Estimating biomass of mixed and uneven-aged forests using spectral data and a hybrid model combining regression trees and linear models
Pablito M López-Serrano (1), Carlos A López-Sánchez (2) , Ramón A Díaz-Varela (3), José J Corral-Rivas (2), Raúl Solís-Moreno (4), Benedicto Vargas-Larreta (5), Juan G Álvarez-González (6)
iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry, Volume 9, Issue 2, Pages 226-234 (2015)
doi: https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor1504-008
Published: Sep 21, 2015 - Copyright © 2015 SISEF
Research Articles
Abstract
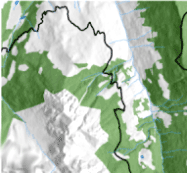
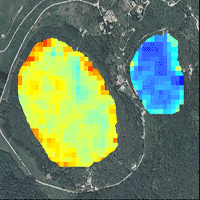
The Sierra Madre Occidental mountain range (Durango, Mexico) is of great ecological interest because of the high degree of environmental heterogeneity in the area. The objective of the present study was to estimate the biomass of mixed and uneven-aged forests in the Sierra Madre Occidental by using Landsat-5 TM spectral data and forest inventory data. We used the ATCOR3® atmospheric and topographic correction module to convert remotely sensed imagery digital signals to surface reflectance values. The usual approach of modeling stand variables by using multiple linear regression was compared with a hybrid model developed in two steps: in the first step a regression tree was used to obtain an initial classification of homogeneous biomass groups, and multiple linear regression models were then fitted to each node of the pruned regression tree. Cross-validation of the hybrid model explained 72.96% of the observed stand biomass variation, with a reduction in the RMSE of 25.47% with respect to the estimates yielded by the linear model fitted to the complete database. The most important variables for the binary classification process in the regression tree were the albedo, the corrected readings of the short-wave infrared band of the satellite (2.08-2.35 µm) and the topographic moisture index. We used the model output to construct a map for estimating biomass in the study area, which yielded values of between 51 and 235 Mg ha-1. The use of regression trees in combination with stepwise regression of corrected satellite imagery proved a reliable method for estimating forest biomass.
Keywords
Regression Trees, Stepwise Regression, Remote Sensing, ATCOR3, Terrain Features, Image Texture
Authors’ Info
Authors’ address
DICAF, Universidad Juárez del Estado de Durango, Boulevard del Guadiana 501, Ciudad Universitaria, Torre de Investigación, 34120 Durango, Dgo (México)
José J Corral-Rivas
Instituto de Silvicultura e Industria de la Madera, Universidad Juárez del Estado de Durango, Boulevard del Guadiana 501, Ciudad Universitaria, Torre de Investigación, 34120 Durango, Dgo (México)
Departamento de Botánica - IBADER, Universidad de Santiago de Compostela, Escuela Politécnica Superior, Lugo (España)
Facultad de Ciencias Forestales, Universidad Juárez del Estado de Durango, Río Papaloapan 132, Valle del Sur Durango, 34120 Durango, Dgo (México)
División de Estudios de Posgrado e Investigación, Instituto Tecnológico de El Salto, Mesa del Tecnológico s/n, 34942, El Salto, Dgo (México)
Departamento de Ingeniería Agroforestal, Universidad de Santiago de Compostela, Escuela Politécnica Superior, Lugo (España)
Corresponding author
Paper Info
Citation
López-Serrano PM, López-Sánchez CA, Díaz-Varela RA, Corral-Rivas JJ, Solís-Moreno R, Vargas-Larreta B, Álvarez-González JG (2015). Estimating biomass of mixed and uneven-aged forests using spectral data and a hybrid model combining regression trees and linear models. iForest 9: 226-234. - doi: 10.3832/ifor1504-008
Academic Editor
Davide Travaglini
Paper history
Received: Nov 17, 2014
Accepted: May 17, 2015
First online: Sep 21, 2015
Publication Date: Apr 26, 2016
Publication Time: 4.23 months
Copyright Information
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2015
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Web Metrics
Breakdown by View Type
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 55767
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 45050
Abstract Page Views: 3851
PDF Downloads: 5220
Citation/Reference Downloads: 73
XML Downloads: 1573
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 3796
Overall contacts: 55767
Avg. contacts per week: 102.84
Citation Metrics
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2016): 13
Average cites per year: 1.30
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
References
Mapping aboveground biomass by integrating geospatial and forest inventory data through a k-nearest neighbour strategy in North Central Mexico. Journal of Arid Land 1: 80-96.
