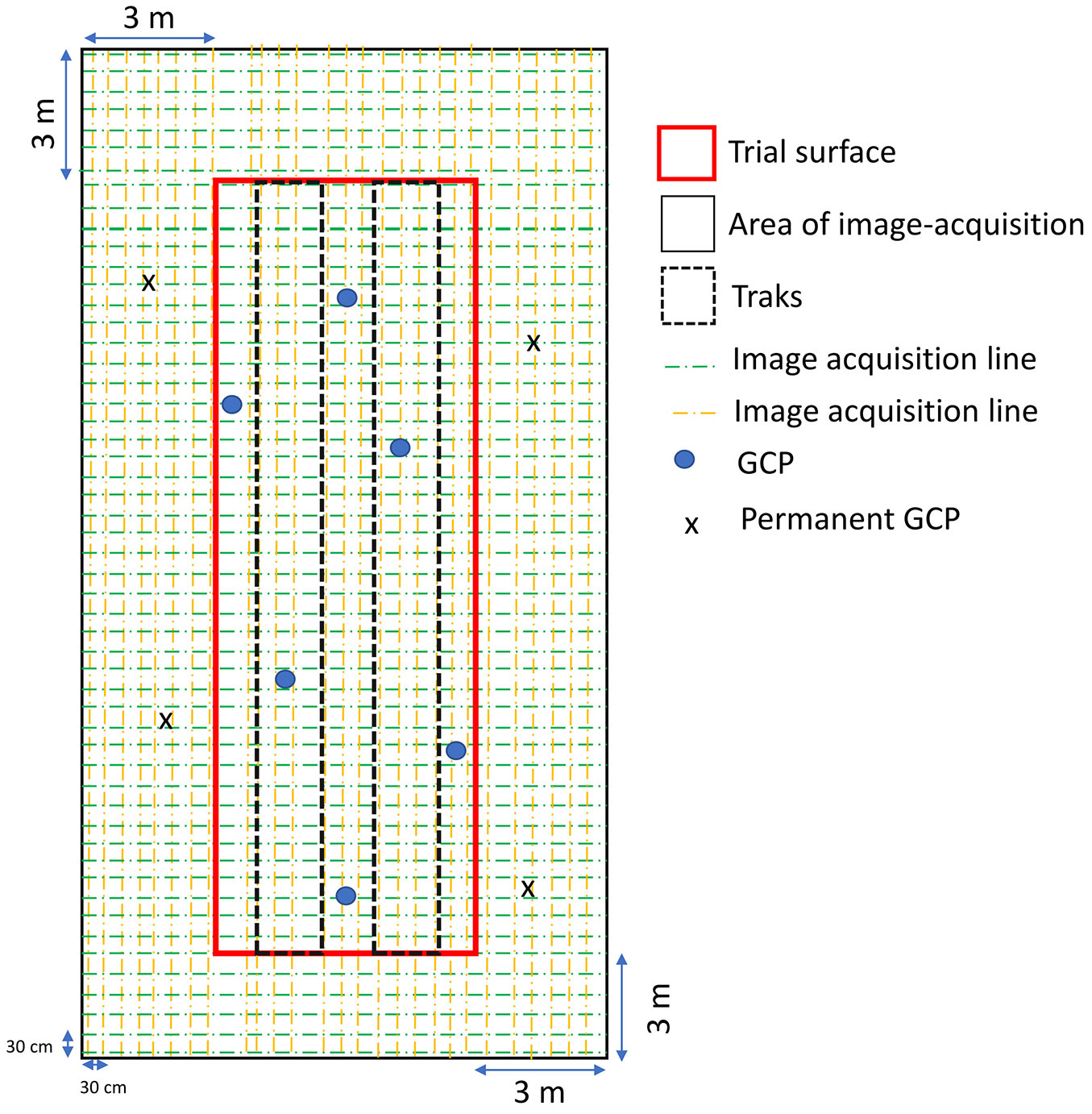
Image acquisition. Pictures in FT and ST plots were collected using a consumer reflex camera (Tab. 1) mounted on a tripod 1.90 m in height. The image points were located at the corner of a rectangular network (Fig. 1). Images were acquired in nadir angle with an overlap and a side lap of 95% every 30 centimetre. The area covered by the images was greater than that of the plots, for a total of 180 m2, in order to have a robust model of the trails. A total of 350 images were acquired for each trail in each period. The image acquisition was done in 20 minutes for each trial in each period.
