Seven spruce species on a mountain site - performance, foliar nutrients, and forest floor properties in stands 20 years old
iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry, Volume 12, Issue 1, Pages 106-113 (2019)
doi: https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor2731-011
Published: Feb 11, 2019 - Copyright © 2019 SISEF
Research Articles
Abstract
Norway spruce is often considered to have a negative impact on a site, yet it is native to many mountain regions of Europe. The relative influence of Norway spruce on site properties has frequently been compared with that of both broadleaved and other coniferous tree species. In our study, growth, as well as needle, forest floor, and topsoil chemistry were compared between Norway spruce and introduced spruce species (white, black, red, Serbian, Sitka, and blue spruce), all growing on the same, formerly polluted mountain site. There were few differences in needle nutrient status between the introduced spruce species and native Norway spruce. The chemistry of forest floor horizons beneath some of the non-native species showed less acidity and better conditions of the soil sorption complex. There were no significant differences in the nutrient pools, indicating that the influence of the various spruce species on the site was comparable. Given the small differences observed in the various nutritional characteristics, it appears that, under the conditions of the study site, the alternative spruces had substituted for the role of Norway spruce before its recovery in the 2000s. The six spruces grew quite consistently during 2001-2012, while the mean height of Norway spruce shifted from the lowest 176 cm (2001) to one of the tallest. At 710 cm (2012), its height had become comparable with that of Sitka. The poorest performing were black spruce (due to bark beetle attack) and blue spruce (due to bud blight infestation and decline).
Keywords
Introduction
Severe air pollution in the second half of the 20th century had substantial impacts upon forest health across most mountain ranges of Central Europe, but particularly in the Ore Mountains (Krušné hory), which comprise the frontier range between the Czech Republic and Germany, and in the Jizera Mountains (Jizerské hory) straddling the Czech and Polish borders ([25], [22]). Native Norway spruce (Picea abies Karst.) was the tree species most affected, suffering severe dieback that resulted in large-scale clear-felling. Therefore, local foresters had to replace it with plantations of other tree species in order to renew forest cover. Both native and introduced woody species thought to be more resistant to the acid pollutants were tested. Among these, other spruce species were of interest to both researchers ([25], [4]) and forestry practitioners. The practitioners mostly used blue spruce (Picea pungens Engelm.) to restock the cleared areas in the Ore and Jizera mountains ([45], [44]). Because the pollution has diminished since then ([35], [22]), native commercial species are planted today. Experimental stands of non-native species nevertheless still exist within the formerly polluted sites. Knowledge about their performance and functions outside their natural distribution ranges can be of great importance, even under conditions of diminished air pollution. Also other environmental shifts, such as climate change, are likely to show how tree species are able to cope with new conditions ([16]).
Specific needs, properties, and growth rates of tree species affect the utilization of nutrients available at a site in different ways even as their litterfall retroactively influences nutrient cycles ([36]). Although Norway spruce is reported to have negative impacts on soil properties, it is a natural component of the vegetation on most mountain sites of central Europe. It frequently has been reported that Norway spruce produces less-favourable forest floor properties compared with deciduous broadleaves ([6], [3], [12], [8]). Many studies have been also published making comparisons among conifers. For instance, reported forest floor differences have included lower pH under Norway spruce, blue spruce and Serbian spruce (Picea omorika Purk.) compared to Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) and white pine (Pinus strobus L.) on an air-polluted site in the Czech Republic ([15]); lower pH under Norway spruce compared to white pine in Connecticut, USA ([6]); higher pH under Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii [Mirb.] Franco) compared to lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta Douglas - [47]); higher pH under white spruce (Picea glauca [Moench] Voss) compared to black spruce (Picea mariana Mill.) and red pine (Pinus resinosa Aiton) in Ontario, Canada ([23]); comparable litter quality of black spruce and jack pine (Pinus banksiana Lamb.) in Canada ([39]); and no significant pH differences in western red cedar (Thuja plicata Donn ex D. Don), western hemlock (Tsuga heterophylla [Raf.] Sarg.), Douglas-fir, and Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis [Bong.] Carrière) forest floors in Canada ([42]). We took an approach in examining this matter different from those of earlier authors and focused upon the performance of Norway spruce and its effect on site properties in comparison with stands of six other Picea species.
The objective of our study was to compare the performance of a range of spruce species, the chemistry of their needles, and the properties of the forest floor (including topsoil) under young stands growing on a formerly air-polluted site in the Czech Republic. Excepting growth, no major difference between the introduced spruce species (white, black, red, Serbian, Sitka, and blue spruce) and the native Norway spruce were expected.
Methods
Study site
The evaluated forest stands are situated within the Jizerka research plot (see [5]) on the Czech side of the Jizera Mountains (Fig. 1). The research plot was established within a large clear-cut (more than 100 ha in size) created due to SO2 air pollution from Polish and German power plants. According to data from a nearby station ([44]), the air pollution peaked at mean annual SO2 concentration exceeding 40 µg m-3 in 1987, a gradually and markedly decreasing load occurred thereafter, and the level was less than 5 µg m-3 in 2000. The experimental plantations are situated at an altitude of 970 m a.s.l., at a forest site of Piceetum acidophilum. Mean annual temperature of the research plot is 5.0 °C. During 1997-2010, the coldest months were January and February (-4.2 and -3.6 °C) and the warmest ones were July and August (14.4 °C). Mean annual precipitation was 1135 mm, 63% of which fell during the vegetation period (from May to October). The soil is a nutrient-poor, mountain podzol with raw forest floor humus ([31]). Deforested forest floor (F+H) showed a pH of 4.2-4.5 in water ([14]).
