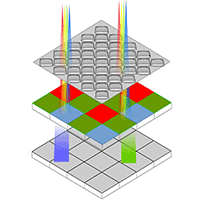
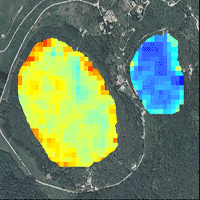
Arid and semi-arid forest ecosystems represent the largest biomes on Earth. However, research on identifying their species using remote sensing techniques is still limited. Understanding the spatial distribution of vegetation is crucial for precision management. This can be achieved through methods that allow for the individual identification and classification of species, which are essential for accurately estimating forest inventory. The objective of this study was to identify and classify forest species present in a xeric shrubland (arid and semi-arid region) based on multispectral images, red-green-blue (RGB) images, and Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) data. All images and data were drone-captured. Machine learning algorithms such as Adaptive boosting (AB), Gradient boosting machine (GBM), Xtreme gradient boosting (XGB), Classification and regression trees (CART), Random Forest (RF), and Support vector machines (SVM) were employed. RF yielded better results for species and shrub class classification, with an accuracy of 0.64 and a Kappa coefficient of 0.56. Classification accuracy values per species were 0.73 (E. antisyphilitica), 0.70 (opuntias), 0.67 (palms), 0.65 (L. tridentata), 0.59 (trees and shrubs), and 0.55 (A. lechuguilla), all of which were obtained by combining the three types of data used. Spectral variables contributed the most metrics, followed by LiDAR and RGB. The results support the adoption of remote drone-mounted sensing systems for characterizing the complex forest vegetation in arid and semi-arid regions, thereby providing a decision-support tool for its management.
Keywords
, , ,
Citation
Hernández-Ramos A, Valdez-Lazalde JR, De Los Santos-Posadas HM, Reyes-Hernández VJ, López-Serrano PM, Cano-Pineda A, Flores-Magdaleno H (2025). Classification of xeric scrub forest species using machine learning and optical and LiDAR drone data capture. iForest 18: 357-365. - doi: 10.3832/ifor4720-018
Academic Editor
Francesco Ripullone
Paper history
Received: Sep 05, 2024
Accepted: Sep 14, 2025
First online: Dec 07, 2025
Publication Date: Dec 31, 2025
Publication Time: 2.80 months
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2025
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.

Breakdown by View Type
(Waiting for server response...)
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 2100
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 739
Abstract Page Views: 852
PDF Downloads: 444
Citation/Reference Downloads: 0
XML Downloads: 65
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 96
Overall contacts: 2100
Avg. contacts per week: 153.13
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
(No citations were found up to date. Please come back later)
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
(1)
Beloiu M, Heinzmann L, Rehush N, Gessler A, Griess VC (2023)Individual tree-crown detection and species identification in heterogeneous forests using aerial RGB imagery and deep learning. Remote Sensing 15 (5): 1463.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(2)
Cao L, Pan J, Li R, Li J, Li Z (2018)Integrating airborne LiDAR and optical data to estimate forest aboveground biomass in arid and semi-arid regions of China. Remote Sensing 10: 532.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(3)
Dalponte M, Coomes DA (2016)Tree-centric mapping of forest carbon density from airborne laser scanning and hyperspectral data. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 7: 1236-1245.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(4)
Dashti H, Poley A, Glenn NF, Llangakoon N, Spaete L, Roberts D, Enterkine J, Flores AN, Ustin SL, Mitchell JJ (2019)Regional scale dryland vegetation classification with an integrated LiDAR-hyperspectral approach. Remote Sensing 11: 2141.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(5)
FAO (2019)Trees, forests and land use in drylands: the first global assessment. Forestry Paper, Food and Agriculture Organization - FAO, Rome, Italy, pp. 184.
