Modeling of early stage litter decomposition in Mediterranean mixed forests: functional aspects affected by local climate
Marcello Vitale (1) , Flavia Savi (1), Daniela Baldantoni (2), Fabio Attorre (1)
iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry, Volume 8, Issue 4, Pages 517-525 (2014)
doi: https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor1202-007
Published: Nov 18, 2014 - Copyright © 2014 SISEF
Research Articles
Abstract
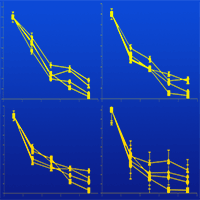
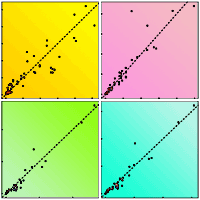
Litter decomposition is an important process occurring in forest ecosystems, where it affects the carbon balance as a whole. In Mediterranean area, seasonal changes and climate variations associated to latitude and structural characteristics of forest stands have a real effect on decomposition rates. Current leaf litter decomposition models are frequently too general to represent local climate variations in Mediterranean forests. We developed a new dynamic semi-empirical-based model, which simulated the early stage of decomposition of leaf litter based on local climate conditions and few operational parameters. Leaf litter was divided in two components, settled on different carbon compound concentrations. The effects of temperature and moisture were characterized by specific equations and the decomposition rates were time-depending functions. Equations were calibrated by the best fitting procedure performed on field data obtained by the litterbag method followed in mixed deciduous forests in central Apennines (Italy). Model validation showed an excellent correlation between observed and predicted values (R2 between 0.89 and 0.95), predicting thus differences in decomposition rates among different local climates. The simple structure of the model and the satisfactory reliability of outputs are important features for a practical alternative to other CO2 release evaluation methods applied to forest ecosystems.
Keywords
Decomposition Rate, Litterbags, Mediterranean Climate, Semi-empirical Models
Authors’ Info
Authors’ address
Flavia Savi
Fabio Attorre
Department of Environmental Biology, “Sapienza” University of Rome, p.le Aldo Moro 5, I-00185 Rome (Italy)
Department of Chemistry and Biology, University of Salerno, v. Giovanni Paolo II 132, I-84084 Fisciano (SA, Italy)
Corresponding author
Paper Info
Citation
Vitale M, Savi F, Baldantoni D, Attorre F (2014). Modeling of early stage litter decomposition in Mediterranean mixed forests: functional aspects affected by local climate. iForest 8: 517-525. - doi: 10.3832/ifor1202-007
Academic Editor
Giorgio Matteucci
Paper history
Received: Dec 13, 2013
Accepted: Aug 27, 2014
First online: Nov 18, 2014
Publication Date: Aug 02, 2015
Publication Time: 2.77 months
Copyright Information
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2014
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Web Metrics
Breakdown by View Type
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 57272
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 47479
Abstract Page Views: 3751
PDF Downloads: 4526
Citation/Reference Downloads: 18
XML Downloads: 1498
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 4134
Overall contacts: 57272
Avg. contacts per week: 96.98
Citation Metrics
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2015): 2
Average cites per year: 0.18
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
References
Crop evapotranspiration - guidelines for computing crop water requirements. FAO Irrigation and Drainage paper 56, FAO, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, Italy, pp. 15.
Gscholar
Plant Litter: decomposition, humus formation, carbon sequestration (2nd edn). Springer, Berlin, Germany, pp. 340.
Gscholar
Litter mass loss rates in pine forests of Europe and Eastern United States: some relationships with climate and litter quality. Biogeochemistry 20 (3): 127-159.
CrossRef | Gscholar
Evaluating and testing models of terrestrial biogeochemistry: the role of temperature in controlling decomposition. In: “Models in ecosystems science” (Canham CD, Cole JJ, Lauenroth WK, eds). Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey, USA, pp. 225-253.
Online | Gscholar
Control of water pollution from cropland. An overview (vol. 2). USDA Agriculture Research Service, Beltsville, MD, USA, pp. 188.
Gscholar
Le bilan d’eau des sols: relation entre les précipitations, l’évaporation et l’écoulement [Soil water balance: relationship between precipitation, evaporation and runoff]. Annales Agronomiques Série A (5): 491-595. [in French]
Gscholar
Determination of lignin and cellulose in acid-detergent fibre with permanganate. Association of Official Analytical Chemists Journal 51: 780-785.
Gscholar