The experimental plantings consist of five North American spruce species and two of European origin. The treatments of white spruce (P. glauca, Pg) from Sundown Creek and Eastville, Canada; black spruce (P. mariana, Pm) from Petawawa, Canada; red spruce (P. rubens, Pr) from Timber Lake, Canada; Sitka spruce (P. sitchensis, Ps) from Cranberry River, Canada; blue spruce (P. pungens, Pp) from Rio Grande, USA; Norway spruce (Picea abies, Pa) from Deštné in the Orlice Mountains, Czech Republic; and Serbian spruce (P. omorika, Po) from Sarajevo, Federation of Bosnia and Hercegovina, were planted during 1990-1991 at 1 × 2 m spacing in pure square plots 10 × 10 m in size. Three replicates were analysed for each spruce species in a design similar to a Latin square.
Pm gradually declined and was attacked by bark beetles in 2010. Since 2009, Pp has been infested by bud blight disease (Gemmamyces piceae - [10]), which causes its decline. Bud blight infestation of Pg also was found sporadically in the study plot.
Stand performance analyses
Each year (but with a two-year interval at the end of the experiment) the height (h, in cm) of individual trees was measured within the experimental stands and the occurrence of stem deformation or other damage was evaluated in autumn. The height growth of individual tree species was assessed in this study until 2012, when these stands were thinned. Diameter at breast height (DBH, in cm) and h/DBH (slenderness) ratio also were evaluated. The evaluation was made using data for 20% of the tallest trees from the actual number on each plot because they constitute the most dominant, vigorous trees.
Foliar nutrient sampling and analysis
In November 2011, samples of current-year needles and one-year-old needles were taken for each spruce species. Needles were not sampled for black spruce due to decay of its stand in 2010. In five trees performing well on a plot, two branches were taken from the upper part of the crown. In the laboratory, a composite sample was produced for the individual needle age classes per parcel. For each spruce species, three composite samples were taken (i.e., three replications).
For each needle sample, the contents of basic nutrients (N, P, K, Ca, Mg, and S) and of silicon were analysed using methods described by Zbíral ([49]) and which are comparable with those of the ICP-Forests methodology ([41]). The samples were mineralized, total nitrogen (N) concentration was analysed by the Kjeldahl method, phosphorus (P) was determined colorimetrically, potassium (K) was measured using an atomic absorption spectrophotometer, calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) were determined by atomic absorption after addition of lanthanum, and sulphur (S) and silicon (Si) were measured by the Balks method. The nutrient concentrations of Norway spruce were compared with foliar nutrition thresholds published by Mellert & Göttlein ([28]).
Forest floor and topsoil analysis
In autumn 2013, topsoil samples were taken using a sampling frame of internal size 25 × 25 cm below the closed canopies of Pa, Pg, Pr, and Ps stands, and in 2015 the topsoil was analysed also in Pp and Po stands. L+F and F+H horizons were separated and their total dry weight was determined. The A horizon also was separated. Each tree species was represented by three plots with three replications of samplings in each parcel (i.e., 9 replications per tree species).
Analysed parameters included oxidizable carbon (Cox), nitrogen according to Kjeldahl, acidity (pH/H2O and pH/KCl), sorption complex characteristics (base cation content - BCC, cation exchange capacity - CEC, base saturation - BS) and nutrient contents by the Mehlich III method ([27]).
Data processing
