Retranslocation of foliar nutrients of deciduous tree seedlings in different soil condition under free-air O3 enrichment
iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry, Volume 9, Issue 5, Pages 835-841 (2016)
doi: https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor1889-009
Published: Jun 17, 2016 - Copyright © 2016 SISEF
Research Articles
Collection/Special Issue: IUFRO RG7.01.00 - Nice (France 2015)
Global Challenges of Air Pollution and Climate Change to Forests
Guest Editors: Elena Paoletti, Pierre Sicard
Abstract
Retranslocation is the amount of an element that is depleted from old plant components and is provided for new growth. Leaf senescence is usually accelerated at elevated O3 (eO3), and leaf shedding is influenced by soil nutrient availability (and acidification). In this study, we focused on the net retranslocation and allocation dynamics of foliar nutrients (N, P, Mg, K, Ca, Mn, Fe and Al) to investigate the effect of eO3 on birch (Betula platyphylla var. japonica), oak (Quercus mongolica var. crispula), and beech (Fagus crenata) seedlings grown in different soil conditions. Seedlings of the 3 species were planted in a free-air O3 enrichment system under 3 soil types (brown forest soil, serpentine soil, volcanic ash soil) for one growing season. All tree species were grown with 3 replications per each plot at elevated O3 (about 80 ppb) and ambient condition (O3 ranging 25-35 ppb). Leaf samples were taken from the top part of seedlings during the growing season in mid-September, and senescing leaves were sampled in mid-November. Both were collected for chemical composition analysis. Retranslocation rate of P was markedly increased by eO3 in birch and significantly differed among soil types in oak seedlings, while was constant across treatments in beech seedlings. Retranslocation of N in oak seedlings was significantly affected by soil type. Retranslocation of other elements was most sensitive to both eO3 and soil type in beech seedlings. The influence of differential growth patterns among species in modulating the physiological response of seedlings to high levels of ozone and different soil conditions are discussed.
Keywords
Retranslocation, Foliar Nutrients, Ozone, Volcanic Ash Soil, Serpentine Soil
Introduction
Retranslocation of foliar nutrients can be considered as the amount of certain elements depleted from aged plant organs and used for production in other parts of the plant ([37], [23]). It is one of the most essential processes in nutrient dynamics and ecosystem function via decomposition processes, especially for broadleaf species ([28]).
Retranslocation can be quantified by the parameter of nutrient resorption efficiency (NURE), which is defined as the percentage of the foliar nutrient pool absorbed ([17], [7]). Positive NURE values indicate that plants are able to reuse rather than lose their internal nutrients with senescence, therefore plant growth, reproduction and competitive ability will be facilitated and vice versa for negative NURE values ([7]).
Retranslocation has been characterized as an important strategy for trees to conserve nutrients, which eventually affects nutrient competition, absorption and productivity ([36]). It is an essential mechanism for improving plant growth as well as nutrient competitiveness and species conservation ([37], [42]).
These processes of nutrient retranslocation in plants are likely to be affected by plant genetic make-up or plant species, soil fertility, as well as other environmental conditions ([9]). Despite the fact that research has been conducted on the retranslocation response of foliar nutrients, most studies has mainly targeted one or various species ([12], [36]) under different soil statuses, for instance, water irrigation and nitrogen fertilization ([37], [50]). Therefore, little information is available for understanding the effects of elevated ozone (hereafter: eO3) and its relations and interactions with soil fertility (or acidification) on the retranslocation process of foliar nutrients ([42]).
Recently, ground level O3 concentration has been continuously increasing in northeast Asia and is negatively affecting the forest health ([39], [30]). Furthermore, elevation of O3 is expected to continuously increase for at least several decades in the foreseeable future ([35]). In addition, eO3 can accelerate foliar senescence ([14]) and reduce the retranslocation rate of nitrogen (N - [18]), resulting in nutrient deficiencies in leaves caused by the decline of N acquisition ([19]).
Brown forest soil (mostly Cambisols, pH 5.4) which is a common soil type for deciduous broad-leaved forests, contains the necessary elements for plant growth ([20], [24]). Serpentine soil (pH 7.4) is derived from weathered serpentine rock ([3], [21]) and is characterized by excessive Mg and heavy metals but a low contents of Ca and several essential nutrients ([3]). It has a high pH value and is also known to be widely distributed throughout Japan ([21]). Volcanic ash soil (pH 3.6) is an acidic soil that contains high levels of aluminum (Al) and iron (Fe), but low contents in magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), manganese (Mn), nitrogen (N) and potassium (K - [20], [44]). As the response of retranslocation seems to be influenced by soil fertility ([47]) as well as soil acidification ([8], [1]), we have planted seedlings on brown forest soil, volcanic ash soil and serpentine soil. These soil conditions represent rich fertility with neutral soil, medium fertility with acidic soil and poor fertility with alkaline soil, respectively.
As the representative of deciduous species in the northern forests of Japan, Japanese white birch (henceforth birch: Betula platyphylla var. japonica), Mizunara oak (oak: Quercus mongolica var. crispula), and Siebold’s beech (beech: Fagus crenata) were chosen, since they all provide social, economic and environmental benefits that are important to the cool temperate forests of Japan ([27], [29]). According to Yamaguchi et al. ([49]), O3 tolerance capacity of these 3 species can be ranked from low to high as follows: birch < beech < oak. In general, most early successional tree species retranslocate less nutrients from their leaves before shedding, compared to late successional trees, especially in plants grown in infertile soil condition ([23], [28]).