Tab. 1 - Details for camera and sensors used in the current study.
| Camera model | Nikon D90® |
| Image resolution (pixel) | 4288×2848 |
| Focal length (mm) | 22 |
| Pixel size (mm) | 1×1 |
Fig. 1 - Schema of image acquisition and location of ground control points (GCPs). Images were acquired in the intersection of the line acquisition (i.e. every 30 cm).
Ground control points. Ground control points (GCPs) were identified for image geolocation. Two types were measured in each trial: (i) six GCPs to georeference each model; and (ii) four permanent GCPs outside the trails that were used to co-register the three models obtained (Fig. 1). The X, Y and Z coordinates of each GCP were measured with a total station Leica TCA1800® (Leica Geosystems AG, Heerbrugg, Switzerland). The GCPs were translocated into the geographic coordinates system (UTM32N-WGS84) using the coordinates of one fixed control point measured by a GPS receiver (Trimble JUNO® Series 3B, GeoMobile Innovations, Corvallis, OR, USA). The permanent GCPs were represented in the field by a survey geodetic marker and were protected from the passage of forest machines.
Photogrammetry process. The SfM technique was applied to obtain a 3D georeferenced point cloud from which a digital surface model (DSM) was derived. Data were processed using the Agisoft PhotoScan® Structure for Motion (SfM) photogrammetric software package (http://www.agi soft. com/), which has been successfully used in different analyses ([53], [27], [60], [46]). The workflow was comprised of the following steps: (i) image import; (ii) image alignment; (iii) georeferencing; (iv) optimisation of image alignment; (v) creation of the point cloud; and (vi) generation of the DSM. After the alignment, all photos were oriented, and the raw point cloud was georeferenced. The GCPs were then used to optimise the alignment of camera positions and the orientation of the data, which allowed for better accuracy and reconstruction results. Based on the estimated camera positions and GCPs, the depth information for each image was calculated using Agisoft PhotoScan®, to be combined into a single dense point cloud dataset. The georeferentiation errors calculated by the software along the x, y and z coordinates for each 3D point cloud models obtained via the structure-from-motion methodology (i.e., FT1, FT2, FT3, SK1, SK2, SK3) for X, Y and Z coordinate was < 1 cm.
Co-registration of model and difference calculation. The three-dense point clouds obtained by SfM workflow (FT1, FT2, FT3 and SK1, SK2, SK3) were co-registered using the four permanent GCPs outside the trail area by means of a point-based alignment the open source freeware CloudCompare ver. 2 (⇒ http://cloudcompare.org/). This tool coarsely aligns two-point clouds using the “4 points Congruent Sets For Robust Registration” algorithm ([3]). After the co-registration process, the point clouds were rasterised with the rasterisation tools present in CloudCompare to create very high-resolution digital terrain models (DTMs) of each period for FT (FT-DTM1, FT-DTM2, FT-DTM3) and SK (SK-DTM1, SK-DTM2, SK-DTM3), with pixels of 0.1 × 0.1 cm. For each raster cell, the average elevation of the points in the pixel area was found and recorded in the cell.
The digital terrain models before logging (DTM1), half-way through logging operations (DTM2) and after logging operations (DTM3) were compared using map algebra tools, and differences in terrain elevation (Δz) after forest operations were computed as Δ12 = DTM1-DTM2, Δ23 = DTM2-DTM3 and Δ13 = DTM1-DTM3. Pixels with Δ < 0 were considered to be in ruts and pixels with Δ > 0 were considered to be in bulges along the surface of the two trails. The average, minimum and standard deviation were computed for Δ < 0 pixels, whereas the average, maximum and standard deviation were computed for Δ > 0 pixels for Δ12, Δ23 and Δ13.