Based upon exploratory data analysis (EDA), data consistency was first assessed. Some nutrient ratios (N/P, N/K, N/Ca, K/Mg, Ca/Mg), describing nutrient balance were computed for macroelements in the needles. Using dry weight and nutrient ratios, nutrient pools in soil were computed for the L+F and F+H horizons.
The data set from the analysis of particular needle age classes and soil horizons was evaluated by principal component analysis (PCA) using the FactoMineR package ([21]) in the R statistical software ([40]). The evaluated parameters were the input variables and spruce species were the factors. The results of the analysis were visualized using the “ggbiplot” function ([48]).
Using Student’s t-test with Holm’s adjustment ([13]), the characteristics determined in individual introduced spruce species were compared statistically with the values determined in Norway spruce taken as a standard. The tests were run in the R statistical computing environment ver. 3.1.3 ([40]) by means of the R Stats Package.
Results
Stand development
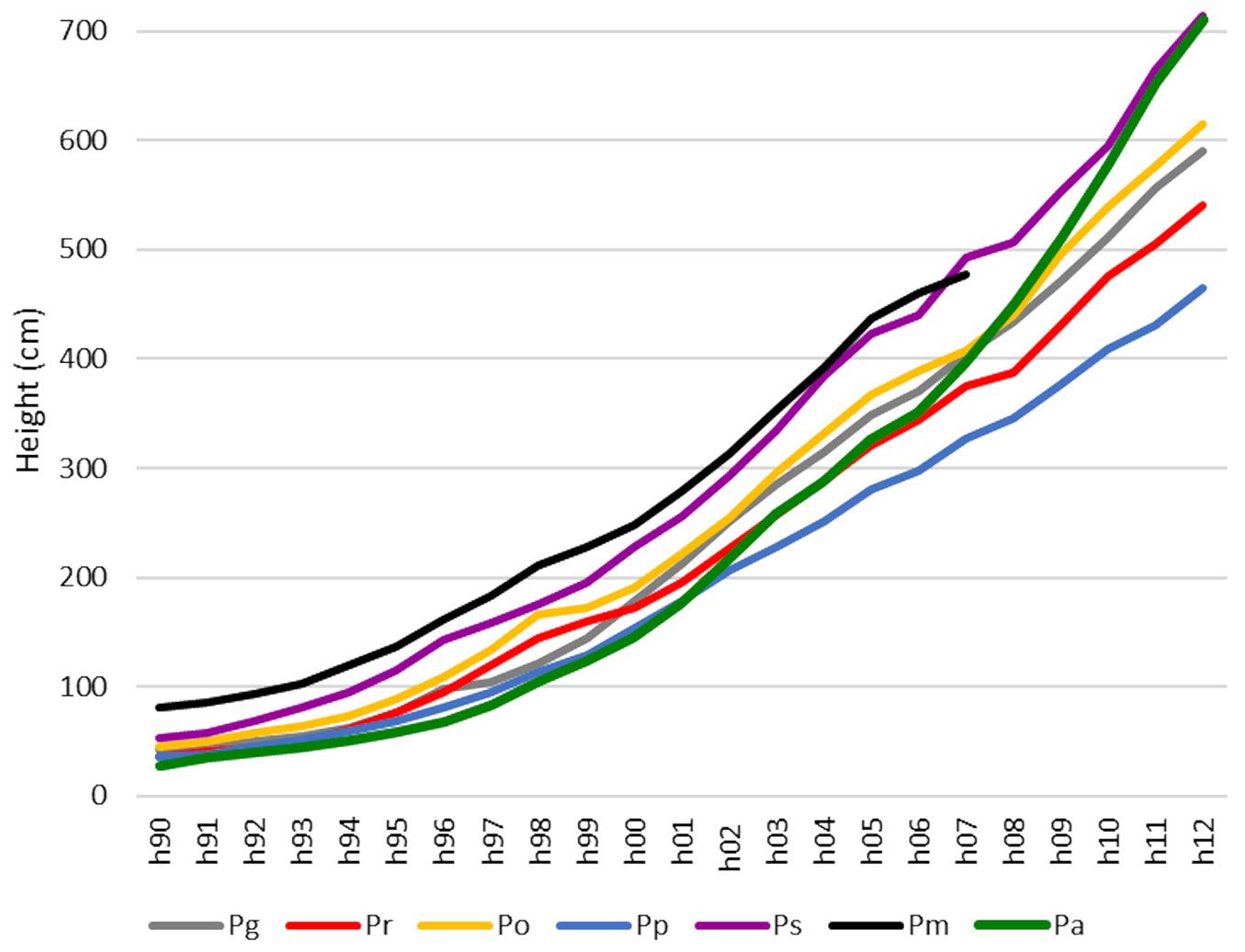
In the first ten years after planting, the mean height growth rate of the tallest 20% of Pa individuals was slower compared to those of the other spruces. In the following period up to 2012, however, its increment increased so as to catch up with the growth of the Ps, which was the tallest treatment after 20 years (height of 7.1 m in 2012 - Fig. 2). The height growth of Pm was comparable with that of Ps at the beginning, but the decay of its stand due to bark beetle occurred in 2010. Pp was the slowest-growing species and it was affected by bud blight. Pp stands also showed the highest average mortality rate (41%) while the lowest mortality was in Ps (22%). The differences between these mortality rates and that of Pa were not, however, statistically significant (Tab. 1). In the second half of the 1990s, necrotic damage to the needles of Po, Pm, and Pa was observed at the studied locality during winter. Current-year needles of Pr were also damaged at that time.
Fig. 2 - Mean height growth of the tree species within analysed stands (20% of the tallest trees for each species) over the period 1990-2012. The years 2008-2009 were measured retrospectively. Relevant data are no longer available for Pm due to forest stand damage. (Pa): Picea abies; (Pg): P. glauca; (Pr): P. rubens; (Po): P. omorika; (Pp): P. pungens; (Ps): P. sitchensis; (Pm): P. mariana.
Tab. 1 - Cumulative mortality during 1990-2012, as well as height (h), DBH, and slenderness ratios (h/d) of individual tree species in 2012. Asterisks indicate significant differences between Norway spruce (first row) and the respective non-native spruce species (t-test with Holm’s adjustment). (*): p<0.05; (**): p<0.01; (SD): standard deviation; (Pa): Picea abies; (Pg): P. glauca; (Pr): P. rubens; (Po): P. omorika; (Pp): P. pungens; (Ps): P. sitchensis; (Pm): P. mariana.
| Species | Mortality (%) | h (cm) | DBH (cm) | h/d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | |
| Pa | 27.5 | 13.5 | 709.5 | 64.2 | 12.9 | 2.6 | 56.7 | 10.3 |
| Pg | 25.5 | 9.0 | 590.4** | 48.3 | 10.4** | 1.7 | 57.9 | 7.0 |
| Pr | 29.3 | 15.4 | 541.4** | 46.4 | 9.8** | 2.0 | 57.2 | 11.7 |
| Po | 29.0 | 3.0 | 615.0** | 36.0 | 11.4 | 2.1 | 55.7 | 9.5 |
| Pp | 41.0 | 12.0 | 465.4** | 52.4 | 10.4** | 1.6 | 45.2** | 5.4 |
| Ps | 22.0 | 2.0 | 714.1 | 66.5 | 11.9 | 2.2 | 61.6 | 9.8 |
In 2012, both Pa and Ps were significantly taller than the other spruce species while Pa had significantly greater DBH compared to Pg, Pr, and Pp. The 2012 slenderness ratio was similar among the species, with the exception that Pp showed a significantly lower h/DBH ratio compared to Pa (Tab. 1).
Deep snow cover in the 2004-2005 and 2005-2006 winter seasons (more than 200 cm at some places) caused trunk and top breaks of Pr and Pm trees (42% and 40% of individuals, respectively) while the break frequency in Pa (24%) was close to the overall average.
