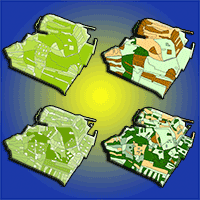
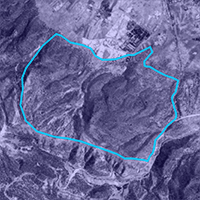
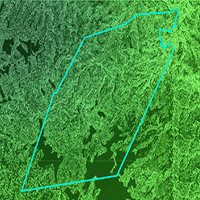
The selection of trees to be harvested is a core tenet of uneven-aged forest management; however, few studies have focused on the process of tree selection. A set of stand structural parameters (uniform angle index, W; mingling index, M; dominance index, U) based on tree neighbor-spatial relationships, are particularly suitable for expressing the structural characteristics of forest stands. Such indices were used to parameterize thinning in three plots (a-c, each 100 × 100 m2) in a Korean pine broad-leaved forest in northeastern China and one plot (h, 70 × 70 m2) in a pine-oak mixed forest in northwest China. Low-intensity single-tree selection was applied according to the principles of structure-based forest management (SBFM), i.e., to promote high mixture, obvious size differentiation, and random pattern with the aim of improving the overall structure of the managed plots. A group of thinning priority indices (v_ij, k_ij and z_ij) were calculated according to the bivariate distributions of the structural characteristics of harvested trees and stands before harvest. Our results demonstrated that v_ij, k_ij and z_ij adequately describe the spatial relationship between each tree and its nearest neighbors, and their combinations can be efficiently used to set thinning priorities on harvested trees with different structural characteristics. Their application can reduce the subjectivity of the selection process and improve the speed and accuracy of the choice of trees to be harvested in uneven-aged mixed forests.
Keywords
, , , , , ,
Citation
Li Y, Hui G, Wang H, Zhang G, Ye S (2017). Selection priority for harvested trees according to stand structural indices. iForest 10: 561-566. - doi: 10.3832/ifor2115-010
Academic Editor
Giorgio Alberti
Paper history
Received: May 16, 2016
Accepted: Feb 19, 2017
First online: May 05, 2017
Publication Date: Jun 30, 2017
Publication Time: 2.50 months
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2017
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.

Breakdown by View Type
(Waiting for server response...)
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 50252
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 42001
Abstract Page Views: 3217
PDF Downloads: 3688
Citation/Reference Downloads: 32
XML Downloads: 1314
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 3224
Overall contacts: 50252
Avg. contacts per week: 109.11
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2017): 21
Average cites per year: 2.33
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
(1)
Cogliastro A, Paquette A (2012)Thinning effect on light regime and growth of under planted red oak and black cherry in post-agricultural forests of south-eastern Canada. New Forests 43: 941-954.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(2)
Del Río M, Calama R, Cañellas I, Roig S, Montero G (2008)Thinning intensity and growth response in SW-European Scots pine stands. Annals of Forest Science 65 (3): 308.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(3)
Dung BX, Gomi T, Miyata S, Sidle RC, Kosugi K (2012)Runoff responses to forest thinning at plot and catchment scales in a headwater catchment draining Japanese cypress forest. Journal of Hydrometeorology 444-445: 51-62.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(4)
Franklin JF, Mitchell RJ, Palik BJ (2007)Natural disturbance and stand development principles for ecological forestry. General Technical Report NRS-19, Northern Research Station, USDA Forest Service, Delaware, USA, pp. 44.
Online |
Gscholar
(5)
Gadow KV, Hui G (1998)Modelling forest development. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Netherlands, pp. 51-300.
Gscholar
(6)
Gadow KV, Zhang C, Wehenkel C, Pommerening A, Corral-Rivas J, Korol M, Myklush S, Hui G, Kiviste A, Zhao X (2012)Forest structure and diversity. Springer, Berlin, Germany, pp. 30-62.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(7)
Grayson SF, Buckley DS, Henning JG, Schweitzer CJ, Gottschalk KW (2012)Understory light regimes following silvicultural treatments in central hardwood forests in Kentucky, USA. Forest Ecology and Management 279: 66-76.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(8)
Gronewold CA, D’Amato AW, Palik BJ (2010)The influence of cutting cycle and stocking level on the structure and composition of managed old-growth northern hardwoods. Forest Ecology and Management 259: 1151-1160.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(9)
Hui G, Gadow KV (2003)Quantitative analysis of forest spatial structure. China Science and Technology Press, Beijing, China, pp. 16-18.
Gscholar
(10)
Hui G, Gadow KV, Hu Y, Xu H (2007)Structure-based forest management. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing, China, pp. 28-70.
Gscholar
(11)
Hui G, Zhao Z, Hu Y (2010)A guide to structure-based forest management. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing, China, pp. 20-144.
Gscholar
(12)
Kang X (2011)Forest management. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing, China, pp. 230-236.
Gscholar
(13)
Kint V, Meirvenne MV, Nachtergale L, Geuden G, Lust N (2003)Spatial methods for quantifying forest stand structure development: a comparison between nearest-neighbors indies and variogram analysis. Forest science 49: 36-49.
