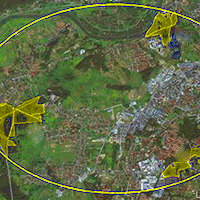
The effects of afforestation on physical, physico-chemical, and biological properties of grassland soils were investigated in three sites (215-230 m a.s.l.) located within the urban area of Krakow (southern Poland) after 45-60 years since the introduction of forest tree species. We compared the contents of nutrients and the composition of humus between forest and adjacent grassland soils, as well as the quality of the forest soils in relation to the introduced tree species (alder, pine, oak, birch, maple, elm). We hypothesized that afforestation of grassland soils results in the increase of acidity and nutrient contents. Studied soils belong to Dystric Gleysols (forest) and Eutric Gleysols (grassland). Overall, 168 soil samples were taken from two layers (0-10 cm and 10-30 cm) both from forest and grassland soils. The results showed an increase of organic carbon (up to 150%), total nitrogen (up to 70%) and total acidity (up to 18 times), as well as a decrease of pH (up to 40%) and activity of dehydrogenase (up to 60%) in forest soils in relation to the respective grassland soils. The most intensive changes were observed in the topsoil layers (0-10 cm). We also calculated the Soil Quality index (SQI) based on PCA in which only soil parameters with high load factors were taken into consideration. SQI ranged from 0.39 to 0.41 in grassland soils and from 0.33 to 0.37 in forest soils. Among forest soils, the highest value of SQI was obtained for stands dominated by black alder, indicating that such species is the most suitable for afforestation purposes under the study conditions. The results may be helpful in the realization of afforestation plans of humid grassland soils.
Keywords
, ,
Citation
Podwika M, Solek-Podwika K, Ciarkowska K (2018). Changes in the properties of grassland soils as a result of afforestation. iForest 11: 600-608. - doi: 10.3832/ifor2556-011
Academic Editor
Gianfranco Minotta
Paper history
Received: Jul 18, 2017
Accepted: Jun 28, 2018
First online: Sep 25, 2018
Publication Date: Oct 31, 2018
Publication Time: 2.97 months
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2018
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.

Breakdown by View Type
(Waiting for server response...)
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 49126
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 40706
Abstract Page Views: 4019
PDF Downloads: 3513
Citation/Reference Downloads: 6
XML Downloads: 882
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 2726
Overall contacts: 49126
Avg. contacts per week: 126.15
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2018): 11
Average cites per year: 1.38
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
(1)
Alban DH (1981)Effects of nutrient accumulation by aspen, spruce and pine on soil properties. Soil Science Society of America Journal 46 (4): 853-861.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(2)
Aleksandrowicz S, Wrochniak-Stopka W (1959)Phosphorite concretions in turonian sediments of Krakow region. Geological Institute 9: 197-206. [in Polish]
Gscholar
(3)
Amacher MC, O’Neil KP, Perry CH (2007)Soil vital signs: a new Soil Quality Index (SQI) for assessing forest soil health. Research Paper RMRS-RP-65WWW, Rocky Mountain Research Station, USDA Forest Service, Fort Collins, CO, USA, pp. 15.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(4)
Andivia E, Rolo V, Jonard M, Formánek P, Ponett Q (2016)Tree species identity mediates mechanisms of top soil carbon sequestration in a Norway spruce and European beech mixed forest. Annals of Forest Science 73: 437-447.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(5)
Andrews SS, Karlen DL, Mitchell JP (2002)A comparison of soil quality indexing methods for vegetable production systems in Northern California. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 90: 25-45.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(6)
Bastida F, Zsolnay A, Hernández T, García C (2008)Past, present and future of soil quality indices: a biological perspective. Geoderma 147: 159-171.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(7)
Blonska E, Januszek K (2010)The influence of tree species on the enzyme activity and physical-chemical properties of forest soils. Soil Science Annual 61 (2): 5-14. [in Polish]
Gscholar
(8)
Blonska E, Januszek K (2013)Usability of enzyme activity in estimation of forest soil quality. Folia Forestalia Polonica 55 (1): 18-26.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(9)
Blonska E, Lasota J, Zwydak M (2017)The relationship between soil properties, enzyme activity and land use. Forest Research Papers 78 (1): 39-44.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(10)
Brozek S, Wanic T (2002)Impact of forest litter of
Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn.,
Alnus incana (L.) Moench,
Alnus viridis (Chaix) Lam. et DC,
Abies alba Mill., and
Fagus sylvatica L. on chosen soil properties. Electronic Journal of Polish Agricultural Universities 5 (1): 122-127.