Foliar nutrient content
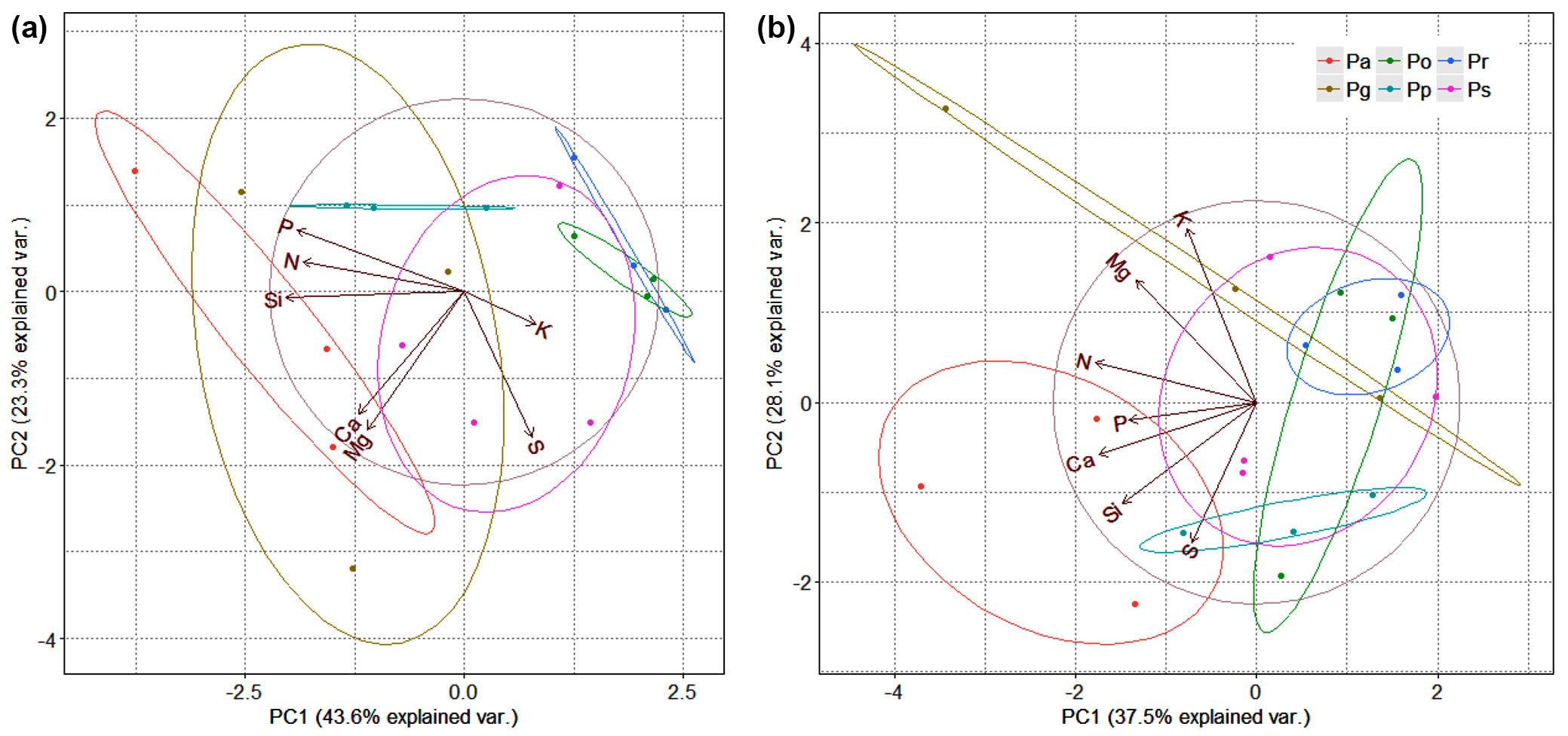
In current-year needles, the first two axes of PCA explained 66.9% of data variance. The distribution of samples in multivariate space was indicated by differences in the chemistry of Pa needles, especially in comparison to Pr and Po, and great data variance in Pg and Ps (Fig. 3a). In one-year-old needles, the two axes of PCA explained 65.6% of the total variance (Fig. 3b). The position of Pa points differs most markedly from those of the Pr and Pg points.
Fig. 3 - Ordination diagram from principal component analysis of macroelement contents in current-year (a) and one-year-old (b) needles. Percentage expresses variance explained by the two axes. (Pa): Picea abies; (Pg): P. glauca; (Pr): P. rubens; (Po): P. omorika; (Pp): P. pungens; (Ps): P. sitchensis; (Pm): P. mariana.
Statistical comparison of the parameters corresponded with the multivariate analysis. There was a trend for higher average content of N, P, and Ca in Pa needles compared to needles of the other spruces, but the differences were rarely significant. In the case of nitrogen, there was a significantly greater content in Pa compared to Po in current-year needles and to Pr in both needle age classes. Higher phosphorus in Pa needles was significant only in current-year needles in comparison with Po and Ps. Calcium was also significantly higher in both needle age classes of Pa compared to Pr and in current-year needles in comparison with Ps (Tab. 2).
Tab. 2 - Percentage content of macroelements and silicon (mean and standard deviation, SD) in current-year (cy) and one-year-old (oy) needles of tested spruce species. Asterisks indicate significant differences in nutrient contents within needle age classes between Norway spruce and the respective non-native spruce species (t-test with Holm’s adjustment): (*): p < 0.05; (**): p<0.01. (Pa): Picea abies; (Pg): P. glauca; (Pr): P. rubens; (Po): P. omorika; (Pp): P. pungens; (Ps): P. sitchensis; (Pm): P. mariana.