Physical parameters
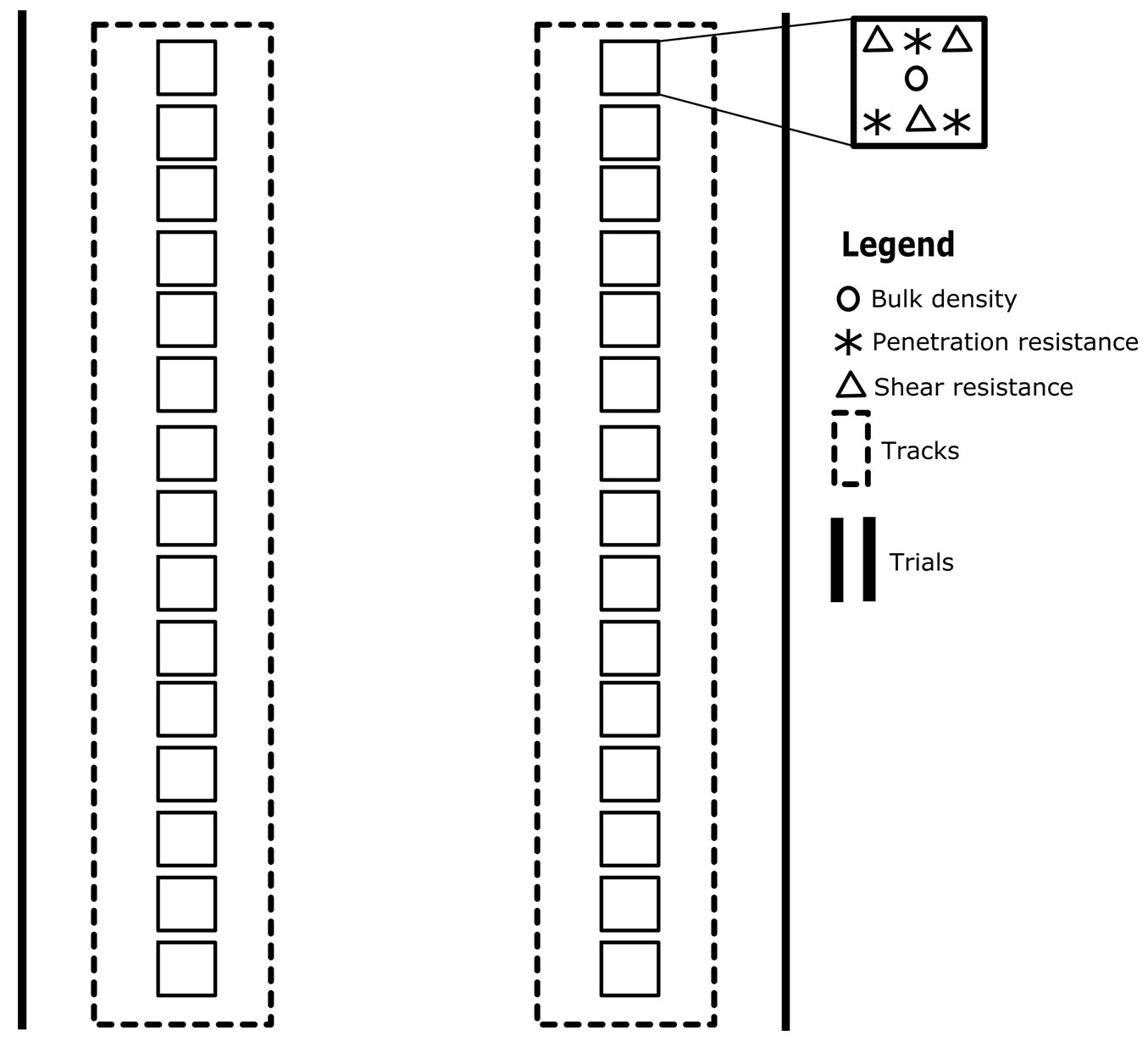
Thirty soil samples were collected at Times 1, 2 and 3, for a total of 90 (30 × 3) samples (Fig. 2). Samples were extracted from the topsoil layer using a rigid metallic cylinder (8.5-cm height and 5.0-cm inner diameter) after litter removal and used for determining bulk density. Penetration and shear resistance were measured in triplicate close to each sampling point, using a TONS/FT2 penetrometer (Eijkelkamp, Giesbeek, Netherlands) and a GEONOR 72412 scissometer (Geonor, Augusta, NJ, USA), respectively. Soil samples were taken along the tire tracks of the two machines (Fig. 1).
Fig. 2 - Sampling scheme of soil physical parameters in left and right track caused by a forwarder or skidder.
All soil samples were weighed in the laboratory before (“moist weight”) and after oven drying at 105 °C to a constant weight (“dry weight”). Bulk density was determined as the ratio between soil sample dry weight and volume. Soil porosity (PO) was determined using the following equation (eqn. 1):
where Dp is the particle density measured by a pycnometer (Multipycnometer, Quantachrome, Boynton Beach, FL, USA) on the same soil samples used to determine the bulk density (BD).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were carried out using the software package STATISTICA® ver. 7.1 (StatSoft, Tulsa, OK, USA). All data were checked for normality (Kolmogorov-Smirnov test) and homogeneity of variance (Levene’s test) before the analysis. MANOVA and post-hoc Tukey’s HSD test were applied to physical parameters to assess the statistical differences among times (1-2, 2-3 and 1-3) and between machines (FT and ST).