Online |
Gscholar
(6)
Flores-Rodríguez AG, Flores-Garnica JG, González-Eguiarte DR, Gallegos-Rodríguez A, Zarazúa-Villaseñor P, Mena-Munguía S (2020)Revisión de métodos de sensores remotos para la detección y evaluación de la severidad de incendios forestales [Review of remote sensing methods for the detection and evaluation of the severity of forest fires]. Gestión y Ambiente 23 (2): 273-283. [in Spanish]
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(7)
Gao X, Hao F, Pi W, Zhu X, Zhang T, Bi Y, Zhang Y (2023)Identification and classification of degradation-indicator grass species in a desertified steppe based on HSI-UAV. Spectroscopy 38 (11): 14-20.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(8)
Hall-Beyer M (2017)Practical guidelines for choosing GLCM textures to use in landscape classification tasks over a range of moderate spatial scales. International Journal of Remote Sensing 38 (5): 1312-1338.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(9)
Hell M, Brandmeler M, Briechle S, Krzystek P (2022)Classification of tree species and standing dead trees with LiDAR point clouds using two Deep Neural Networks: PointCNN and 3DmFV-Net. Journal of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Geoinformation Science 90: 103-121.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(10)
Hernández-Ramos A, Cano-Pineda A, Flores-López C, Hernández-Ramos J, García-Cuevas X, Martínez-Salvador M, Martínez LA (2019)Modelos para estimar biomasa de
Euphorbia antisyphilitica Zucc. en seis municipios de Coahuila [Models to estimate biomass of
Euphorbia antisyphilitica Zucc. in six townships of Coahuila]. Madera y Bosques 25(2): e2521806. [in Spanish]
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(11)
Huang Y, Ou B, Meng K, Yang B, Carpenter J, Jung J, Fei S (2024)Tree species classification from UAV canopy images with deep learning models. Remote Sensing 16 (20): 3836.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(12)
Hurtado JLA, Lizarazo I (2022)Nuevo índice espectro-temporal para la detección de pérdida forestal en áreas de bosque tropical. Caso de estudio Amazonia colombiana [New Spectro-temporal index for the detection of forest loss in tropical forest areas. A Colombian Amazon case study]. Revista Cartográfica 104: 11-35. [in Spanish]
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(13)
Immitzer M, Atzberger C, Koukal T (2012)Tree species classification with random forest using very high spatial resolution 8-band Worldview-2 satellite data. Remote Sensing 4: 2661-2693.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(14)
James G, Witten D, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2023)An introduction to statistical learning with applications in R. Springer Texts in Statistics, New York, NY, USA, pp. 604.
Gscholar
(15)
Kowalczyk A (2017)Support vector machines succinctly. Syncfusion, Inc., Morrisville, NC, USA, pp. 114.
Gscholar
(16)
Kuhn M (2008)Building predictive models in R using the caret package. Journal of Statistical Software 28 (5): 28.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(17)
Kursa MB, Rudnicki RW (2010)Feature selection with the Boruta Package. Journal of Statistical Software 36: 11.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(18)
Lin H, Liu X, Han Z, Cui H, Dian Y (2023)Identification of tree species in forest communities at different altitudes based on multi-source aerial remote sensing data. Applied Sciences 13: 4911.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(19)
Liu L, Coops NC, Aven NW, Pang Y (2017)Mapping urban tree species using integrated airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR remote sensing data. Remote Sensing of Environment 200: 170-182.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(20)
Liu Y, Zhang X, Ma Z, Dong N, Xie D, Li R, Johnston DM, Gao GY, Li Y, Lei Y (2022)Developing a more accurate method for individual plant segmentation of urban tree and shrub communities using LiDAR technology. Landscape Research 48 (3): 313-330.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(21)
Lu B, He Y (2017)Species classification using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-acquired high spatial resolution imagery in a heterogeneous grassland. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 128: 73-85.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(22)
Lucas C, Bouten W, Koma Z, Kissling WD, Seijmonsbergen AC (2019)Identification of linear vegetation elements in a rural landscape using LiDAR point clouds. Remote Sensing 11: 292.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(23)
Mayra J, Keski-Saari S, Kivinen S, Tanhuanpaa T, Hurskainen P, Kullberg P, Poikolainen L, Viinikka A, Tuominen S, Kumpula T, Vihervaara P (2021)Tree species classification from airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR data using 3D convolutional neural networks. Remote Sensing of Environment 256: 112322.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(24)
Naji TAH (2018)Study of vegetation cover distribution using DVI, PVI, WDVI indices with 2D-space plot. Journal of Physics - Conference Series 1003: 012083.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(25)
Norton CL, Hartfield K, Collins CDH, Leeuwen WJD, Metz LJ (2022)Multi-temporal LiDAR and hyperspectral data fusion for classification of semi-arid woody cover species. Remote Sensing 14: 2896.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(26)
Pervin R, Robeson SM, McBean N (2022)Fusion of airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR canopy-height data for estimating fractional cover of tall woody plants, herbaceous vegetation, and other soil cover types in a semi-arid savanna ecosystem. International Journal of Remote Sensing 43 (10): 3890-3926.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(27)
Qian C, Yao C, Ma H, Xu J, Wang J (2023)Tree species classification using airborne LiDAR data based on individual tree segmentation and shape fitting. Remote Sensing 15: 406.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(28)
Qin H, Zhou W, Yao Y, Wang W (2022)Individual tree segmentation and tree species classification in subtropical broadleaf forests using UAV-based LiDAR, hyperspectral, and ultrahigh-resolution RGB data. Remote Sensing of Environment 280: 113143.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(29)
R Core Team (2022)R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria.