CrossRef | Gscholar
Conditioning diagnostics, collinearity and weak data in regression. John Wiley and Sons Inc, New York, USA, pp. 396.
Gscholar
Análisis de textura en panes usando la matriz de coocurrencia [Analysis of texture in breads using the co-occurrence matrix]. Revista Politécnica 6 (10): 74-80. [in Spanish]
Gscholar
Classification and regression trees. Chapman and Hall, New York, USA, pp. 368.
Gscholar
Utilización y conservación de los ecosistemas terrestres de México: pasado, presente y futuro [Use and conservation of terrestrial ecosystems of Mexico: past, present and future]. Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad/Instituto de Biología, UNAM/Agrupación Sierra Madre, México, DF, pp. 847. [in Spanish]
Gscholar
Guía para el establecimiento de sitios de inventario periódico forestal y de suelos del estado de Durango [Guidelines for the establishment of permanent sample plots in forests of Durango State]. Facultad de Ciencias Forestales, Universidad Juárez del Estado de Durango, Mexico, pp. 81. [in Spanish]
Gscholar
Estimación de la biomasa residual forestal mediante técnicas de teledetección y SIG en masas puras de Pinus halepensis y P. sylvestris [Estimation of residual forest biomass using remote sensing technology and GIS in pure stands of Pinus halepensis and P. sylvestris]. In: Proceedings of the “IV Congreso Forestal Español de la Sociedad Española de Ciencias Forestales”. Paper no. 4CFE05-342-T1, 308, Sociedad Española de Ciencias Forestales, Palencia, Spain, pp. 5. [in Spanish]
Gscholar
Acerca de los índices de vegetación [About vegetation indices]. Revista de Teledetección 8: 1-10. [in Spanish]
Gscholar
Good practice guidance for land use, land-use change and forestry. IPCC National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programme, Hayama, Japan, pp. 590.
Gscholar
Landscape assessment of soil erosion and non-point source pollution. Journal of the Minnesota Academy of Science 55 (1): 18-24.
Gscholar
Classical and modern regression with applications (2nd edn). Duxbury Press, Belmont, CA, USA, pp. 488.
Gscholar
Applied linear statistical models: regression, analysis of variance and experimental designs (3rd edn). Irwin, Boston, MA, USA, pp. 842.
Gscholar
User manual ATCOR2 and ATCOR3, ATCOR for IMAGINE 2013: haze reduction, atmospheric and topographic correction. DLR Oberpfaffenhofen, Institute of Ptoelectronics, D-82234, Version 15.01.2013, Wessling, Germany, pp. 240.
Gscholar
Concepts and techniques of vegetation mapping. In: “Land classifications based on vegetation: applications for resource management” (Ferguson D, Morgan P, Johnson FD eds). Gen. Tech. Rep. INT-257, Intermountain Forest and Range Experiment Station, USDA Forest Service, Ogden, UT, USA, pp. 90-96.
Gscholar
Conservación de ecosistemas templados de montaña en México [Conservation of temperate mountain ecosystems in Mexico]. Instituto Nacional de Ecología, INE-SEMARNAT, México, DF, pp. 315. [in Spanish]
Gscholar
Radiometric slope correction for forest biomass estimation from SAR data in the Western Sayani Mountains, Siberia. Remote Sensing of Environment 79 (2-3): 279-287.
Gscholar
Estimación del potencial de los bosques de Durango para la mitigación del cambio climático. Modelización de la biomasa forestal [Assessing the potential of forests of Durango for mitigating climate change. Modelling of forest biomass]. Proyecto FOMIX-DGO-2011-C01-165681, Comisión Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología, CONACYT, Mexico, pp. 53. [in Spanish]
Gscholar
Guía de campo para la estimación de biomasa y carbono forestal [Field guide to estimate forest biomass and carbon] (version 1.0). Woods Hole Research Center, Falmouth, MA, USA, pp. 53. [in Spanish]
Gscholar