A t-test was applied to the values of changes in ground surface level (Δ < 0 = ruts/soil removal and Δ > 0 = bulges/soil increase) between Δ12 and Δ23 in order to assess statistically significant differences between both times (2 and 3) and machines (FT and ST).
Results
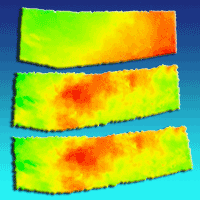
The high-resolution surface models were derived by SfM workflow. Changes in soil surface level after logging are indicated with different colours in Fig. 3 and Fig. 4.
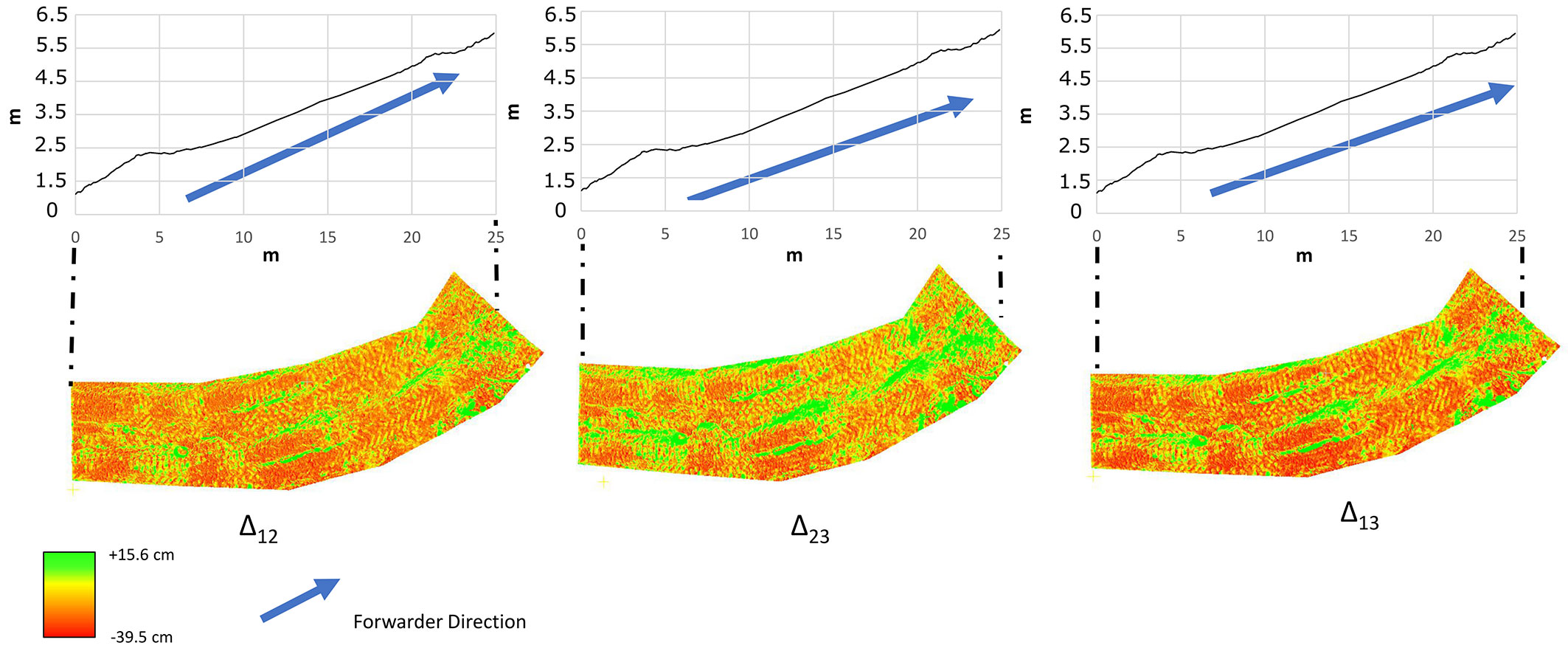
Fig. 3 - Effects on soil produced by forwarder passes between Time 1 and Time 2 (Δ12), Time 2 and Time 3 (Δ23), and between Time 1 and Time 3 (Δ13).