| Species | Needle age class | N | P | K | Ca | Mg | S | Si | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | ||
| Pa | cy | 1.38 | 0.10 | 0.086 | 0.010 | 0.54 | 0.02 | 0.47 | 0.00 | 0.106 | 0.011 | 0.157 | 0.023 | 0.27 | 0.03 |
| oy | 1.45 | 0.22 | 0.082 | 0.015 | 0.55 | 0.09 | 0.77 | 0.04 | 0.097 | 0.009 | 0.169 | 0.015 | 0.49 | 0.03 | |
| Pg | cy | 1.28 | 0.17 | 0.070 | 0.010 | 0.39* | 0.05 | 0.54 | 0.16 | 0.106 | 0.018 | 0.151 | 0.017 | 0.19 | 0.02 |
| oy | 1.32 | 0.29 | 0.061 | 0.008 | 0.64 | 0.13 | 0.60 | 0.17 | 0.138 | 0.052 | 0.139 | 0.003 | 0.31** | 0.03 | |
| Pr | cy | 1.05* | 0.07 | 0.063 | 0.001 | 0.59 | 0.04 | 0.28** | 0.02 | 0.084 | 0.002 | 0.160 | 0.013 | 0.12** | 0.01 |
| oy | 1.08* | 0.08 | 0.062 | 0.010 | 0.60 | 0.07 | 0.42* | 0.04 | 0.091 | 0.013 | 0.150 | 0.015 | 0.16** | 0.03 | |
| Po | cy | 1.08* | 0.05 | 0.058* | 0.003 | 0.59 | 0.06 | 0.36 | 0.05 | 0.089 | 0.006 | 0.151 | 0.006 | 0.08* | 0.05 |
| oy | 1.26 | 0.11 | 0.058 | 0.006 | 0.52 | 0.10 | 0.47 | 0.19 | 0.087 | 0.009 | 0.163 | 0.012 | 0.13** | 0.08 | |
| Pp | cy | 1.24 | 0.06 | 0.079 | 0.004 | 0.46* | 0.02 | 0.37 | 0.04 | 0.094 | 0.007 | 0.142 | 0.011 | 0.18* | 0.03 |
| oy | 1.21* | 0.02 | 0.071 | 0.011 | 0.42 | 0.03 | 0.56 | 0.19 | 0.069* | 0.010 | 0.157 | 0.003 | 0.34** | 0.03 | |
| Ps | cy | 1.22 | 0.11 | 0.059* | 0.009 | 0.64 | 0.12 | 0.38* | 0.03 | 0.107 | 0.015 | 0.155 | 0.016 | 0.16* | 0.03 |
| oy | 1.20 | 0.09 | 0.052 | 0.018 | 0.54 | 0.09 | 0.67 | 0.09 | 0.090 | 0.007 | 0.149 | 0.017 | 0.23** | 0.03 | |
Potassium contents in individual spruce species were more differentiated, with significantly lower content found in current-year needles of Pg and Pp compared to Pa. Magnesium was significantly lower only in one-year-old needles of Pp.
Sulphur contents in needles of all introduced species were similar to the values in Pa. The largest differences were measured in silicon content, which was significantly lower in the non-native spruce species compared to Pa in both needle age classes (except the current-year needles in the case of Pg - Tab. 2).
The N/P ratio in Pa was among the lowest, but with the exception of current-year needles of Ps these differences were not significant (Tab. 3). In current-year needles, the N/K ratio in Pa was significantly higher than were those for Pr and Po. The N/Ca ratio was highly variable and no statistical differences were found. The K/Mg ratio was lowest in Pg, followed by Pa; compared to Pa it was significantly higher in current-year needles of Pr and Po. The Ca/Mg ratio in Pa needles was significantly higher in current-year needles compared to Pr and Ps and in one-year-old needles in comparison with Pr and Pg (highly significant - Tab. 3).
Tab. 3 - Nutrient ratios (mean and standard deviation, SD) in current-year (cy) and one-year-old (oy) needles of tested spruce species. Asterisks indicate significant differences in nutrient ratios within needle age classes between Norway spruce and the respective non-native spruce species (t-test with Holm’s adjustment): (*): p < 0.05; (**): p<0.01. (Pa): Picea abies; (Pg): P. glauca; (Pr): P. rubens; (Po): P. omorika; (Pp): P. pungens; (Ps): P. sitchensis; (Pm): P. mariana.
| Species | Needle age class |
N/P | N/K | N/Ca | K/Mg | Ca/Mg | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | ||
| Pa | cy | 16.1 | 0.7 | 2.6 | 0.2 | 2.9 | 0.2 | 5.1 | 0.7 | 4.5 | 0.5 |
| oy | 18.0 | 2.5 | 2.7 | 0.4 | 1.9 | 0.2 | 5.7 | 1.4 | 7.9 | 0.7 | |
| Pg | cy | 18.4 | 1.2 | 3.3 | 0.5 | 2.7 | 1.1 | 3.8 | 0.3 | 5.2 | 1.3 |
| oy | 21.6 | 4.1 | 2.1 | 0.3 | 2.2 | 0.2 | 4.9 | 1.0 | 4.5** | 0.3 | |
| Pr | cy | 16.6 | 1.0 | 1.8* | 0.3 | 3.8 | 0.5 | 7.1* | 0.4 | 3.3* | 0.1 |
| oy | 17.8 | 2.7 | 1.8 | 0.3 | 2.6 | 0.4 | 6.8 | 1.8 | 4.8* | 1.2 | |
| Po | cy | 18.8 | 1.7 | 1.8** | 0.2 | 3.1 | 0.6 | 6.6* | 0.3 | 4.0 | 0.6 |
| oy | 22.2 | 4.0 | 2.5 | 0.4 | 3.1 | 1.2 | 6.0 | 0.8 | 5.6 | 2.6 | |
| Pp | cy | 15.7 | 1.0 | 2.7 | 0.2 | 3.3 | 0.4 | 4.9 | 0.5 | 4.0 | 0.1 |
| oy | 17.5 | 2.8 | 2.9 | 0.2 | 2.6 | 1.2 | 6.2 | 0.9 | 7.9 | 2.3 | |
| Ps | cy | 21.1* | 2.7 | 1.9 | 0.3 | 3.2 | 0.4 | 6.0 | 0.7 | 3.6* | 0.3 |
| oy | 26.5 | 9.9 | 2.3 | 0.4 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 6.0 | 0.7 | 7.5 | 0.8 | |
Forest floor and soil
Dry matter of the L+F horizon in individual spruce species accounted on average for 8.5% (in Po) to 30.3% (in Ps) of the total dry matter of forest floor (L+F+H). Mean total dry weight of forest floor layers in stands of the analysed species ranged from 12.4 to 14.3 kg m-2, without significant differences between Pa and the other spruce species. The greatest variation in values was observed under Pa (Tab. 4).