In this study, we focus on the retranslocation and allocation dynamics of foliar nutrients (N, P, Mg, K, Ca, Mn, Fe and Al) to achieve the following major objectives: (i) to determine how O3 concentration affects foliar nutrients retranslocation in birch, beech and oak; (ii) to quantify foliar nutrient retranslocation of element N, P, Mg, K, Ca, Mn, Fe and Al, as well as to examine foliar nutrients retranslocation in different soil sites; (iii) to evaluate the combined effects of both O3 and soil on foliar nutrients retranslocation in birch, beech and oak. Based on the achieved results, we also discuss the plausible understanding of the ecophysiological meaning of retranslocation of each element in leaves in relation to specific traits of O3 effect.
Materials and methods
Plant materials
Two-year old seedlings of Japanese white birch (birch: Betula platyphylla var. japonica), Siebold’s beech (beech: Fagus crenata) and Mizunara oak (oak: Quercus mongolica var. crispula) were obtained near Sapporo (Hokkaido, Japan), and were planted in mid-July 2014 at the nursery of Hokkaido University, Sapporo. These 3 deciduous tree species are the major components of cool temperate forests in Japan ([27], [29]). All the seedlings were grown in the same soil-environment and growth media.
Experimental site description
The experimental site was located in Experimental Nursery of Hokkaido University Forests in the central part of Sapporo, northern Japan (43° 04′ N, 141° 20′ E, 15 m a.s.l.) with about a population of 2 million people. Annual mean temperature and the total precipitation in 2014 were 8.2 °C and 1129 mm respectively. A free-air O3 enrichment system was utilized at the university experimental nursery with each system having 3 soil types (brown forest soil, serpentine soil, volcanic ash soil) and with each soil type being about 30 cm in depth. The enrichment lasted for one growing season. The experimental site consists of 3 control and 3 treatment circular plots 6.5 m in diameter, and with each system being surrounded by 5 m high dispersal pipes ([24]). Details of the O3 exposure in field station as well as the plot design can be found in Watanabe et al. ([46]). O3 concentration of 80 ± 7 nmol mol-1 was applied during daylight hours (about 7 h per day) from early-August to mid-November in treatment plots, while at the same time, the control plots were subjected to ambient daytime O3 concentration of 26.5 nmol mol-1 ([18])
Each of the free-air enrichment plot was unevenly divided into 3 parts, replaced with 3 different soil types: about 84% of the plot area was divided into 2 parts, each equally consisting of brown forest soil (B) and volcanic ash soil (V); about 16% of the area was serpentine soil (S). All of these soil types are widely distributed across northern Japan ([24]). Brown forest soil is native to the Sapporo Experimental nursery, immature volcanic ash soil was brought from the Tomakomai Experimental Forest of Hokkaido University ([24]) and serpentine soil was brought from the eastern part of Teshio Experimental Forest ([45]), where serpentine soil is dominant ([21]).
When taken together, the system was set up with 6 factorial combination treatments of O3 exposure and soil types in the experimental nursery as follow: ambient O3 × B (AB), eO3 × B (EB), ambient O3 × S (AS), eO3 × S (ES), ambient O3 × V (AV), eO3 × V (EV).
Collection of samples and measurements
Samples of live and senescing leaves were taken from 3 seedlings per species in each treatment (4 trees per replication) in two-stages: for live leaves, samples were taken in mid-September during the peak nutritional activities of seedlings, while for senescing leaves samples were taken in mid-November ([40]). The top crown or second leaf counted from the shoot-top was collected as live leaves. After rinsing their surface with distilled water, both collected live and senescing leaves were dried at 70 °C for at least 5 days. Afterward, all the leaves were mill ground into powder to be used for further analysis.
In order to analyze the projected elements (N, P, Mg, K, Ca, Mn, Fe and Al), the powdered leaf samples were digested by nitric acid, hydrogen peroxide method and the concentration was measured with an Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS, IRIS/IRIS Advantage ICAP, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., MA, USA) analysis. N concentration was determined by the combustion method using a NC analyzer (NC-900, Sumica, Osaka, Japan).
For evaluating the retranslocation rate and determining the proportion of the foliar nutrients resorbed before leaf abscission, the nutrient resorption efficiency (NURE) from senescing leaves was calculated as follows (eqn. 1):
where NURE is the nutrient resorption efficiency, Clive is the nutrient concentration of live leaves and Csenescing is the nutrient concentration of senescing leaves ([12], [17], [36]). For each specific nutrient X, (X)RE represents the resorption efficiency of nutrient X, where X = N, P, Mg, K, Ca, Mn, Fe and Al.
Statistical analysis
Parameter values for each species and each treatment were averaged over at least 3-4 replications, in order to provide the sample estimate for the actual replicate. Each NURE was subjected to linear mix model as follows (eqn. 2);
where GAS is the treatment of ozone (ambient and eO3), Soil is the treatment of soil (B, S and V), GAS × Soil is the interaction of ozone and soil, and Plot is the location of each circular plot. We used GAS, Soil and GAS × Soil as fixed factors, and Plot as a random factor. The effects of each fixed factors were analyzed by likelihood ratio test, and we applied Tukey’s post-hoc test when the likelihood ratio test was significant (p < 0.05). These analyses were performed separately on each species. These statistical analyses were performed using R (version 3.1.0 - ⇒ http:// www.r-project.org/) with the “lmer” function of lme4 package (Version 1.1-7 - ⇒ http://CRAN.R-project.org/p-ackage=lme4).
For the mineral elements Mg, K, Ca, Mn, Fe and Al, two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to test the effects of O3 exposure and soil types as well as their interaction. Results were considered significant when p < 0.05. Duncan’s Multiple Range tests were utilized to compare the NURE differences among the 6 treatments. These statistical analyses were performed using the software package SPSS® ver. 21.0 (IBM, NY, USA).
