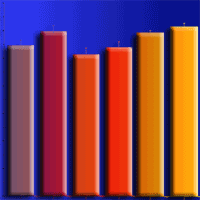
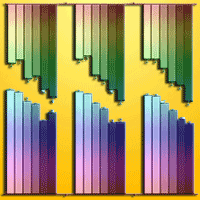
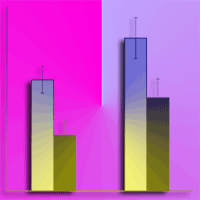The importance of conservation and ecological restoration of the rare and economically important tree Phoebe zhennan is increasingly recognized. To this purpose, phosphorus (P) addition has been proposed to improve soil biological attributes and face the anticipated drought under climate change, though few studies have investigated its effect on the interaction between the soil microorganisms and plant host, as well as on ecosystem productivity. We investigated the effect of P addition on soil chemical properties, microbial communities, and enzyme activities in a soil planted with P. zhennan under two levels of water treatments (optimum water and drought treatments). P additions had no significant effect on microbial communities, dissolved organic nitrogen (DON), pH and soil moisture (SM), though the available P (aP) increased. Compared with no P treatment, alkaline phosphate and β-fructofuranosidase activities increased with P additions in the drought treatment. Drought decreased the total phospholipid-derived fatty acids (PLFAs), arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi (AMF), and fungi PLFAs compared to the well-watered. These findings indicated that P additions does not ameliorate the impact of drought on soil microbial communities and enzyme activities, except alkaline phosphate and β-fructofuranosidase, and P may not be responsible for regulating biochemical processes essential for maintaining the fertility of soil planted with P. zhennan under drought conditions. It is hypothesized that the lack of effects of P addition on the majority of the microbial properties could be due to the soil mechanism employed by P. zhennan to tolerate harsh conditions.
Keywords
, , , , ,
Citation
Olatunji OA, Pan K, Tariq A, Zhang L, Wu X, Sun X, Luo H, Song D, Li N (2018). The responses of soil microbial community and enzyme activities of Phoebe zhennan cultivated under different soil moisture conditions to phosphorus addition. iForest 11: 751-756. - doi: 10.3832/ifor2725-011
Academic Editor
Tamir Klein
Paper history
Received: Jan 09, 2018
Accepted: Aug 27, 2018
First online: Nov 15, 2018
Publication Date: Dec 31, 2018
Publication Time: 2.67 months
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2018
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.

Breakdown by View Type
(Waiting for server response...)
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 51518
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 43901
Abstract Page Views: 3605
PDF Downloads: 3090
Citation/Reference Downloads: 20
XML Downloads: 902
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 2640
Overall contacts: 51518
Avg. contacts per week: 136.60
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2018): 3
Average cites per year: 0.38
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
(1)
Bossio DA, Scow KM (1998)Impacts of carbon and flooding on soil microbial communities: phospholipid fatty acid profiles and substrate utilization patterns. Microbial Ecology 35: 265-278.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(2)
Cao J, Shang H, Chen Z, Tian Y, Yu H (2016)Effects of elevated ozone on stoichiometry and nutrient pools of
Phoebe bournei (Hemsl.) Yang and
Phoebe zhennan S. Lee et F. N. Wei seedlings in Subtropical China. Forests 7 (4): 78.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(3)
Cavagnaro TR (2016)Soil moisture legacy effects: Impacts on soil nutrients, plants and mycorrhizal responsiveness. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 95: 173-179.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(4)
Chapin SF (1980)The mineral nutrition of wild plants. Annual Review in Ecology and Systematic 11: 233-260.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(5)
Cramer MD, Hawkins HJ, Verboom GA (2009)The importance of nutritional regulation of plant water flux. Oecologia 161: 15-24.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(6)
Frostegard A, Tunlid A, Baath E (2011)Use and misuse of PLFA measurements in soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 43: 1621-1625.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(7)
Gao Y, Cooper DJ, Ma X (2016a)Phosphorus additions have no impact on plant biomass or soil nitrogen in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Applied Soil Ecology 106: 18-23.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(8)
Gao J, Zhang W, Li J, Long H, He W, Li X (2016b)Amplified fragment length polymorphism analysis of the population structure and genetic diversity of
Phoebe zhennan (Lauraceae), a native species to China. Biochemistry Systematic and Ecology 64: 149-155.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(9)
Gunina A, Smith AR, Godbold DL, Jones DL, Kuzyakov Y (2017)Response of soil microbial community to afforestation with pure and mixed species. Plant and Soil 412: 357-368.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(10)
Hu Y, Wang B, Hu T, Chen H, Li H, Zhang W, Zhong Y, Hu H (2015)Combined action of an antioxidant defence system and osmolytes on drought tolerance and post-drought recovery of
Phoebe zhennan S. Lee saplings. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 37 (4): 489.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(11)
Huang J, Hu B, Qi K, Chen W, Pang X, Bao W, Tian G (2016)Effects of phosphorus addition on soil microbial biomass and community composition in a subalpine spruce plantation. European Journal of Soil Biology 72: 35-41.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(12)
Kaiser C, Frank A, Wild B, Koranda M, Richter A (2010)Negligible contribution from roots to soil-borne phospholipid fatty acid fungal biomarkers 18: 2ω6. 9 and 18: 1ω9. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 42: 1650-1652.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(13)
Koyama A, Steinweg JM, Haddix ML, Dukes JS, Wallenstein MD (2017)Soil bacterial community responses to altered precipitation and temperature regimes in an old field grassland are mediated by plants. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 94 (1): 1.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(14)
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962)A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytical Chimica Acta 27: 31-36.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(15)
Olatunji OA, Luo H, Pan K, Tariq A, Sun X, Chen W, Wu X, Zhang L, Xiong Q, Li Z, Song D, Zhang A, Sun F (2018)Influence of phosphorus application and water deficit on the soil microbiota of N2-fixing and non-N-fixing tree. Ecosphere.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(16)
Olsen SR, Sommers LE (1982)Phosphorus. In: “Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2” (Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR eds). Agronomy Society of America and Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, USA, pp. 403-430.