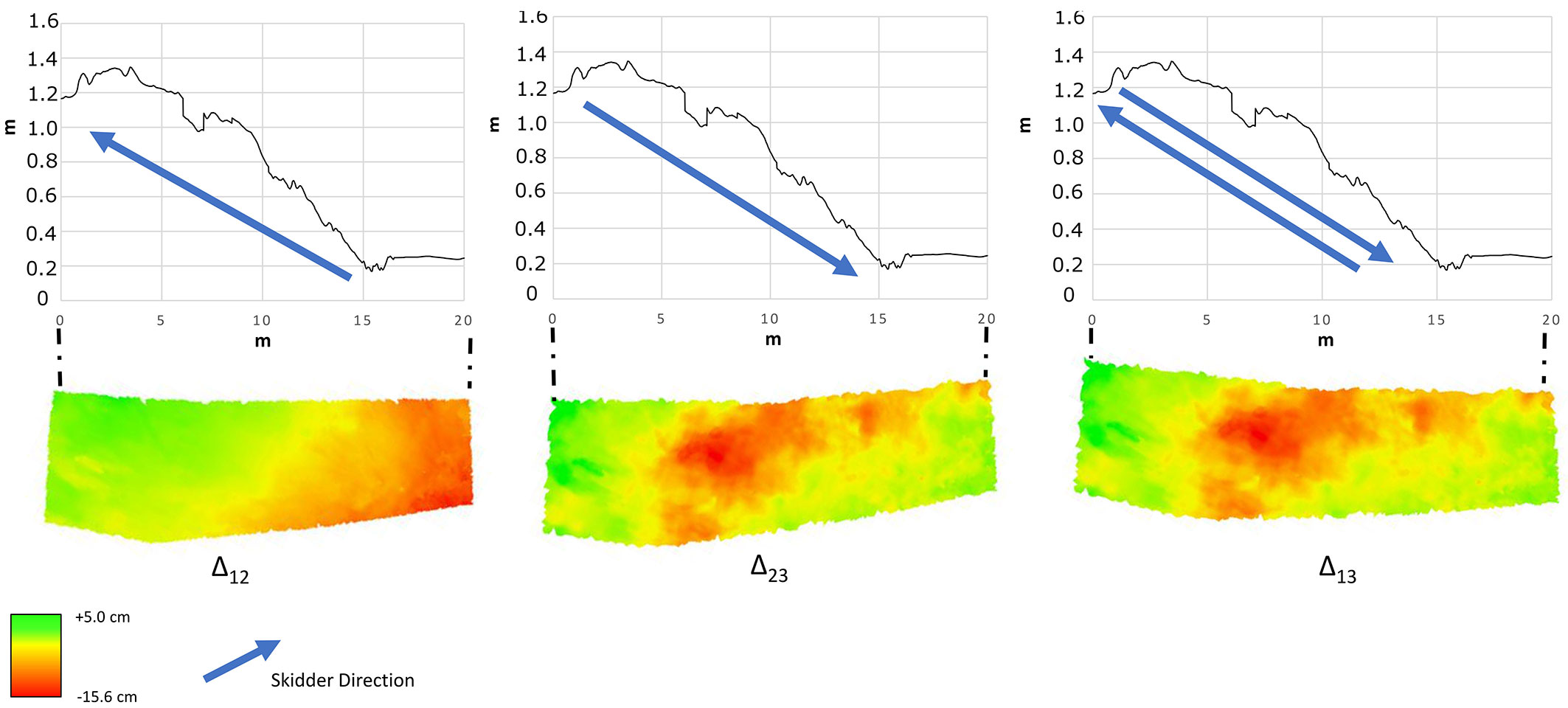
Fig. 4 - Effects on soil produced by skidder passes between Time 1 and Time 2 (Δ12), Time 2 and Time 3 (Δ23), and between Time 1 and Time 3 (Δ13).
Significant differences (p < 0.05) between FT and ST were found when comparing ruts/soil removal and bulges/soil increases at both time intervals Δ12 and Δ23 (Tab. 2). Specifically, significant differences in bulge height/soil increase were recorded between vehicles at both time intervals (Δ12 and Δ23), whereas rut depth/soil removal showed significant differences only in the first period (Δ12). FT treatment showed greater rut depth and bulge height than did ST (Tab. 2). For both FT and ST, the greatest variation in ground surface was recorded in the first period (Δ12). The effects on soil produced by the skidder and forwarder also differed in terms of disturbance type and shape. On FT, the two ruts caused by forwarder passes were clearly visible along the trail and were associated with bulges at both sides of the ruts, but soil displacement along the trail was not detectable (Fig. 3). On the contrary, ruts (wheel tracks) were not visible on ST, but soil displacement was clearly detectable along the trail (Fig. 4). On ST, the comparison between Time 1 (control) and Time 2 (seven days of logging) showed soil displacement in the same direction as that of timber extraction. In the second part of logging, from Time 2 to Time 3, soil was further displaced due to the increasing number of passes. Specifically, a certain quantity of soil was removed on ST at the beginning of the steeper part of the trail and replaced in the flat area at the end of the plot in the skidding direction (Fig. 4).
