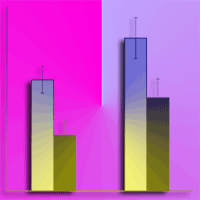Wood-soil interactions in soil bioengineering slope stabilization works
MC Moscatelli (1) , M Romagnoli (2), S Cenfi (2), A Lagomarsino (1), A Di Tizio (1), S Spina (2), S Grego (1)
iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry, Volume 2, Issue 5, Pages 187-191 (2009)
doi: https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor0513-002
Published: Oct 15, 2009 - Copyright © 2009 SISEF
Research Articles
Abstract
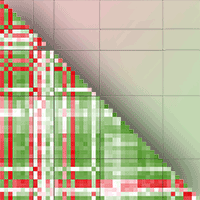
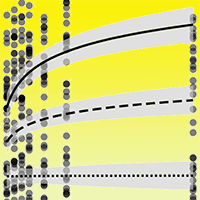
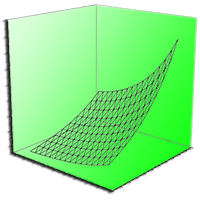
In this work we propose the use of soil quality indicators with the aim of assessing the environmental impact of soil bioengineering works. This study was carried out in central Italy where soil bioengineering slope stabilization works were established using chestnut wood. In particular the goal of this study was to determine the occurrence of a wood-effect, that is changes of soil properties due to the presence of decomposing logs in two sites characterized by different time span since works setting up. The presence of the logs did not affect soil physico-chemical properties. Conversely, soil biochemical properties such as soil microbial biomass, basal and cumulative respiration activities as well as microbial indexes, were influenced by the presence of the logs confirming the role of these bioindicators as early predictors of changes occurring in soil. Although a general positive trend was observed for the biochemical properties at both sites with respect to the control soils, significant differences were recorded mainly at the site where works were established six years before soil sampling. Soil bioengineering slope stabilization works establish a positive feed-back which ultimately can benefit plants; in fact the increase in microbial mineralization activity can enhance nutrient cycling and thus promote adequate growth conditions for the plant cuttings used in the wooden-work.
Keywords
Wood decomposition, Microbial biomass, Microbial respiration, Soil quality, Soil bioengineering
Authors’ Info
Authors’ address
A Lagomarsino
A Di Tizio
S Grego
Dipartimento di Agrobiologia e Agrochimica, Università della Tuscia, Viterbo (Italy)
S Cenfi
S Spina
Dipartimento di Tecnologie, Ingegneria e Scienze dell’Ambiente e delle Foreste, Università della Tuscia, Viterbo (Italy)
Corresponding author
Paper Info
Citation
Moscatelli MC, Romagnoli M, Cenfi S, Lagomarsino A, Di Tizio A, Spina S, Grego S (2009). Wood-soil interactions in soil bioengineering slope stabilization works. iForest 2: 187-191. - doi: 10.3832/ifor0513-002
Academic Editor
Roberto Tognetti
Paper history
Received: May 07, 2009
Accepted: Aug 18, 2009
First online: Oct 15, 2009
Publication Date: Oct 15, 2009
Publication Time: 1.93 months
Copyright Information
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2009
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Web Metrics
Breakdown by View Type
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 63936
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 53648
Abstract Page Views: 4348
PDF Downloads: 4792
Citation/Reference Downloads: 24
XML Downloads: 1124
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 5974
Overall contacts: 63936
Avg. contacts per week: 74.92
Citation Metrics
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2009): 6
Average cites per year: 0.35
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
References
Biotechnical and soil bioengineering slope stabilization: a practical guide for erosion control. Wiley, New York, USA.
Gscholar
Influence of coarse woody debris on soil organic substance in a lodgepole pine forest. Agronomy Abstracts 91: 306-308.
Gscholar
Ecological significance of biological activity in soil. In: “Soil biochemistry”, vol. 6 (Bollag JM, Stotzky G eds). Marcel Dekker, New York, USA, pp. 293-355.
Gscholar
Granulometria. Metodi di analisi fisica del suolo. Parte III. Ed. Ministero dell’Agricoltura e Foreste.
Gscholar
Manuale di ingnegneria naturalistica. Applicabile al settore idraulico. Assessorato all’ambiente, Dipartimento ambiente e protezione civile, Regione Lazio, Roma.
Gscholar
Manuale di ingegneria naturalistica-sistemazione dei versanti. Vol. III. Assessorato all’ambiente, Dipartimento ambiente e protezione civile, Regione Lazio, Roma.
Gscholar
Soil microbial biomass, activity and nutrient cycling as indicators of soil health. In: “Biological indicators of soil health” (Pankhurst CE, Doube BM, Gupta VVSR eds). CAB International, Wallingford, pp. 97-119.
Gscholar
Humus chemistry - genesis, composition and reactions. John Wiley and Sons. USA.
Gscholar
Soil biota, nutrients, and organic matter dynamics under decomposing wood. PhD thesis, Department of Biology, Faculty of natural sciences, University of Puerto Rico. Rio Pedras Compres, pp. 136.
Gscholar