Results and discussion
In general, foliar elements are transported through xylem and phloem, and their content results from the balance between influx via xylem and phloem, and efflux via phloem ([31]). Water soluble elements such as N, P and K are known to be mobile in the phloem and readily retranslocated from older to younger leaves ([32]). Consequently, N, P and K become unstable during leaf senescence, and are usually transported to other parts of the plant, resulting in a decrease of their concentration in senescing leaves ([12]).
On the other hand, the non-mobile mineral elements Ca, Mn, Fe and Al are transported from roots to leaves through xylem but are poorly mobile in phloem ([38], [32], [40]). Therefore, content deficiencies of these elements commonly occur in younger leaves.
Mg is the central atom of chlorophyll pigment, and is essential for ribosome aggregation. In addition, it is often regarded as one of the indicators for leaf greenness and many physiological functions ([23]). Because of its mobility and availability in plants ([8]), Mg is usually considered to decrease with leaf senescence ([12]). Therefore, positive values for N, P, K and Mg, along with negative values of NURE for Ca, Mn, Fe and Al may be the expected results.
Birch
Notwithstanding the above considerations, (Mg)RE in birch was unexpectedly negative under every treatment (Tab. 1). This result is in agreement with the study of Carr et al. ([4]), who reported an increased Mg concentration in aged leaves. It is possible that the dynamics of Mg in live leaves was suppressed by the increased foliar K, as we detected a negative correlation between Mg and K ([21]).
Tab. 1 - Mean (± standard deviation) nutrient resorption efficiency (NURE) of Mg, K, Ca, Mn, Fe and Al in birch seedlings grown on 3 soil types (B: brown forest soil; S: serpentine soil; V: volcanic ash soil) under 2 gas treatments (A: ambient O3; E: elevated O3). Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Duncan’s Multiple Range tests were used to compare the NURE differences among the 6 treatments (3 replicates each). Different letters within each row (nutrient) indicate significant differences among treatments (α = 0.05). (ns): treatment effect not significant ; (*): p <0.05 ; (**): p <0.01 ; (***): p <0.001 (ANOVA).
| Birch | AB | EB | AS | ES | AV | EV | Gas | Soil | Gas×Soil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | -0.472 ± 0.086 a | -0.010 ± 0.314 a | -0.177 ± 0.249 a | -0.510 ± 0.173 a | -0.227 ± 0.098 a | -0.472 ± 0.066 a | ns | ns | ns |
| K | 0.261 ± 0.009 a | 0.257 ± 0.031 a | 0.239 ± 0.046 a | 0.242 ± 0.015 a | 0.334 ± 0.026 a | 0.157 ± 0.084 a | ns | ns | ns |
| Ca | -0.624 ± 0.160 cd | -0.744 ± 0.078 d | -0.242 ± 0.075 a | -0.364 ± 0.021 abc | -0.258 ± 0.077 ab | -0.541 ± 0.064 bc | * | ** | ns |
| Mn | -0.650 ± 0.269 a | -0.605 ± 0.113 a | -0.611 ± 0.043 a | -0.508 ± 0.057 a | -0.328 ± 0.049 a | -1.050 ± 0.065 b | ns | ns | * |
| Fe | -3.180 ± 0.504 b | -3.224 ± 0.517 b | -1.262 ± 0.039 a | -1.579 ± 0.073 a | -1.513 ± 0.275 a | -1.854 ± 0.224 a | ns | *** | ns |