Tab. 4 - Dry weight (mean and standard deviation, SD) of forest floor horizons (L+F, F+H, and in total). Differences between Pa and other spruce species were not significant. (Pa): Picea abies; (Pg): P. glauca; (Pr): P. rubens; (Po): P. omorika; (Pp): P. pungens; (Ps): P. sitchensis; (Pm): P. mariana.
| Horizon | Pa (kg m-2) | Pg (kg m-2) | Pr (kg m-2) | Po (kg m-2) | Pp (kg m-2) | Ps (kg m-2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | |
| L+F | 3.12 | 1.45 | 3.30 | 1.32 | 3.63 | 1.57 | 1.14 | 0.45 | 2.07 | 1.59 | 4.21 | 0.74 |
| F+H | 11.15 | 5.18 | 9.40 | 3.89 | 8.72 | 5.13 | 12.29 | 2.84 | 10.85 | 3.17 | 9.68 | 3.51 |
| Total | 14.26 | 4.50 | 12.70 | 2.97 | 12.35 | 3.76 | 13.43 | 2.58 | 12.91 | 4.00 | 13.89 | 3.20 |
The PCA multivariate comparison of particular horizons data provided no interpretable outputs in spite of the relatively high probability of data variance explained (the first two axes explained 60.1-65.7% of the variance).
The soil pH values for all horizons were very strongly acid (according to [43]). No differences in pH/H2O values were found between soil horizons under Pa and the other species. The pH/KCl value in Pa was significantly lower in the F+H horizon compared to that of the Po and Pp stands (Tab. S1 in Supplementary material).
Among the sorption complex characteristics, a significantly higher value of CEC-BCC difference was revealed in the L+F horizon in Pa compared to Pg, Po, and Pp; in the F+H horizon, it was also higher than in Ps. In the soil under Pa within the L+F horizon, the CEC value was significantly higher than for Po and in F+H higher than for Pg and Ps.
With the exception of significantly higher P content in the A horizon under Pp, no other significant differences in element contents in soil horizons were found between Pa and the introduced spruce species (Tab. S1 in Supplementary material).
Nutrient pools
Even though there was great variability in the forest floor nutrient pools (kg ha-1) under stands of individual spruce species, few statistically significant differences were apparent (Tab. 5). Although the average pool of Cox in the L+F layer differed between Pa and Po and between Pa and Pp, these differences were not statistically significant. Only a smaller pool of P and K under Po compared to Pa was confirmed. The pools of elements in the F+H layer, similarly to the sums of the pools of both forest floor horizons (L+F+H), did not show any significant differences.
Tab. 5 - Nutrient pools (mean and standard deviation, SD) in L+F and F+H horizons. Asterisks indicate significant differences between Pa and particular non-native spruce species (t-tests with Holm’s adjustment). (*): p < 0.05; (**): p<0.01. (Pa): Picea abies; (Pg): P. glauca; (Pr): P. rubens; (Po): P. omorika; (Pp): P. pungens; (Ps): P. sitchensis; (Pm): P. mariana.
| Horizons | Stand | Cox (kg ha-1) | N (kg ha-1) | P (kg ha-1) | K (kg ha-1) | Ca (kg ha-1) | Mg (kg ha-1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | mean | SD | ||
| L+F | Pa | 1269.2 | 507.4 | 53.3 | 18.1 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 2.81 | 0.72 | 6.61 | 2.24 | 1.54 | 0.73 |
| Pg | 1227.6 | 482.7 | 50.6 | 22.3 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 1.83 | 0.61 | 6.08 | 2.36 | 1.68 | 1.35 | |
| Pr | 1343.3 | 571.2 | 55.3 | 24.5 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 2.15 | 1.28 | 6.52 | 3.17 | 1.79 | 1.17 | |
| Po | 519.7 | 197.2 | 21.2 | 8.7 | 0.08* | 0.04 | 0.74* | 0.28 | 3.19 | 2.01 | 0.48 | 0.14 | |
| Pp | 860.3 | 716.4 | 45.8 | 51.2 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 1.87 | 1.56 | 6.38 | 5.43 | 1.39 | 1.26 | |
| Ps | 1781.4 | 518.5 | 63.4 | 11.7 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 3.00 | 1.31 | 9.41 | 1.96 | 2.34 | 0.37 | |
| F+H | Pa | 3603.4 | 2022.8 | 149.1 | 89.3 | 0.41 | 0.25 | 4.27 | 2.15 | 17.37 | 10.46 | 5.55 | 4.57 |
| Pg | 2914.5 | 1363.4 | 132.8 | 66.2 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 3.10 | 1.70 | 12.25 | 6.26 | 3.48 | 1.38 | |
| Pr | 2683.9 | 1943.6 | 120.7 | 84.0 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 2.65 | 1.72 | 14.47 | 10.19 | 4.63 | 3.64 | |
| Po | 3878.9 | 977.5 | 182.5 | 34.0 | 0.36 | 0.18 | 4.30 | 0.88 | 20.31 | 5.34 | 6.42 | 2.08 | |
| Pp | 3198.1 | 928.5 | 165.7 | 39.1 | 0.47 | 0.26 | 4.02 | 1.58 | 18.25 | 4.55 | 5.63 | 2.07 | |
| Ps | 2120.4 | 976.2 | 86.4 | 44.8 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 2.13 | 0.74 | 11.85 | 5.08 | 3.58 | 2.21 | |
Discussion
Spruce species growth and health
Norway spruce was the slowest growing among all the spruce species tested during 1990-2001. Its growth rate then accelerated and the height was found to be comparable with that of Sitka spruce, which performed well from the very beginning. The improvement in the growth parameters of Norway spruce reflected the diminishing stress from air pollution ([44], [35], [22], [34]). Novotny et al. ([33]) had found a relationship between decreasing defoliation and increasing height increment among Norway spruce in the Ore Mountains during a period (1995-2010) closely corresponding to that of our study (1990-2012) in the Jizera Mountains.
Winter necrotic injury of needles observed in most spruce species was associated with periods of extremely low temperature, and this has been reported also in other regions. For example, winter injury of red spruce needles is well known from its natural distribution range ([20]). Because the occurrence of this spruce species in Central European forests is negligible, we need not be worried about its susceptibility to freezing necrosis of needles.