Tab. 2 - Quantification of the ground surface variation produced by forwarder trails (FT) and skidder trails (ST) after different time periods, calculated considering all Δ < 0 pixels as rutting and all Δ > 0 pixels as bulges. Upper-case letters represent significant differences between FT and ST at the same period, whereas lower-case letters represent significant differences between different periods for the same vehicle (t-test). (STD): standard deviation; (*): p < 0.05; (**): p<0.001.
| Trail | Time interval | Ground Surface Variation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rut depth/soil removal (Δ < 0) | Bulge/soil increase (Δ > 0) | ||||
| Minimum (cm) |
Mean ± STD (cm) |
Maximum (cm) |
Mean ± STD (cm) |
||
| FT | Δ12 | -36.5 | -17.9 ± 12.1 a* A* | 13.5 | 9.5 ± 2.5 a* A* |
| Δ23 | -12.3 | -4.7 ± 3.6 b* A | 5.3 | 3.7 ± 2.1 b* A* | |
| Δ13 | -39.5 | -12.3 ± 8.2 | 15.6 | 9.8 ± 2.6 | |
| ST | Δ12 | -21.4 | -8.9 ± 2.9 a** B* | 5.0 | 4.1 ± 1.0 a* B* |
| Δ23 | -10.7 | -4.8 ± 2.5 b** A | 1.4 | 1.1 ± 0.8 b* B* | |
| Δ13 | -15.6 | -6.1 ± 5.3 | 3.5 | 2.2 ± 1.6 | |
On FT, soil moisture, bulk density, porosity, and shear and penetration resistance were significantly higher after logging operations (at Time 2 and Time 3) as compared with control (Time 1). The same parameters did not show significant differences between Time 2 and Time 3, thus suggesting that most of the compaction was reached within the first several logging days. Similar results were obtained on ST, except that soil moisture did not show differences between Time 1 and Time 2 (Tab. 3).
Tab. 3 - Results of MANOVA (mean ± standard deviation) to evaluate differences in soil parameters between trails used by different logging vehicles (Wilks test’s F = 42.33, p < 0.001). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between Time 1, Time 2 and Time 3 after Tukey’s HSD tests (p < 0.05, N = 90). Different uppercase letters indicate significant differences between FT and ST at the same time after Tukey’s HSD tests (p < 0.05, N = 60). (FT): forwarder trail; (ST): skidder trail.
| Trail | Time | Soil moisture (%) |
Bulk density (g cm-3) |
Porosity (%) |
Shear resistance (kPa) |
Penetration resistance (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FT | 1 | 19.38 ± 4.86 aA | 0.81 ± 0.07 aA | 66.28 ± 6.55 aA | 68.02 ± 2.54 aA | 0.35 ± 0.43 aA |
| 2 | 11.09 ± 1.55 bA | 1.69 ± 0.24 bA | 35.89 ± 9.45 bA | 77.81 ± 7.92 bA | 0.46 ± 0.34 bA | |
| 3 | 11.13 ± 1.56 bA | 1.71 ± 0.25 bA | 35.88 ± 9.44 bA | 77.80 ± 7.93 bA | 0.45 ± 0.35 bA | |
| ST | 1 | 19.37 ± 4.86 aA | 0.82 ± 0.07 aA | 66.26 ± 6.55 aA | 68.04 ± 2.54 aA | 0.33 ± 0.43 aA |
| 2 | 19.24 ± 4.70 aB | 1.06 ± 0.16 bB | 61.03 ± 6.59 bB | 72.40 ± 8.20 bB | 0.42 ± 0.47 bB | |
| 3 | 19.26 ± 4.72 aB | 1.07 ± 0.18 bB | 60.54 ± 6.62 bB | 72.33 ± 8.23 bB | 0.41 ± 0.51 bB |
Discussion
At present, the physical parameters of soil are generally assumed to be the most useful for the assessment of impacts on soil due to vehicle traffic ([9]). This is why we used bulk density, penetration resistance, shear resistance and soil porosity for measuring soil compaction. In agreement with the results of previous studies ([56], [58], [55], [20]), our findings showed that the investigated physical parameters of soil were significantly affected mainly by the first vehicle passes (comparison between Time 1 and Time 2). Further machine passes slightly increased or did not affect soil physical parameters.