| Al | -4.575 ± 0.371 b | -2.503 ± 0.268 a | -2.250 ± 0.312 a | -2.649 ± 0.139 a | -2.597 ± 0.363 a | -2.186 ± 0.058 a | * | ** | ** |
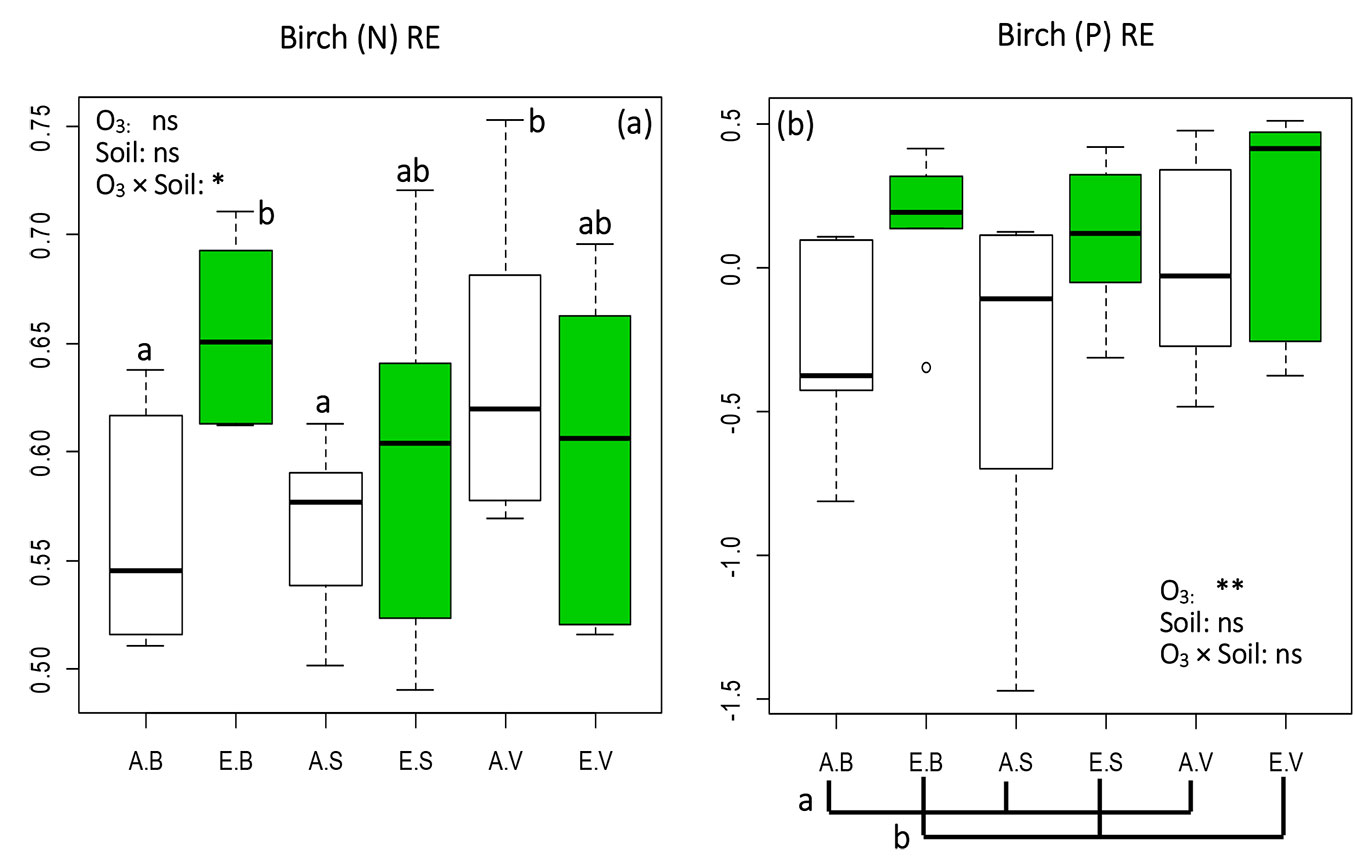
Previous research suggested that nutrient retranslocation in late successional species can increase at nutrient-poor sites ([28]). In this study, similar results were obtained at ambient O3 for 5 elements (N, P, Ca, Fe, Al - Fig. 1, Tab. 1) and at eO3 condition for (Ca)RE and (Fe)RE (Tab. 1). However, the contrasting result observed for (N)RE at eO3 (Fig. 1a) suggests that NURE may be independent of the gradient of the nutrients in the soil ([34]). Alternatively, NURE is likely decreased at nutrient-poor sites by the interaction effects of eO3 and soil fertility, as (N)RE was found to be significant in interaction of eO3 and soils (Fig. 1a). In any case, NURE was likely to be limited by the availability of nutrient gradients, as NURE of N, Ca and Fe at eO3 and NURE of P, Ca, Fe and Al at the ambient site did not show significant differences in both V and S soils (Fig. 1 and Tab. 1).
Fig. 1 - Box-plot of nutrient resorption efficiency (NURE) values of (a) Nitrogen [(N)RE] and (b) Phosphorus [(P)RE] in birch seedlings subjected to 6 treatments (3 replications each). Green boxes indicate elevated O3 treatments (EB, ES, EV), white boxes ambient O3 treatments (AB, AS, AV). B, S, and V indicate different soil types (see Tab. 1). Effects of each fixed factors were tested by the likelihood ratio (LR) test, and Tukey’s post-hoc test was used when LR test was significant. Different letters indicate significant pairwise differences between treatments (α=0.05). Box: interquartile range; whiskers: lower and upper quartiles; thick horizontal line within boxes: median; circles: extreme values. (ns): treatment effect not significant; (*): p<0.05; (**): p<0.01.
We expected that O3 would be detrimental to plant photosynthetic performances ([42], [30]) and nutrient dynamics, resulting in a lower NURE at eO3 due to the O3-induced reduction of translocation from older to younger leaves. As an example, the (Mn)RE value of plants grown in the V soil (Tab. 1) was significantly decreased by eO3. Such decrease may be attributed to the reduction of Mn in live leaves caused by the decline of photosynthetic functions and by the low Gs induced by eO3 ([49], [40]). Contrastingly, NURE of N, P (Fig. 1a, Fig. 1b) and Al (Tab. 1) were markedly increased by eO3. According to Hoshika et al. ([16]), live leaves show a higher capacity of avoidance for O3-induced low Gs, thus being less susceptible to O3 stress than senescing leaves in birch ([14], [16]). Therefore, the decreased concentration of the above elements in senescing leaves at eO3 may be the result of their increased NURE.
Furthermore, Mn showed a significantly higher accumulation in senescing leaves of plants grown in V soil at eO3, as compared with other soils at eO3 (Tab. 1). According to the literature ([25]), Mn tends to have a lower mobility when it is limiting to the plant, thus the deficiency of Mn in the V soil may explain its higher accumulation in the leaves of plants grown under eO3.