Gscholar
(17)
Nielsen UN, Prior S, Delroy B, Walker JKM, Ellsworth DS, Powell JR (2015)Response of belowground communities to short-term phosphorus addition in a phosphorus-limited woodland. Plant and Soil 391: 321-331.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(18)
Pei Z, Eichenberg D, Bruelheide H, Krober W, Kuhn P, Li Y, Oheimb G, Purschke O, Scholten T, Buscot F, Gutknecht JLM (2016)Soil and tree species traits both shape soil microbial communities during early growth of Chinese subtropical forests. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 96: 180-190.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(19)
Richardson AE, Lynch JP, Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Smith FA, Smith SE, Harvey PR, Ryan MH, Veneklaas EJ, Lambers H, Oberson A, Culvenor RA, Simpson RJ (2011)Plant and microbial strategies to improve the phosphorus efficiency of agriculture. Plant and Soil 349: 121-156.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(20)
Rivest D, Paquette A, Shipley B, Reich BP, Messier C (2015)Tree communities rapidly alter soil microbial resistance and resilience to drought. Functional Ecology 29: 570-578.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(21)
Sardans J, Penuelas J (2012)The role of plants in the effects of global change on nutrient availability and stoichiometry in the plant-soil system. Plant Physiology 160: 1741-1761.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(22)
Sanaullah M, Blagodatskaya E, Chabbi A, Rumpel C, Kuzyakov Y (2011)Drought effects on microbial biomass and enzyme activities in the rhizosphere of grasses depend on plant community composition. Applied Soil Ecology 48: 38-44.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(23)
Sayer EJ, Oliver AE, Fridley JD, Askew AP, Mills RTE, Grime JP (2016)Links between soil microbial communities and plant traits in a species-rich grassland under long-term climate change. Ecology and Evolution 7: 855-862.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(24)
Sun F, Pan K, Li Z, Wang S, Tariq A, Olatunji OA, Sun X, Zhang L, Shi W, Wu X (2018)Soybean supplementation increases the resilience of microbial and nematode communities in soil to extreme rainfall in an agroforestry system. Science of the Total Environment 626: 776-784.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(25)
Tabatabai MA, Bremner JM (1969)Use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for assay of soil phosphate activity. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 1: 301-307.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(26)
Tabatabai MA (1982)Soil enzymes. In: “Chemical and Microbiological Properties. Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2 (2nd edn)” (Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR eds). American Society of Agronomy-Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, USA, pp. 903-947.
Gscholar
(27)
Tariq A, Pan K, Olatunji OA, Graciano C, Li Z, Sun F, Sun X, Song D, Chen W, Zhang A, Wu X, Zhang L, Mingrui D, Xiong Q, Liu C (2017)Phosphorous application improves drought tolerance of
Phoebe zhennan. Frontiers in Plant Science 8: 745.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(28)
Temesgen D, Gonzalo J, Turrion MB (2016)Effects of short-rotation
Eucalyptus plantations on soil quality attributes in highly acidic soils of the central highlands of Ethiopia. Soil Use and Management 32: 210-219.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(29)
Torres IF, Garcia C, Ruiz-Navarro A, Hernandez T, Bastida F (2016)The enzymatic and physiological response of the microbial community in semi arid soil to carbon compounds from plants. European Journal of Soil Science 67: 456-469.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(30)
Wei Z, Hu X, Li X, Zhang Y, Jiang L, Li J, Guan Z, Cai Y, Liao X (2017)The rhizospheric microbial community structure and diversity of deciduous and evergreen forests in Taihu Lake area, China. PLoS ONE 12 (4): e0174411.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(31)
Xu ZZ, Zhou GS, Shimizu H (2009)Are plant growth and photosynthesis limited by pre-drought following rewatering in grass? Journal of Experimental Botany 60: 3737-3749.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(32)
Yang K, Zhu J (2015)The effects of N and P additions on soil microbial properties in paired stands of temperate secondary forests and adjacent larch plantations in Northeast China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 90: 80-86.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(33)
You Y, Wang J, Huang X, Tang Z, Liu S, Sun JO (2014)Relating microbial community structure to functioning in forest soil organic carbon transformation and turnover. Ecology and Evolution 4 (5): 633-647.
CrossRef |
Gscholar