Online |
Gscholar
(14)
Kuuluvainen T, Penttinen A, Leinonen K, Nygren M (1996)Statistical opportunities for comparing stand structural heterogeneity in managed and primeval forests: an example from boreal spruce forests in Southern Finland. Silva Fennica 30: 315-328.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(15)
Kyereh B, Swaine MD, Thompson J (1999)Effect of light on the germination of forest trees in Ghana. Journal of Ecology 87: 772-783.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(16)
Li Y, Hui G, Zhao Z, Hu Y (2012)The bivariate distribution characteristics of spatial structure in natural Korean pine broad-leaved forest. Journal of Vegetation Science 23: 1180-1190.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(17)
Li Y, Hui G, Zhao Z, Hu Y, Ye S (2014a)Spatial structural characteristics of three hardwood species in Korean pine broad-leaved forest - Validating the bivariate distribution of structural parameters from the point of tree population. Forest Ecology and Management 314: 17-25.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(18)
Li Y, Ye S, Hui G, Hu Y, Zhao Z (2014b)Spatial structure of timber harvested according to structure-based forest management. Forest Ecology and Management 322: 106-116.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(19)
Lindenmayer DB, Cunningham RB, Donnelly CF, Franklin JF (2000)Structural features of old-growth Australian montane ash forests. Forest Ecology and Management 134: 189-204.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(20)
Long JN, Vacchiano G (2014)A comprehensive framework of forest stand property-density relationships: perspectives for plant population ecology and forest management. Annals of Forest Science 71: 325-335.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(21)
Lyons KG, Brigham CA, Traut BH, Schwartz MW (2004)Rare species and ecosystem functioning. Conservation Biology 19: 1019-1024.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(22)
Ma K (1999)Ecosystem diversity of warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest in Dongling Mountain. In: “Ecosystem diversity in key areas of China” (Ma K ed). Zhejiang Science and Technology Press, Hangzhou, China, pp. 53-2108.
Gscholar
(23)
Mäkinen H, Isomäki A (2004)Thinning intensity and growth of Scots pine stands in Finland. Forest Ecology and Management 201: 311-325.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(24)
Mazza G, Amorini E, Cutini A, Manetti MC (2011)The influence of thinning on rainfall interception by
Pinus pinea L. in Mediterranean coastal stands (Castel Fusano - Rome). Annals of Forest Science 68: 1323-1332.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(25)
McHenry MT, Wilson BR, Lemon JM, Donnelly DE, Growns IG (2006)Soil and vegetation response to thinning White Cypress pine (
Callitris glaucophylla) on the north western slopes of New South Wales, Australia. Plant and Soil 285: 245-255.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(26)
Mills LS, Soulé ME, Doak DF (1993)The keystone-species concept in ecology and conservation. Bioscience 43: 219-224.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(27)
Myers GP, Newton AC, Melgarejo O (2000)The influence of canopy gap size on natural regeneration of Brazil nut (
Bertholletia excelsa) in Bolivia. Forest Ecology and Management 127: 119-128.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(28)
Nahm M, Holst T, Matzarakis A, Mayer H, Rennenberg H, Gessler A (2006)Soluble N compound profiles and concertrations in European beech (
Fagus sylvatica L.) are influenced by local climate and thinning. European Journal of Forest Research 125: 1-14.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(29)
Negro M, Vacchiano G, Berretti R, Chamberlain DE, Palestrini C, Motta R, Rolando A (2014)Effects of forest management on ground beetle diversity in alpine beech (
Fagus sylvatica L.) stands. Forest Ecology and Management 328: 300-309.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(30)
Nowak J, Asaro C, Klepzing K, Billings R (2008)The southern pine beetle prevention initiative: working for health forests. Journal of Forestry 106: 261-267.
Online |
Gscholar
(31)
O’Hara KL (2007)Integrating dynamics into management of complex forests: seeking balance in an unbalanced world. In: Proceedings of the Conference “Complex Stand Structures and Associated Dynamics: Measurement Indices and Modelling Approaches”. Sault Ste. Marie (Ontario, Canada), 29 Jul-2 Aug 2007. Ontario Forest Research Institute, Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Canada, pp. 20.
Gscholar
(32)
Pastorella F, Paletto A (2013)Stand structure indices as tools to support forest management: an application in Trentino forests (Italy). Journal of Forest Science 59: 159-168.
Online |
Gscholar
(33)
Pommerening A (2008)Analyzing and modelling spatial woodland structure. PhD thesis, Bangor University, Bangor, Maine, UK, pp. 36-227.
Gscholar
(34)
Qiu S, Bell RW, Hobbs RJ, McComb AJ (2013)Overstorey and juvenile response to thinning and drought in a jarrah (
Eucalyptus donnex Sm.) forest of southwestern Australia. Plant and Soil 365: 291-305.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(35)
Schulte BJ, Buongiorno J (1998)Effects of uneven-aged silviculture on the stand structure, species composition, and economic returns of loblolly pine stands. Forest Ecology and Management 111: 83-101.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(36)
Tao D, Li Y, Lu D, Luo Y, Yu S, Ye S (2016)The essential oil components of
Cinnamomum cassia: an analysis under different thinning models of plantation
Pinus massoniana. Journal of Forestry Research 3: 707-717.
CrossRef |
Gscholar