A massive decline of black spruce was recorded due to an attack in summer 2010 by bark beetles, in particular by pine bark beetle (Pityogenes chalcographus) and the smaller eight-toothed spruce bark beetle (Ips amitinus). Both bark beetles were reported as dangerous for young stands of Norway spruce on the Polish side of the Jizera Mountains ([11]). Black spruce normally grows on waterlogged sites ([39]), but the study plot is not such a site. Hence, it is assumed that the black spruce trees were weakened by environmental conditions different from those of its natural range.
Foliar nutrient content
Nutrient contents in Norway spruce needles indicated a sufficient nitrogen reserve ([29], [46]). More specifically, it was at the boundary between the lower normal level (1.40-1.50% N) and latent deficiency (1.18-1.40% N - [28]). The level of phosphorus was identified at the threshold of extreme deficiency below 0.09% of dry matter. The potassium level was at the low end of normal, between 0.52 and 0.61%. Calcium ranged from intermediate normal to the abundant level (0.44-0.81%), and magnesium was at the intermediate normal level (between 0.09 and 0.12% of dry matter - [28]). No substantial differences in foliar nutrient contents were revealed between individual spruce species. Nevertheless, finding similar foliar contents among conifers at the same site is not surprising, given that Alexander ([2]) documented non-significant differences in Mg foliar content in needles of ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa), Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii), and incense cedar (Calocedrus decurrens [Torr.] Florin), even though soil Mg had been significantly influenced by serpentine bedrock compared to the soil on gabbro bedrock. Neither did Kranabetter & Coates ([18]) find any differences in N content in the needles of a white spruce × Sitka spruce hybrid, of western red cedar (Thuja plicata), and of western hemlock (Tsuga heterophylla) growing in conditions of previously clear-cut, partial-cut, and unharvested forest. Kranabetter & Banner ([17]) reported no significant differences in hemlock needles among stands on four different bedrocks (granodiorite, gneiss diorite, amphibolite, and limestone), though such soil properties as pH/H2O, P, and Mg and forest floor properties as pH/H2O, N, P, S, and C/N showed significant differences. In air-polluted conditions, such soil-improving measures as additions of fertilizing rocks have been found promising ([30]) and also have been tested many times. Blonska et al. ([7]) found the addition to soil of dolomite (2-4 Mg ha-1), magnesite (2-4 Mg ha-1), and serpentine (2-4 Mg ha-1) did not improve the foliar nutrient status of Norway spruce compared to a no-fertilizer control. As measured by nutrient concentrations in Norway spruce needles, application of dolomitic limestone within the Jizerka study site (see methods and [5]) was not observed to have any explicit effect. Limed sample trees at the Jizerka site did, however, produce more dry matter, and consequently they had larger pools of N, P, K, Ca, Mg, and S than did a control ([19]). Therefore, even minor differences in nutrient concentrations in the plant material of individual spruces in our study may be manifested as significant due to differences in total biomass. Thus, biomass nutrient pools are likely to be driven also by parameters such as height, as documented by Power et al. ([37]) for black spruce and white spruce in examining the relationship between total tree foliage biomass and DBH, total height, and crown length.
Matsushima et al. ([26]) documented an increase in foliar N in white spruce needles after removing competitive ground vegetation and fertilizing with nitrogen, which increased the availability of this nutrient. Silvicultural measures such as weed control and N-fertilization can help to improve foliar status of spruce stands in the boreal conditions characteristic of the study site. Mason ([24]) reported moderate differences in foliar contents of N, P, and K in Sitka spruce needles when grown in pure stands versus when admixed with Japanese larch (Larix kaempferi [Lam.] Carrière) and tamarack (Larix laricina [Du Roi] K. Koch). In needles of 25-year-old Sitka spruce, Mason ([24]) revealed a moderate increase in N and K and at the same time a moderate decrease in P in treatments mixed with both larches, but statistical significance of these differences was not mentioned. For Sitka spruce in the Jizera Mountains, foliar N content (1.22%) corresponded with that of 15-year-old Sitka (1.23%) in the north-east of Scotland ([24]), but P (0.06%) and K (0.64%) contents were excessively low compared to the 0.3% P and 1.34% K reported by Mason ([24]). Our results indicated very low phosphorus concentrations ranging from 0.06 to 0.09% in current-year needles and from 0.05 to 0.08% in one-year-old needles in all sampled spruce species (Tab. 2), likely reflecting insufficient nutrition ([46]). This also affected substantially the values of N/P (Tab. 3), as optimal N/P should range from 7.01 to 10.00 according to Srámek et al. ([46]). A previous study from the same study site ([14]) also had documented very low foliar phosphorus (0.07%) in Norway spruce needles. The deficiency of available phosphorus in the soil layer of 0-30 cm was previously documented in this part of the eastern Jizera Mountains where the study plot is situated (Boruvka in [44]). It is apparent that neither the supply of available nutrients nor efficient intake by the plant strictly determine tree performance. For example, Nitschke et al. ([32]) stated that white spruce, as a more efficient nutrient user, is capable of thriving on sites with limited nutrient availability on sites in south-eastern Yukon, Canada. Castle & Neff ([9]) concluded that foliar concentrations are not good indicators of nutrient availability in topsoil. Prescott et al. ([38]) reported a very weak relationship between nutrient contents in assimilation organs and in forest floor, and this corresponds also with our findings.
Forest floor and soil
A part of the forest floor whose properties can be directly influenced by tree species is the upper, least decomposed layer of litter and detritus (L+F). In our study, the smallest amount of L+F material was found under Serbian spruce. At deeper layers (F+H), however, no differences in the amount of forest floor were observed between the non-native spruces and Norway spruce. The accumulation of this material through litterfall substantially influences the total pool of nutrients in forest floor ([23]). For the six spruces, the calculation of nutrient reserve in humus horizons based on their dry matter revealed no statistically significant differences between Norway spruce and the other spruce species, thus indicating their comparable roles in accumulating nutrients in soil.