Gscholar
(11)
Casida LE, Klein DA, Santoro T (1964)Soil dehydrogenase activity. Soil Science 98: 371-376.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(12)
Ciarkowska K, Solek-Podwika K, Filipek-Mazur B, Tabak M (2017)Comparative effects of lignite-derived humic acids and FYM on soil properties and vegetable yield. Geoderma 303: 85-92. . org.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(13)
Claessens H, Oosterbaan A, Savill P, Rondeux J (2010)A review of the characteristics of black alder (
Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn.) and their implications for silvicultural practices. Forestry 83 (2): 163-175.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(14)
CSO (2014)Report on the forests state in Poland. Environment protection. Statistical information and elaborations. Central Statistical Office, Statistical Publishing Establishment. Warsaw, Poland, pp. 540. [in Polish]
Gscholar
(15)
CSO (2015)Environment protection. Statistical information and elaborations. Central Statistical Office, Statistical Publishing Establishment, Warsaw, Poland, pp. 580. [in Polish]
Gscholar
(16)
Das B, Chakraborty D, Singh VK, Ahmed M, Singh AK, Barman A (2016)Evaluating fertilization effects on soil physical properties using a soil quality index in an intensive rice-wheat cropping system. Pedosphere 26 (6): 887-894.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(17)
Duchaufour P, Jacquin F (1966)Nouvelle recherches sur I’extraction etle fractionnement des composes humiques [New research on the extraction and fractionation of humic compounds]. Bulletin ENSA, Nancy, France 8: 1-24. [in French]
Gscholar
(18)
Farley KA, Kelly EF (2004)Effects of afforestation of a páramo grassland on soil nutrient status. Forest Ecology and Management 195: 281-290.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(19)
FPI (2012)Forest protection instruction. General Directorate of the State Forests, Warsaw, Poland, pp. 124.
Gscholar
(20)
Giardina CP, Huffman S, Binkley D, Caldwell BA (1995)Alders increase soil phosphorus availability in Douglas-fir plantation. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 25: 1652-1657.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(21)
Gonet S, Debska B, Dziamski A, Banach-Szott M, Zaujec A, Szombathova N (2009)Properties of organic matter in haplic luvisol under arable, meadow and forest management. Polish Journal of Soil Science 42 (2): 139-148.
Gscholar
(22)
Gorlach E, Mazur T (2001)Agricultural chemistry: basics of nutrition and principles of fertilization. PWN, Warsaw, Poland, pp. 125. [in Polish]
Gscholar
(23)
Griffiths R, Madritch M, Swanson A (2005)Conifer invasion of forest meadows transforms soil characteristics in the Pacific Northwest. Forest Ecology and Management 208: 347-358.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(24)
Holubík O, Podrázsky V, Vopravi J, Khel T, Remeš J (2014)Effect of agricultural lands afforestation and tree species composition on the soil reaction, total organic carbon and nitrogen content in the uppermost mineral soil profile. Soil and Water Research 9 (4): 192-200.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(25)
Innangi M, Danise T, D’Alessandro F, Curcio E, Fioretto A (2017)Dynamics of organic matter in leaf litter and topsoil within an italian alder (
Alnus cordata (Loisel.) Desf.) ecosystem. Forests 8 (240): 1-16.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(26)
Jobbágy EG, Jackson RB (2003)Patterns and mechanisms of soil acidification in the conversion of grasslands to forests. Biogeochemistry 64: 205-229.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(27)
Jonczak J (2013)Soil organic matter properties in stagnic luvisols under different land use types. Acta Agrophysica 20 (4): 565-576.
Online |
Gscholar
(28)
Jonczak J, Parzych A, Sobisz Z (2015)Decomposition of four tree species leaf litters in headwater riparian forest. Baltic Forestry 21 (1): 133-143.
Online |
Gscholar
(29)
Jonczak J, Olejniczak M, Parzych A, Sobisz Z (2016)Dynamics, structure and chemistry of litterfall in headwater riparian forest on the area of Middle Pomerania. Journal of Elementology 21 (2): 381-392.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(30)
Krzaklewski W, Pietrzykowski M, Wos B (2012)Survival and growth of alders (
Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn. and
Alnus incana (L.) Moench) on fly ash technosols at different substrate improvement. Ecological Engineering 49: 35-40. . org.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(31)
Lu D, Moran E, Mausel P (2002)Linking Amazonian secondary succession forest growth to soil properties. Land Degradation Development 13: 331-343.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(32)
Maly S, Fiala P, Reininger D, Obdrálková E (2014)The relationships among microbial parameters and the rate of organic matter mineralization in forest soils, as influenced by forest type. Pedobiologia 57: 235-244.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(33)
Matuszko D (2007)The climate of Krakow in the 20th century. Institute of Geography and Spatial Management of the Jagiellonian University, Krakow, Poland, pp. 251. [in Polish]
Gscholar
(34)
Miletić Z, Kneević M, Stajić S, Košanin O, Dordević I (2012)Effect of European black alder monocultures on the characteristics of reclaimed mine soil. International Journal of Environmental Research 6 (3): 703-710.
