Seasonal development of lesions caused by Hymenoscyphus fraxineus on young Fraxinus excelsior trees in Latvia
Ilze Matisone , Roberts Matisons, Kristine Kenigsvalde, Talis Gaitnieks, Natalija Burneviča
iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry, Volume 11, Issue 1, Pages 17-23 (2018)
doi: https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor2283-010
Published: Jan 09, 2018 - Copyright © 2018 SISEF
Research Articles
Abstract
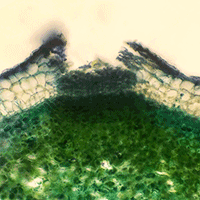
The spread of the ascomycete Hymenoscyphus fraxineus, causing dieback of common ash (Fraxinus excelsior) in Europe, is rapid and the damage is pronounced, as young ashes can perish over the course of only a few months following infection. The objective of this study was to investigate the rate and extent of lesion formation on young (5-8-year-old) ashes during a vegetation season in the hemiboreal zone in Latvia. Continuous surveys (with monthly intervals) of the health condition of 30 young ash and measurements of lesion area in three stands were performed during the vegetation season of 2015. From June to September of that year, the number of observed lesions gradually rose from 58 to 87. New lesions emerged on branches (55%, 0.5 per tree), top shoots (28%, 0.3 per tree), and stems (17%, 0.2 per tree), mostly appearing at the beginning of the observation period (45%, 52%, and 3% in June, July, and August, respectively). During the vegetation season, 20% of the existing and 28% of the newly-emerged lesions on branches, as well as 20% and 25% of top shoot lesions, respectively, reached the main stem. Some (< 20% of cases) transitions of lesions from the tops and branches to the stems were observed. The extension of lesions was significant until August, and ceased afterwards in a similar fashion in all stands. The mean extension of area significantly differed between the previously-existing and newly-emerged lesions. During the vegetation season, the new lesions expanded by 25.1 ± 4.8 cm2, whereas the existing ones grew by only 7.3 ± 1.1 cm2. The extension of the new lesions varied according to their location on a tree. The spread of emerging lesions on stems was considerably slower than on branches or top shoots (1.9 ± 0.7, 7.3 ± 1.5, and 14.5 ± 4.1 cm2 per lesion per month, respectively). During the studied vegetation season (summer), the overall health score of trees decreased twice, yet the relationship between heath status and development of lesions lacked significance.
Keywords
Authors’ Info
Authors’ address
Roberts Matisons
Kristine Kenigsvalde
Talis Gaitnieks
Natalija Burneviča
Latvian State Forest Research Institute Silava, Rigas str. 111, Salaspils, LV-2169 (Latvia)
Corresponding author
Paper Info
Citation
Matisone I, Matisons R, Kenigsvalde K, Gaitnieks T, Burneviča N (2018). Seasonal development of lesions caused by Hymenoscyphus fraxineus on young Fraxinus excelsior trees in Latvia. iForest 11: 17-23. - doi: 10.3832/ifor2283-010
Academic Editor
Alberto Santini
Paper history
Received: Nov 16, 2016
Accepted: Oct 23, 2017
First online: Jan 09, 2018
Publication Date: Feb 28, 2018
Publication Time: 2.60 months
Copyright Information
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2018
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Web Metrics
Breakdown by View Type
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 47904
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 40593
Abstract Page Views: 2934
PDF Downloads: 3259
Citation/Reference Downloads: 12
XML Downloads: 1106
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 2963
Overall contacts: 47904
Avg. contacts per week: 113.17
Citation Metrics
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2018): 2
Average cites per year: 0.25
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
References
Latvijas PSR mežu klasifikacijas pamati [Basis of forest classification in SSR of Latvia]. LRZTIPI, Riga, Latvia, pp. 34. [in Latvian]
Gscholar
Ošu bojaeju izraisoša sene Chalara fraxinea Latvija [Fungus Chalara fraxinea as a causal agent for ash decline in Latvia]. Mežzinatne 21 (54): 110-120. [in Latvian]
Gscholar
Beobachtungen zum sexuellen Stadium des Eschentriebsterben-Erregers Chalara fraxinea in Österreich [Observations on the sexual stage of the ash dieback pathogen Chalara fraxinea in Austria]. Forstschutz Aktuella 48: 21-25. [in German]
Gscholar
The current situation of ash dieback caused by Chalara fraxinea in Austria. In: Proceedings of the “IUFRO working party 7.02.02” (Dogmus-Lehtijärvi T ed). Egirdira (Turkey) 11-16 May 2009. SDU Faculty of Forestry Journal, Serial A, Special Issue, pp. 97-119.
Online | Gscholar
Silvicultural strategies for forest stands with ash dieback. Fortschutz Aktuell 55: 18-20.
Gscholar
Fungi associated with the decline of Fraxinus excelsior in the Baltic States and Sweden. In: “Possible limitation of dieback phenomena in broadleaved stands” (Oszako T, Woodward S eds). Forest Research Institute, Warsaw, Poland. pp. 45-53.
Gscholar