Similar results concerning the impact of forwarder extraction on soil were recorded for the same parameters during timber extraction in the Italian Alps by Cambi et al. ([10]). Other studies, however, have found opposing results. Gondard et al. ([19]) assessed the impacts of clear-cutting in Aleppo pine (Pinus halepensis) forests in southern France using both forwarders and skidders, observing deep disturbance (i.e., “topsoil removed, subsoil exposed’’, according to methods and classification proposed by [35]) only when a skidder was used and no ruts. Similar results were reported by Deconchat ([14]) in mixed oak coppices (Quercus robur, Q. petraea and Q. pubescens) in southern France under an Oceanic climate. In this study, the observed greater soil disturbance was due to skidders rather than forwarders, though skidders were responsible for less than 1% of ruts. However, it should be considered that both the aforementioned studies were based on methods developed for assessing soil surface disturbance by the simple observation of soil conditions after logging, thereby less visible effects, such as soil compaction, cannot immediately detected ([48]). Moreover, it is worth noting that the first study was carried out under dry soil conditions, when soil is highly resistant to compaction and only the scratching action of dragged logs may have any effect.
Despite our results highlighted a larger soil disturbance caused by forwarders than skidders, we cannot draw any general conclusions about differences between the two machines. In fact, neither data about the number of machine passes nor the wood volumes transported over each trial area were available in this study. Without this information any general conclusion could be misleading. The most common planning of harvesting operations gives as a result that skidders are driven in a more dense extraction trail network than what forwarders do ([20]). This could be interpreted as the result of different soil disturbance at the harvesting site, which is more concentrated to a fewer extraction trails using forwarders and more spread using skidders.
Soil compaction also depends on machine size, weight and the pressure exerted on soil ([26], [36], [8], [16], [33]). To measure rutting, manual measurements of cross-sectional and longitudinal profiles are commonly applied ([31]). These methods are used for determining the rut depth at intervals along the trail and may be used to obtain a rough estimate of the volume of soil displaced. Our study indicated that the use of SfM photogrammetry may be very useful for the precise measurement of rutting and soil displacement. The analysis of differences in ground surface shape through the use of image-based models derived by SfM may offer detailed information about changes in the characteristics of ruts along the trail and may highlight soil displacement in all directions (e.g., from the tracks to the trail’s centre and sides, along the trail). Our results showed that in the first time interval, the FT caused deeper ruts and higher bulges than ST (Tab. 3). In the digital terrain model for FT obtained using SfM photogrammetry, ruts were clearly identifiable, whereas soil displacement along the trail was not detectable. In contrast, ruts were not visible on ST, but soil displacement along the trail was clearly detectable. These difference between FT and ST were likely due to the different types of timber extraction. In fact, rutting is caused by machine wheels both in FT and ST, but in ST the passing of the top end of the dragged logs ([59]) may change the impacts on soil in two ways: (i) the top ends of the dragged logs reshape the ground after the skidder passes, hiding the rut left by the wheels; (ii) the top ends of the dragged logs displace a certain quantity of soil in the dragging direction during each extraction trip. The latter effect may be particularly intense close to slope changes, because the heads of the logs scratch and displace the soil ([58], [22], [23], [1]). Soil compaction and soil crumbling and displacement may result in increased water runoff and soil erosion ([58], [9], [52]), with a consequent loss of fertile soil ([52]).
Forest soil is extremely fragile in physical terms and the improvement of methods for investigating the effects of soil disturbance is very important ([41]). With the use of image-based models derived from SfM photogrammetry, the quantification of soil displacement is highly improved in comparison to traditional sampling methods. The use of image-based models allows a new approach to the quantification of soil disturbance, improving the analysis of soil displacement due to logging, comparable with results obtained by point cloud derived by TLS ([31]). The use of a consumer reflex camera combined with the use of SfM software, however, can produce accuracy models at low cost, with respect to the use of TLS. The use of this methodology ([42], [43], [31]) can produce information along the entire trail, not only at the sampling points. This information is very important for forest managers, as it allows for monitoring of soil ecosystems after forest operations and planning of soil recovery practices ([44]).