Gscholar
(35)
Mishra G, Giri K, Dutta A, Hazarika S, Borgohain P (2016)Short communication: a laboratory study to validate the impact of the addition of
Alnus nepalensis leaf litter on carbon and nutrients mineralization in soil. Nusantara Bioscience 8 (1): 5-7.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(36)
Monnier G, Turc L, Jeanson-Lunsiuang C (1962)Une methode de fractionnement densimetrique pour centrifugation des matiers organiques du sol [A densimetric fractionation method for centrifugation of soil organic matter]. Annales Agronomique 13: 55-63. [in French]
Gscholar
(37)
Moran E, Brondizio ES, Tucker JM, Silva-Forsberg M, McCracken S, Falesi I (2000)Effects of soil fertility and land-use on forest succession in Amazonia. Forest Ecology and Management 139: 93-108.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(38)
Niemyska-Lukaszuk J, Zaleski T, Mazurek R, Szwagrzyk J, Bodziarski J, Podwika M (2001)Characteristics of the soil and habitat conditions of the municipal forests of Kraków. W. Szafer Foundation for Polish Botany, Krakow, Poland, pp. 22.
Gscholar
(39)
Orczewska A, Piotrowska A, Lemanowicz J (2012)Soil acid phosphomonoesterase activity and phosphorus forms in ancient and post-agricultural black alder (
Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn.) woodlands. Acta Societatis Botanicorum Poloniae 81 (2): 81-86.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(40)
Ostrowska A, Gawlinski S, Szczubialka Z (1991)Procedures for soil and plants analysis. Institute of Environmental Protection, Warsaw, Poland, pp. 333. [in Polish]
Gscholar
(41)
Ross DJ, Tate KR, Scott NA, Feltham CW (1999)Land-use change: effects on soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus pools and fluxes in three adjacent ecosystems. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 31: 803-813.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(42)
Sinha S, Masto RE, Ram LC, Selvi VA, Srivastava NK, Tripathi RC, George J (2009)Rhizosphere soil microbial index of tree species in a coal mining ecosystem. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 41: 1824-1832.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(43)
Schulp CJE, Nabuurs G-H, Verburg PH, De Waal RW (2008)Effect of tree species on carbon stocks in forest floor and mineral soil and implications for soil carbon inventories. Forest Ecology and Management 256: 482-490.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(44)
Smal H, Ligeza S, Olszewska M (2004)The effect of afforestation of sandy post-arable soils on the quality of organic matter and chemical composition of soil solution. Soil Science Annual 55 (4): 139-148.
Gscholar
(45)
Smal H, Olszewska M (2008)The effect afforestation with Scots pine (
Pinus silvestris L.) of sandy post-arable soils on their selected properties. II. Reaction, carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. Plant and Soil 305: 171-187.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(46)
Tan KH (2005)Soil sampling, preparation and analysis. Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton, London, New York, Singapore, pp. 408.
Online |
Gscholar
(47)
Tanner LH, Smith DL, Curry J, Twist J (2014)Effect of land use change on carbon content and CO
2 flux of cloud forest soils, Santa Elena, Costa Rica. Open Journal of Soil Science 4: 64-71.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(48)
Temperton VM, Grayston SJ, Jackson G, Barton CVM, Millard P, Jarvis PG (2003)Effects of elevated carbon dioxide concentration on growth and nitrogen fixation in
Alnus glutinosa in a long-term field experiment. Tree Physiology 23: 1051-1059.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(49)
Uri V, Lõhmus K, Mander U, Ostonen I, Aosaar J, Maddison M, Helmisaari HS, Augustin J (2011)Long-term effects on the nitrogen budget of a short-rotation grey alder (
Alnus incana (L.) Moench) forest on abandoned agricultural land. Ecological Engineering 37: 920-930.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(50)
Vesterdal L, Schmidt IK, Callesen I, Nilsson LO, Gundersen P (2008)Carbon and nitrogen in forest floor and mineral soil under six common European tree species. Forest Ecology and Management 255: 35-48.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(51)
WRB (2015)Soil resources reports 106. WRB recommendations, FAO-UN, Rome, Italy, pp. 192.
Gscholar