Online |
Gscholar
(30)
Roussel JR, Auty D, Coops NC, Tompalski P, Goodbody TRH, Sánchez MA, Bourdon JF, De Boissieu F, Achim A (2020)lidR: an R package for analysis of Airborne Laser Scanning (ALS) data. Remote Sensing of Environment 251: 112061.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(31)
Sankey T, Donager J, McVay J, Sankey JB (2017)UAV lidar and hyperspectral fusion for forest monitoring in the southwestern USA. Remote Sensing of Environment 195: 30-43.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(32)
Sankey TT, McVay J, Swetnam TL, McClaran MP, Heilman P, Nichols M (2018)UAV hyperspectral and lidar data and their fusion for arid and semi-arid land vegetation monitoring. Remote Sensing in Ecology and Conservation 4 (1): 20-33.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(33)
Silva CA, Hudak AT, Vierling LA, Valbuena R, Cardil A, Mohan M, Almeyda DRA, Broadbent EN, Almeyda AMZ, Wilkinson B, Sharma A, Drake JB, Medley PB, Vogel JG, Prata GA, Atkins JW, Hamamura C, Johnson DJ, Klauberg C (2022)treetop: a shiny-based application and R package for extracting forest information from LiDAR data for ecologists and conservationists. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 13: 1164-1176.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(34)
Sivanandam P, Lucieer A (2022)Tree detection and species classification in a mixed species forest using Unoccupied Aircraft System (UAS) RGB and multispectral imagery. Remote Sensing 14: 4963.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(35)
Tang J, Liang J, Yang Y, Zhang S, Hou H, Zhu X (2022)Revealing the structure and composition of the restored vegetation cover in semi-arid mine dumps based on LiDAR and hyperspectral images. Remote Sensing 14: 978.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(36)
Wang S, Bi Y, Du J, Zhang T, Gao X, Jin E (2023)The Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-based hyperspectral classification of desert grassland plants in Inner Mongolia, China. Applied Sciences 13 (22): 12245.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(37)
Wu X, Shen X, Cao L, Wang G, Cao F (2019)Assessment of individual tree detection and canopy cover estimation using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle based Light Detection and Ranging (UAV-LiDAR) data in planted forests. Remote Sensing 11: 908.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(38)
Xu X, Luricich F, Floriani L (2023)A topology-based approach to individual tree segmentation from airborne LiDAR data. Geoinformatica 27: 759-788.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(39)
Yang H, Du J (2021)Classification of desert steppe species based on unmanned aerial vehicle hyperspectral remote sensing and continuum removal vegetation indices. Optik 247: 167877.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(40)
Yue K, Li P (2023)The classification characteristics and dynamic changes of desert vegetation based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle remote sensing. Journal of Biobased Materials and Bioenergy 17 (6): 734-741.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(41)
Zhang K, Chen S, Whitman D, Shyu M, Yan J, Zhang C (2003)Progressive morphological filter for removing nonground measurements from airborne LiDAR data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 41 (4): 872-882.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(42)
Zhang Z, Liu X (2013)Support vector machines for tree species identification using LiDAR-derived structure and intensity variables. Geocarto International 28 (4): 364-378.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(43)
Zhong H, Lin W, Liu H, Ma N, Liu K, Cao R, Wang T, Ren Z (2022)Identification of tree species based on the fusion of UAV hyperspectral image and LiDAR data in a coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest in Northeast China. Frontiers in Plant Science 13: 964769.
CrossRef |
Gscholar