Beech
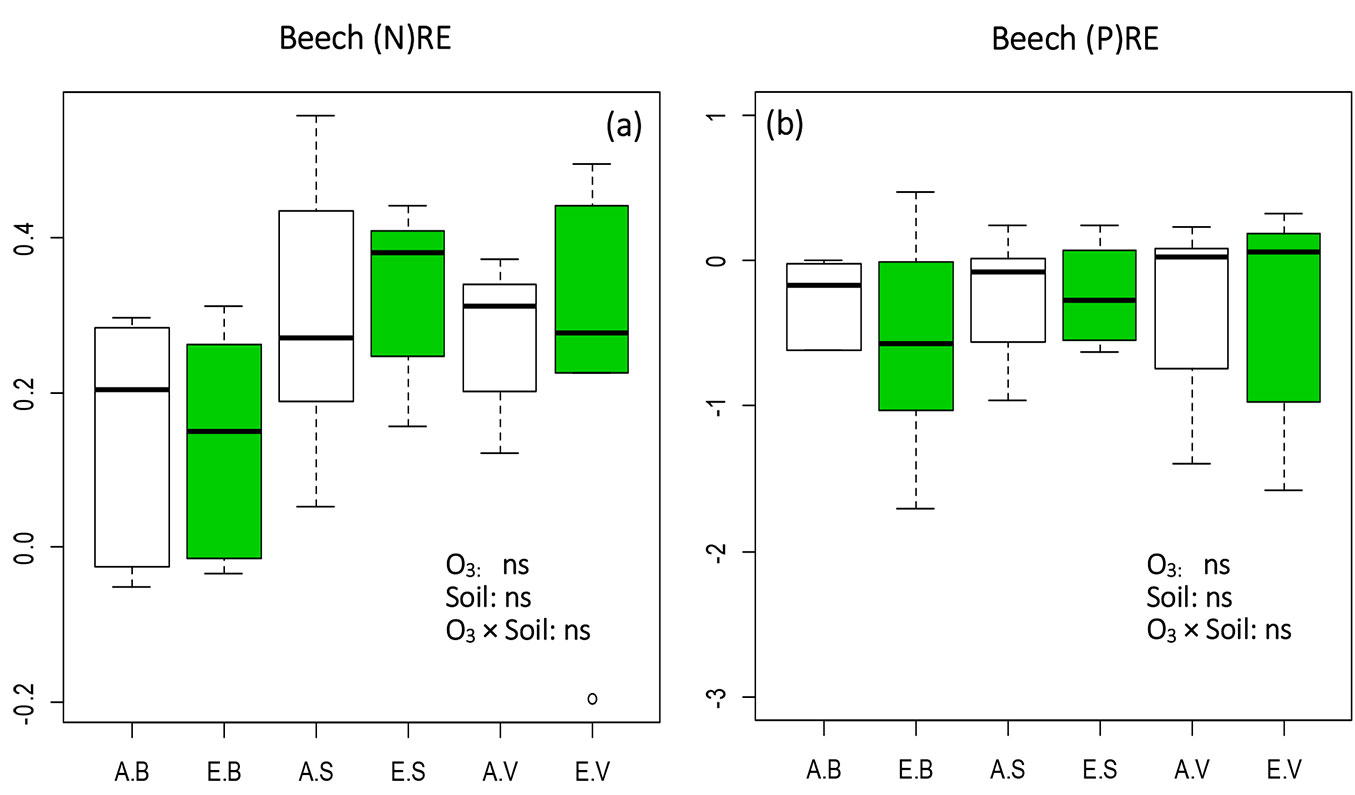
(N)RE and (P)RE were decreased under eO3 in beech, with the exception of (N)RE in the AS and ES treatments. Since no significant effects of O3 and soil (or their interaction) on N and P were detected (Fig. 2), the observed NURE decrease was likely due to the leaching of N and P in senescing leaves under eO3 ([11]). In contrast, (N)RE in the ES treatment reached the highest value compared to other treatments (Fig. 2a), suggesting that more N was allocated to live leaves of beech for plant growth. This is especially important for plants grown in poor fertility soils like S soil in this study.
Fig. 2 - Box-plot of nutrient resorption efficiency (NURE) values of (a) Nitrogen [(N)RE] and (b) Phosphorus [(P)RE] in beech seedlings subjected to 6 treatments (3 replications each). Green boxes indicate elevated O3 treatments (EB, ES, EV), white boxes ambient O3 treatments (AB, AS, AV). B, S, and V indicate different soil types (see Tab. 2). Effects of each fixed factors were tested by the likelihood ratio (LR) test, and Tukey’s post-hoc test was used when LR test was significant. Different letters indicate significant pairwise differences between treatments (α=0.05). Box: interquartile range; whiskers: lower and upper quartiles; thick horizontal line within boxes: median; circles: extreme values. (ns): treatment effect not significant.
Yamaguchi et al. ([48]) reported that the sensitivity of growth and photosynthetic parameters to O3 in beech became high at higher concentrations of N in the soil. Moreover, Hoshika et al. ([16]) concluded that late leaves in birch were more susceptible to O3 stress. In this context, the higher NURE values observed at eO3 in high fertility soils may be a consequence of the lower retention of elements in senescing leaves. Indeed, we found NURE values at eO3 markedly higher in the B soil than in other soils for K, Ca, Mn and Al (Tab. 2).
Tab. 2 - Mean (± standard deviation) nutrient resorption efficiency (NURE) of Mg, K, Ca, Mn, Fe and Al in beech seedlings grown on 3 soil types (B: brown forest soil; S: serpentine soil; V: volcanic ash soil) under 2 gas treatments (A: ambient O3; E: elevated O3). Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Duncan’s Multiple Range tests were used to compare the NURE differences among the 6 treatments (3 replicates each). Different letters within each row (nutrient) indicate significant differences among treatments (α = 0.05). (ns): treatment effect not significant ; (*): p <0.05 ; (**): p <0.01 ; (***): p <0.001 (ANOVA).