Conclusions
The main aim of this study was to describe the effects of logging on both the physical properties of soil and the depth of ruts, through manual measurements in the field and photogrammetry analysis. Our findings highlighted how the use of both manual sampling and image-based models derived via SfM photogrammetry may be very useful to assess the impact of forest operations on soil. Both methods showed significant impacts on soil caused by two different forest machines.
Image-based models proved to be useful for determining distribution and types of disturbance, while the physical parameters of soils investigated in this study may be useful in determining local changes in soil characteristics. Our results showed that image-based models derived through SfM photogrammetric workflow can be useful tools to evaluate soil displacement caused by forest machines, improving monitoring and management of impacts upon soil and giving continuous soil displacement measures along the entire trail surface.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Territorial Office for Biodiversity (Carabinieri Forestale) of Vallombrosa (Firenze, Italy) for its support in the research study and Dr. Giovanni Galipò for his help with the field survey. A special thank to Ms. Ilaria Zorzi for her help with the fieldwork.
References
Gscholar
CrossRef | Gscholar
Gscholar
Gscholar
CrossRef | Gscholar
Gscholar
Gscholar
Authors’ Info
Authors’ Affiliation
Francesca Giannetti
Francesca Bottalico
Davide Travaglini
Gherardo Chirici
Enrico Marchi
Dipartimento di Gestione dei Sistemi Agrari, Alimentari e Forestali (GESAAF), Università di Firenze. v. S. Bonaventura 13, I-50145 Firenze (Italy)
Department of Forest Biomaterials and Technology, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Skogsmarksgränd, Umeå (Sweden)
Corresponding author
Paper Info
Citation
Cambi M, Giannetti F, Bottalico F, Travaglini D, Nordfjell T, Chirici G, Marchi E (2018). Estimating machine impact on strip roads via close-range photogrammetry and soil parameters: a case study in central Italy. iForest 11: 148-154. - doi: 10.3832/ifor2590-010
Academic Editor
Rodolfo Picchio
Paper history
Received: Aug 08, 2017
Accepted: Dec 11, 2017
First online: Feb 07, 2018
Publication Date: Feb 28, 2018
Publication Time: 1.93 months
Copyright Information
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2018
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Web Metrics
Breakdown by View Type
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 51527
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 42632
Abstract Page Views: 3774
PDF Downloads: 3884
Citation/Reference Downloads: 20
XML Downloads: 1217
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 2955
Overall contacts: 51527
Avg. contacts per week: 122.06
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2018): 23
Average cites per year: 2.88
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
Related Contents
iForest Similar Articles
Research Articles
Use of terrestrial laser scanning to evaluate the spatial distribution of soil disturbance by skidding operations
vol. 8, pp. 386-393 (online: 08 October 2014)
Research Articles
Impact of wheeled and tracked tractors on soil physical properties in a mixed conifer stand
vol. 9, pp. 89-94 (online: 22 May 2015)
Research Articles
Use of LIDAR-based digital terrain model and single tree segmentation data for optimal forest skid trail network
vol. 8, pp. 661-667 (online: 22 December 2014)
Research Articles
Influence of slope on physical soil disturbance due to farm tractor forwarding in a Hyrcanian forest of northern Iran
vol. 7, pp. 342-348 (online: 17 April 2014)
Research Articles
Assessment of timber extraction distance and skid road network in steep karst terrain
vol. 10, pp. 886-894 (online: 06 November 2017)
Research Articles
Wood-soil interactions in soil bioengineering slope stabilization works
vol. 2, pp. 187-191 (online: 15 October 2009)
Research Articles
Identification of wood from the Amazon by characteristics of Haralick and Neural Network: image segmentation and polishing of the surface
vol. 15, pp. 234-239 (online: 14 July 2022)
Research Articles
The potential of using xylarium wood samples for wood density calculations: a comparison of approaches for volume measurement
vol. 4, pp. 150-159 (online: 11 August 2011)
Research Articles
Exploring the reliability of CAN-bus data in assessing forwarder rolling resistance under real working conditions
vol. 17, pp. 360-369 (online: 13 November 2024)
Research Articles
Deploying an early-stage Cyber-Physical System for the implementation of Forestry 4.0 in a New Zealand timber harvesting context
vol. 17, pp. 353-359 (online: 13 November 2024)
iForest Database Search
Search By Author
Search By Keyword
Google Scholar Search
Citing Articles
Search By Author
Search By Keywords
PubMed Search
Search By Author
Search By Keyword