Aitkenhead-Peterson et al. ([1]) found a strong negative correlation between foliar N and the C/N ratio of forest floor. Our study pointed to a negligible negative correlation between foliar N and C/N in the upper layer of forest floor (L+F). For current-year needles, the R2 was 0.051 and the R2 for needles one year old was 0.022. The correlation between foliar N and C/N in the F+H layer was already positive (current-year needles R2 = 0.138, one-year-old needles R2 = 0.144). A strong negative correlation (R2 = 0.844) was confirmed between nitrogen continent in the L+F layer and the C/N ratio of the same layer. Although the properties of forest floor can differ in relation to the parent rock, they are far from reflecting its composition ([17]). Strong roles are played also by climate and vegetation. Prescott et al. ([38]) reported only a weak correlation between the element contents in living needles and those in forest floor material, with the only significant relationships observed being those for Ca and K. In our study, there was a significant (but still quite weak) correlation only between foliar P and P content in L+F forest floor (R2 = 0.434). A previous study from the same site had shown conifers such as Norway spruce, mountain pine (Pinus mugo Turra), and European larch (Larix decidua Mill.) to be capable of contributing to the higher phosphorus contents of the forest floor compared to those in broadleaved forest and in grass-dominated patches ([14]).
Conclusions
The comparison of performance, foliar nutrient content, and forest floor under 20-year-old spruce stands on the formerly air-polluted mountain site revealed only minor differences between native Norway spruce (Pa) and the introduced spruces. As regards height growth, in spite of initial differences, the performance of Pa was improving over time relative to those of Pp, Pr, Pg, and Po, while Ps performed well throughout the entire period of interest. Pm (due to bark beetle attack) and Pp (due to growth rate and bud blight decline) performed the worst of all. The differences in foliar nutrient concentrations between Pa and other spruce species were negligible, although mostly lower concentrations in the introduced spruces were indicated. Chemistry of the upper soil horizons under Pa and other spruces was similar. There were no significant differences in the forest floor nutrient pools, thus indicating the comparable impact of Pa and other spruces on the site. There has been an obvious recovery in the growth of native Pa compared to the non-native spruces with the exception of Ps. This indicates that it is no longer necessary to plant non-native tree species as replacements for Norway spruce. Further research could determine whether Sitka spruce, which is native to an oceanic climate, can perform comparably with Norway spruce on a montane site in central Europe’s improved pollution conditions.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Ministry of Agriculture of the Czech Republic within MZE-RO0118 institutional support and research project QJ1520291. The authors would like to thank three anonymous reviewers for valuable comments on an earlier version of the manuscript and also Gale A. Kirking (English Editorial Services) for editing the language.
References
CrossRef | Gscholar
Gscholar
Gscholar
Gscholar
Gscholar
CrossRef | Gscholar
Gscholar
Gscholar
Gscholar
CrossRef | Gscholar
Gscholar
Online | Gscholar
Gscholar
Gscholar
Gscholar
Gscholar
Gscholar
Supplementary Material
Authors’ Info
Authors’ Affiliation
Dušan Kacálek
Vratislav Balcar
Forestry and Game Management Research Institute, Opočno Research Station, Strnady 136, 252 02 Jílovište (Czech Republic)
Corresponding author
Paper Info
Citation
Špulák O, Kacálek D, Balcar V (2019). Seven spruce species on a mountain site - performance, foliar nutrients, and forest floor properties in stands 20 years old. iForest 12: 106-113. - doi: 10.3832/ifor2731-011
Academic Editor
Silvano Fares
Paper history
Received: Jan 18, 2018
Accepted: Nov 26, 2018
First online: Feb 11, 2019
Publication Date: Feb 28, 2019
Publication Time: 2.57 months
Copyright Information
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2019
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Web Metrics
Breakdown by View Type
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 45651
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 38540
Abstract Page Views: 3405
PDF Downloads: 2823
Citation/Reference Downloads: 1
XML Downloads: 882
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 2555
Overall contacts: 45651
Avg. contacts per week: 125.07
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2019): 6
Average cites per year: 0.86
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
Related Contents
iForest Similar Articles
Research Articles
Impacts of Norway spruce (Picea abies L., H. Karst.) stands on soil in continental Croatia
vol. 12, pp. 511-517 (online: 02 December 2019)
Research Articles
Retranslocation of foliar nutrients of deciduous tree seedlings in different soil condition under free-air O3 enrichment
vol. 9, pp. 835-841 (online: 17 June 2016)
Research Articles
Contrasted growth response of hybrid larch (Larix × marschlinsii), jack pine (Pinus banksiana) and white spruce (Picea glauca) to wood ash application in northwestern Quebec, Canada
vol. 14, pp. 155-165 (online: 06 April 2021)
Research Articles
Thinning effects on soil and microbial respiration in a coppice-originated Carpinus betulus L. stand in Turkey
vol. 9, pp. 783-790 (online: 29 May 2016)
Research Articles
Estimation of fuel loads and carbon stocks of forest floor in endemic Dalmatian black pine forests
vol. 13, pp. 382-388 (online: 01 September 2020)
Research Articles
The losses of condensed tannins in six foliar litters vary with gap position and season in an alpine forest
vol. 9, pp. 910-918 (online: 04 August 2016)
Research Articles
The effect of soil conditions on submountain site suitability for Norway spruce (Picea abies Karst.) in Central Europe
vol. 16, pp. 210-217 (online: 31 July 2023)
Research Articles
Soil CO2 efflux in uneven-aged and even-aged Norway spruce stands in southern Finland
vol. 11, pp. 705-712 (online: 06 November 2018)
Research Articles
Potential relationships of selected abiotic variables, chemical elements and stand characteristics with soil organic carbon in spruce and beech stands
vol. 14, pp. 320-328 (online: 09 July 2021)
Research Articles
Effects on soil characteristics by different management regimes with root sucker generated hybrid aspen (Populus tremula L. × P. tremuloides Michx.) on abandoned agricultural land
vol. 11, pp. 619-627 (online: 04 October 2018)
iForest Database Search
Search By Author
Search By Keyword
Google Scholar Search
Citing Articles
Search By Author
Search By Keywords
PubMed Search
Search By Author
Search By Keyword