| Beech | AB | EB | AS | ES | AV | EV | Gas | Soil | Gas×Soil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | -0.020 ± 0.174 ab | -0.849 ± 0.863 c | 0.436 ± 0.006 a | -0.449 ± 0.207 bc | 0.202 ± 0.055 ab | -0.135 ± 0.049 abc | ** | ns | ns |
| K | 0.216 ± 0.053 a | 0.238 ± 0.083 a | 0.310 ± 0.069 a | -0.063 ± 0.070 b | 0.144 ± 0.017 a | -0.020 ± 0.012 b | ** | * | ** |
| Ca | 0.043 ± 0.028 a | -0.093 ± 0.041 ab | -0.099 ± 0.073 ab | -0.345 ± 0.085 c | 0.068 ± 0.021 a | -0.150 ± 0.049 b | ** | ** | ns |
| Mn | 0.487 ± 0.035 a | -0.039 ± 0.043 b | -0.630 ± 0.066 c | -0.352 ± 0.097 c | 0.135 ± 0.072 b | -0.455 ± 0.171 c | ** | *** | ** |
| Fe | -0.148 ± 0.017 a | 0.095 ± 0.125 a | -1.082 ± 0.343 b | 0.005 ± 0.058 a | -1.420 ± 0.246 b | -0.416 ± 0.105 a | *** | ** | ns |
| Al | -0.276 ± 0.058 ab | 0.013 ± 0.030 a | -0.561 ± 0.179 b | -0.353 ± 0.053 b | -1.265 ± 0.239 c | -0.467 ± 0.088 b | *** | *** | * |
In addition, Fe and Al NURE were significantly enhanced by eO3 treatments in both V and S soils and in V soil alone, respectively (Tab. 2). Fe and Al were indicative of the reduced accumulation of elements in senescing leaves at specific treatments. It has recently been shown that N deficiency-induced leaf senescence (as in the case of V and S soil types) enhances Fe mobilization in old leaves, thereby leading to the decline of foliar Fe accumulation ([2], [41]). Regarding the higher Al(RE) observed under eO3 in beech, the possible explanation is similar to that discussed above for birch. However, the O3-induced reduction of Al concentration in older leaves of beech ([16], [48]) may not be adequately counterbalanced by the increase in foliar Al during leaf senescence in plants growing on acidic soils ([8]), and this may explain the increase of (Al)RE in the treatment EV observed in this study (Tab. 2).
On the other hand, a decrease in (Mg)RE in B and S soils, NURE of K and Ca in S and V soils, (Mn)RE in B and V soils were observed in plants grown under eO3 (Tab. 2). Beside the aforementioned O3-induced reduction of translocation, the concentration of those nutrients in live leaves could be affected by leaching ([12], [8], [43]). Previous research demonstrated that foliar leaching of Ca, K and Mg can be observed on acidified soil and is believed to occur via cation exchange ([8]). These results may suggest that foliar leaching is independent from soil acidification, at least in beech. Moreover, the Al toxicity may also cause the inhibition of some mineral nutrients resorption during senescence ([38]).
Oak
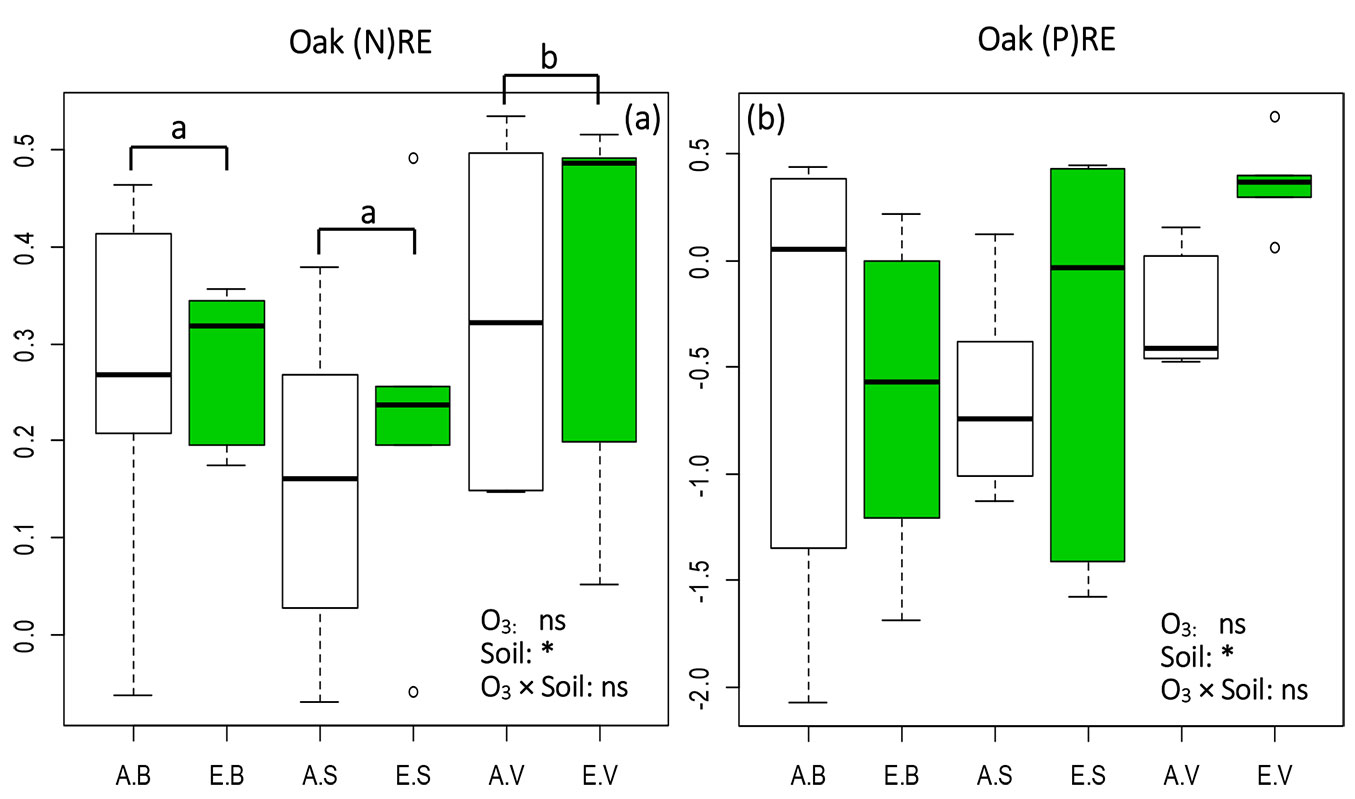
No significant effects of O3 on the NURE of N and P were detected in oak seedlings, though an increase of (N)RE and (P)RE in plants grown in both S and V soils under elevated O3 was observed (Fig. 3). Also, (N)RE and (P)RE were clearly higher in leaves from plants grown in the V soil than in the S soil. Helmisaari ([12]) emphasized that foliar NURE does not vary in response to soil fertilization. Therefore, we hypothesized that higher (N)RE and (P)RE in V soil may reflect soil depletion and acidification. Indeed, depletion-driven losses of N and P in the soil are associated with a decreased retention of N and P in senescent leaves and strongly increased NUREs ([10]). Accordingly, the higher NURE of N and P in V soil (Fig. 3) may result from the high depletion-driven loss in V (acidic) soil, as output N had a high negative correlation with soil pH ([5]).
