Soil and forest productivity: a case study from Stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) stands in Calabria (southern Italy)
F Bravo (1) , M Lucà (2), R Mercurio (2), M Sidari (2), A Muscolo (2)
iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry, Volume 4, Issue 1, Pages 25-30 (2011)
doi: https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor0559-004
Published: Jan 27, 2011 - Copyright © 2011 SISEF
Research Articles
Abstract
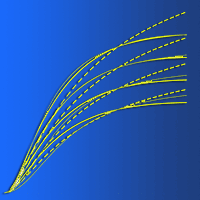
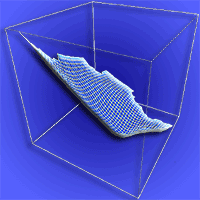
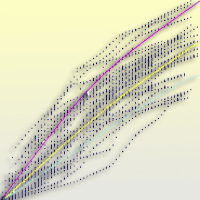
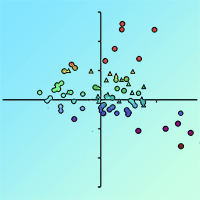
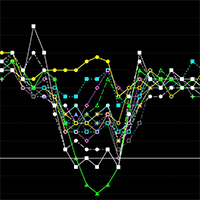
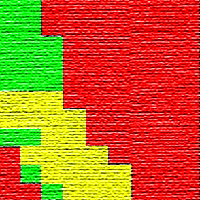
The objective of this study was to determine whether edaphic and/or topographic variables may be used as predictors of site productivity in Stone pine stands in Calabria (southern Italy). To accomplish this goal, a linear discriminant rule was developed using data from 16 pure Stone pine stands, grouped into three different classes based on the mean dominant height annual growth. The discriminant rule was based on three linear models (one for each class) that jointly predicts site class for a given stand. To test the accuracy of the proposed method, cross-validation was carried out by developing 16 alternative discriminant rules (excluding the analyzed data). Predictors tested were edaphic (texture, pH, organic matter) and topographic (altitude and slope) variables. The model obtained allow to discriminate poorest sites accurately (100% of sites were correctly re-classified using the discriminant functions obtained). In more productive areas, sites were correctly re-classified in the 33.33% of cases, while in intermediate sites the correct classification was equal to 50%. Our discriminant rule classifies correctly the poorest stands, suggesting that site index in plain site soils strongly depends on clay percentage. Overall, the edaphic model obtained classifies plots into the correct site index class 61.11% of cases, which is considered an acceptable value for these kinds of studies.
Keywords
Clay, Pinus pinea, Site index, Site productivity, Topographic factor
Authors’ Info
Authors’ address
Sustainable Forest Management Research Institute, University of Valladolid-INIA, avda. de Madrid 57, E-34004 Palencia (Spain)
R Mercurio
M Sidari
A Muscolo
Department of Agricultural and Forest Systems Management, Faculty of Agriculture, University “Mediterranea” (Italy)
Corresponding author
Paper Info
Citation
Bravo F, Lucà M, Mercurio R, Sidari M, Muscolo A (2011). Soil and forest productivity: a case study from Stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) stands in Calabria (southern Italy). iForest 4: 25-30. - doi: 10.3832/ifor0559-004
Paper history
Received: May 03, 2010
Accepted: Dec 17, 2010
First online: Jan 27, 2011
Publication Date: Jan 27, 2011
Publication Time: 1.37 months
Copyright Information
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2011
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Web Metrics
Breakdown by View Type
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 59113
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 48873
Abstract Page Views: 4177
PDF Downloads: 4395
Citation/Reference Downloads: 24
XML Downloads: 1644
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 5494
Overall contacts: 59113
Avg. contacts per week: 75.32
Citation Metrics
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2011): 15
Average cites per year: 1.00
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
References
A practical field method of site evaluation for commercially important southern hardwoods. Gen. Tech. Rep. SO-26, USDA Forest Service, Southern Forest Experiment Station, New Orleans, LA, USA, pp. 51.
Gscholar
Ricerche alsometriche sulle pinete di pino domestico dei tomboli di Cecina. L’Italia Forestale e Montana 28 (5): 191-197.
Gscholar
Cumulative effects of silvicultural technology on sustained forest productivity. In: “Assessing the effects of silvicultural practices on sustained productivity” (Mahendrappa MK, Simpson CM, Smith CT eds). Proceeding of the IEA/BA workshop ’93, Frederickston (NB, Canada) 16-22 May 1993. Information rep. M-X-191. Nat. Res. Can., Can. For. Serv., Maritimes Region, Frederickston, NB, Canada, pp. 59-70.
Gscholar
Piano di assestamento dei boschi della Tenuta di San Rossore per il decennio 1960-1969. Segretariato Generale della Presidenza della Repubblica, Roma.
Gscholar
Tavola alsometrica del pino domestico di Bosco Bellia cresciuto in fustaia coetanea. L’Italia forestale e montana 24 (1): 67-73.
Gscholar
La produzione legnosa e del frutto e la durata del turno economico delle pinete coetanee di pino domestico (Pinus pinea L.) in un complesso assestato a prevalente funzione produttiva in Italia. Annali ISAFA, vol. XII, pp.161-221.
Gscholar
Rimboschimenti e loro risultati in Sardegna. In: Atti del Convegno “Prospettive economico-indutriali della produzione legnosa in Sardegna”, Cagliari, Italy, pp. 79-109.
Gscholar
Le pinete litorali del Veneto. Regione Veneto. Tip. Multigraf, Spinea, Venezia, Italy.
Gscholar
Applied multivariate methods for data analyst. Duxbury Press, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, pp. 567.
Gscholar
Neue methode zurestimmung des stickstoffs in organischen körpen. Zeitschrift fiir Analytische Chemie 22: 366-382.
Gscholar
La pineta della Duna Feniglia. Ricerche sperimentali di dendrometria e di auxometria. Fasc.VIII, Istituto di Assestamento Forestale, Università di Firenze, Tip. Coppini, Firenze, Italy.
Gscholar
Rapid determination of cation and anion exchange properties and pH of soils. Journal of Association Agriculture Chemistry 36: 445-457.
Gscholar
Evidence for long-term productivity change as provided by field trials. In: “Impacts of forest harvesting on long-term site productivity” (Dyck WJ, Cole DW eds). Chapman & Hall, New York, USA, pp. 41-80.
Gscholar
Regiones de procedencia de Pinus pinea L. en España. Organismo Autónomo Parques Nacionales, Madrid.
Gscholar
Computer simulation models and expert systems for predicting productivity decline. In: “Impacts of forest harvesting on long-term site productivity” (Dyck WJ, Cole DW eds). Chapman & Hall, New York, USA, pp. 151-186.
Gscholar
Factors that influence the productivity of western hemlock. Proceeding of XVI IUFRO World Congress, vol. 1, pp. 167-185.
Gscholar
Weed US: database of plants invading natural areas in the United States. Web site.
Gscholar
Determinants of forest stand productivity. In: Proceeding of Symposium on “Principles of maintaining productivity on prepared sites” (Tippen T ed). USDA Forest Service, Southern Region, Asheville, NC, USA, pp. 14-27.
Gscholar