Fig. 3 - Box-plot of nutrient resorption efficiency (NURE) values of (a) Nitrogen [(N)RE] and (b) Phosphorus [(P)RE] in oak seedlings subjected to 6 treatments (3 replications each). Green boxes indicate elevated O3 treatments (EB, ES, EV), white boxes ambient O3 treatments (AB, AS, AV). B, S, and V indicate different soil types (see Tab. 3). Effects of each fixed factors were tested by the likelihood ratio (LR) test, and Tukey’s post-hoc test was used when LR test was significant. Different letters indicate significant pairwise differences between treatments (α=0.05). Box: interquartile range; whiskers: lower and upper quartiles; thick horizontal line within boxes: median; circles: extreme values. (ns): treatment effect not significant; (*): p<0.05.
Similarly, the markedly higher (Ca)RE observed in the V soil compared to the S soil in the ambient O3 treatments (Tab. 3) suggests that higher depletion-driven loss in V soil may also affect Ca. In contrast, significantly lower (Ca)RE in V than in S soil was observed in treatments under eO3, likely due to soil type-O3 interactions. In particular, the enhanced NURE caused by soil was not adequately compensated by O3-induced detrimental effects on NURE. Such combined influences may largely affect other elements in oak plants.
Tab. 3 - Mean (± standard deviation) nutrient resorption efficiency (NURE) of Mg, K, Ca, Mn, Fe and Al in oak seedlings grown on 3 soil types (B: brown forest soil; S: serpentine soil; V: volcanic ash soil) under 2 gas treatments (A: ambient O3; E: elevated O3). Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Duncan’s Multiple Range tests were used to compare the NURE differences among the 6 treatments (3 replicates each). Different letters within each row (nutrient) indicate significant differences among treatments (α = 0.05). (ns): treatment effect not significant ; (*): p <0.05 ; (**): p <0.01 ; (***): p <0.001 (ANOVA).
| Oak | AB | EB | AS | ES | AV | EV | Gas | Soil | Gas×Soil |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | -0.166 ± 0.046 a | 0.269 ± 0.222 a | -0.317 ± 0.252 a | 0.075 ± 0.058 a | 0.172 ± 0.122 a | -0.167 ± 0.179 a | ns | ns | ns |
| K | -0.189 ± 0.022 a | -0.007 ± 0.062 a | 0.068 ± 0.051 a | 0.053 ± 0.183 a | 0.073 ± 0.062 a | -0.308 ± 0.230 a | ns | ns | ns |
| Ca | -0.055 ± 0.064 bc | -0.109 ± 0.026 bc | -0.280 ± 0.020 d | 0.148 ± 0.160 a | 0.049 ± 0.033 ab | -0.157 ± 0.021 cd | ns | ns | *** |
| Mn | -0.753 ± 0.330 b | -0.444 ± 0.203 ab | -1.759 ± 0.444 c | 0.100 ± 0.010 a | -2.121 ± 0.033 c | 0.255 ± 0.034 a | *** | ns | ** |
| Fe | -0.208 ± 0.059 a | -1.730 ± 0.490 b | -0.722 ± 0.181 a | -0.312 ± 0.343 a | -0.327 ± 0.040 a | -0.085 ± 0.048 a | ** | * | ** |
| Al | -0.241 ± 0.092 a | -1.481 ± 0.085 d | -0.593 ± 0.037 b | -0.164 ± 0.090 a | -0.984 ± 0.069 c | -0.513 ± 0.115 b | ns | *** | *** |
(Al)RE in high fertility soil (B soil) was the highest in controls (ambient O3) but clearly the lowest under eO3 (Tab. 3). Retranslocated nutrients are generally essential for the production of new tissues and organs throughout all stages of plant development. This suggests that soil and environmental factors that facilitate plant growth also promote nutrient retranslocation and vice versa ([33]). As a result, NURE is expected to increase in high-fertility soils but to decrease under eO3. Therefore, the markedly highest (Mn)RE and (Al)RE in AB (Tab. 3) may be the result of the relatively high-fertility soil conditions (B soil) where plants were grown, whereas the significant low (Fe)RE and (Al)RE in EB (Tab. 3) may be due to the effect of interactions between O3 and soil. Nevertheless, the declined NURE caused by eO3 may be aggravated by the relative high N in soil and finally results in the low NURE values ([48]).
Comparisons among birch, beech and oak
Considering the overall impacts of the eO3 exposure on the foliar mineral nutrients investigated (Mg, K, Ca, Mn, Fe and Al), beech was the most affected (Tab. 2), followed by oak (Tab. 3) and birch (Tab. 1). This was inconsistent with previous studies reporting birch as the most and beech as the least sensitive species to eO3 ([49]). These contrasting results may be attributable to differences in patterns of leaf development and growth among species ([15], [22]). Indeed, birch shows an indeterminate growth pattern ([27], [16]), while beech and oak typically have determinate ([26]) and semi-determinate patterns ([13]), respectively. However, it is worth noting that such classification of shoot growth patterns is not clear-cut and considerable overlaps do exists in between classes. In any case, indeterminate growth patterns may promote the production of new leaves to compensate the damage caused by eO3 ([15], [16]), and this may explain why birch is the least affected species in terms of effects of eO3 on mineral nutrients, as compared with beech and oak (Tab. 1).
In addition, beech seedlings were the most affected by soil type concerning the mineral nutrients investigated (Tab. 2), whereas oak was the most tolerant species in terms of impact of soil conditions on nutrient retranslocation (Tab. 3). Although beech is a typical late-successional tree species ([28], [26]), it often retranslocates more foliar nutrients before leaf shedding when growing on infertile soils, compared to early or mid-successional species such as birch and oak ([23], [28], [6]). The results obtained in this study further support such evidence.
Conclusion
In summary, NURE is deeply affected by eO3 and soil types in saplings of 3 Japanese representative tree species and considerable differences in nutrient acquisition and loss in leaves were found among species ([28], [10]). The effect of ozone and soil varied across species with different growth patterns. The retranslocation of mineral nutrients was more efficient in beech, which has a determinate shoot growth pattern and showed a relatively high sensitivity of foliar NURE to either eO3 or nutrient content in the soil. Based on our results, foliar NURE may be considered a good indicator of the physiological conditions of plants to be monitored in field surveys. Studies on the retranslocation of foliar nutrients may help develop appropriate strategies of nutrient management in plantations ([36]).
Acknowledgements
We specially thank Dr. E. Paoletti for her valuable suggestions to this study and JSPS basic research (Type B: 26292075) to TK. Many thanks also to Dr. Y. Matsuura for references and to Mr. E. Agathokleous and Mr. D.-G. Kam for their kind help. We finally acknowledge Ms. S. Fujita for amendments to the manuscript language.
References
Gscholar
Gscholar
Gscholar
Gscholar
Gscholar
Gscholar
CrossRef | Gscholar
CrossRef | Gscholar
Gscholar
Authors’ Info
Authors’ Affiliation
Norikazu Eguchi
Fankang Meng
Toshihiro Watanabe
Takayoshi Koike
Graduate School of Agriculture, Hokkaido University, Sapporo 060-8689 (Japan)
Present address: Aichi Prefectural Forestry Research Institute, Aichi 441-1622 (Japan)
College of Life Science, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071 (China)
Hokkaido University Forests, FSC, Sapporo 060-0809 (Japan)
Corresponding author
Paper Info
Citation
Shi C, Eguchi N, Meng F, Watanabe T, Satoh F, Koike T (2016). Retranslocation of foliar nutrients of deciduous tree seedlings in different soil condition under free-air O3 enrichment. iForest 9: 835-841. - doi: 10.3832/ifor1889-009
Academic Editor
Silvano Fares
Paper history
Received: Sep 30, 2015
Accepted: Mar 26, 2016
First online: Jun 17, 2016
Publication Date: Oct 13, 2016
Publication Time: 2.77 months
Copyright Information
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2016
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Web Metrics
Breakdown by View Type
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 51162
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 42850
Abstract Page Views: 3132
PDF Downloads: 3879
Citation/Reference Downloads: 68
XML Downloads: 1233
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 3519
Overall contacts: 51162
Avg. contacts per week: 101.77
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2016): 8
Average cites per year: 0.80
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
Related Contents
iForest Similar Articles
Research Articles
Effects of abiotic stress on gene transcription in European beech: ozone affects ethylene biosynthesis in saplings of Fagus sylvatica L.
vol. 2, pp. 114-118 (online: 10 June 2009)
Research Articles
Soil drench of ethylenediurea (EDU) protects sensitive trees from ozone injury
vol. 4, pp. 66-68 (online: 05 April 2011)
Research Articles
Soil nutrient status, nutrient return and retranslocation in poplar species and clones in northern Iran
vol. 6, pp. 336-341 (online: 29 August 2013)
Research Articles
A comparison between stomatal ozone uptake and AOT40 of deciduous trees in Japan
vol. 4, pp. 128-135 (online: 01 June 2011)
Research Articles
Changes in the proteome of juvenile European beech following three years exposure to free-air elevated ozone
vol. 4, pp. 69-76 (online: 05 April 2011)
Research Articles
Ozone fumigation effects on the morphology and biomass of Norway spruce (Picea abies L.) saplings
vol. 2, pp. 15-18 (online: 21 January 2009)
Research Articles
Prediction of ozone effects on net ecosystem production of Norway spruce forest
vol. 11, pp. 743-750 (online: 15 November 2018)
Research Articles
Ambient ozone phytotoxic potential over the Czech forests as assessed by AOT40
vol. 5, pp. 153-162 (online: 25 June 2012)
Short Communications
Ozone flux modelling for risk assessment: status and research needs
vol. 2, pp. 34-37 (online: 21 January 2009)
Research Articles
Availability and evaluation of European forest soil monitoring data in the study on the effects of air pollution on forests
vol. 4, pp. 205-211 (online: 03 November 2011)
iForest Database Search
Search By Author
Search By Keyword
Google Scholar Search
Citing Articles
Search By Author
Search By Keywords
PubMed Search
Search By Author
Search By Keyword