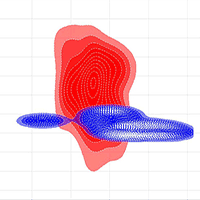
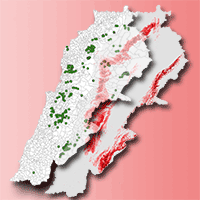
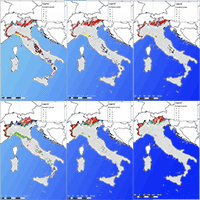
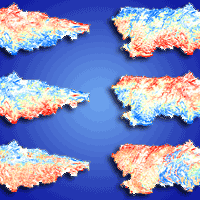
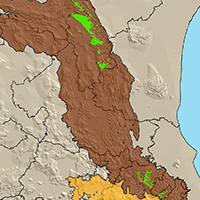
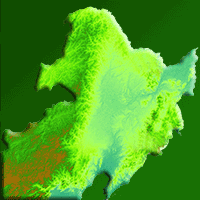
For the rare epiphytic lichen Lobaria pulmonaria (L.) Hoffm., there is a lack of data on ecological niche parameters and distribution factors in the Caucasus, which are necessary to develop an effective system of the species preservation during forest management. The aim of this study was to identify the influence of abiotic, biotic and movement factors on the potential distribution of Lobaria pulmonaria in the Caucasus forests, depending on the spatial scale. We combined species distribution modelling and ecological niche theory based on the BAM (Biotic-Abiotic-Movement) concept. A total of 174 occurrence data were retained in the modelling using Maxent ver. 3.4.3 in R. The distribution models of the main lichen phorophytes in the Caucasus (Pinus sylvestris L. and Fagus orientalis Lipsky) were used as biotic layers in models. The raster of distances from optimal sites, where the probability of the lichen occurrence remained above 0.5, was used as a movement-layer. Different abiotic predictors were significant in the lichen distribution in the Central Caucasus (terrain) and throughout the Caucasus (macroclimate). Interspecific relationships (lichen-phorophyte) were more significant at the local scale. The movement factor contributed most to the local model (80% of the contribution) and limited the lichen distribution to a radius of 20 m in the Central Caucasus and 30 m throughout the Caucasus. Field verification of the local model showed an 85.7% success rate of presence prediction with cutoff values of 0.8. The combination of SDM modelling and ecological niches theory is an effective method for studying the potential localisation and the ecological niches of epiphytic lichens.
Keywords
, , , , ,
Citation
Pshegusov R, Khanov Z, Chadaeva V (2024). Distribution factors of the epiphytic lichen Lobaria pulmonaria (L.) Hoffm. at local and regional spatial scales in the Caucasus: combining species distribution modelling and ecological niche theory. iForest 17: 120-131. - doi: 10.3832/ifor4406-017
Academic Editor
Michele Carbognani
Paper history
Received: Jun 22, 2023
Accepted: Jan 29, 2024
First online: Apr 30, 2024
Publication Date: Apr 30, 2024
Publication Time: 3.07 months
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2024
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.

Breakdown by View Type
(Waiting for server response...)
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 7547
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 2740
Abstract Page Views: 1957
PDF Downloads: 2501
Citation/Reference Downloads: 4
XML Downloads: 345
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 663
Overall contacts: 7547
Avg. contacts per week: 79.68
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2024): 1
Average cites per year: 0.50
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
(1)
Adhikari D, Singh P, Tiwary R, Barik S, Barik K (2019)Modelling the environmental niche and potential distribution of
Magnolia campbellii Hook. f. and Thomson for its conservation in the Indian Eastern Himalaya. In: “Plants of Commercial Values” (Singh B ed.). New India Publishing Agency, New Delhi, india, pp. 277-295.
Gscholar
(2)
Aiello-Lammens ME, Boria RA, Radosavljevic A, Vilela B, Anderson RP (2015)spThin: an R package for spatial thinning of species occurrence records for use in ecological niche models. Ecography 38: 541-545.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(3)
Banerjee AK, Mukherjee A, Guo W, Ng WL, Huang Y (2019)Combining ecological niche modeling with genetic lineage information to predict potential distribution of Mikania micrantha Kunth in South and Southeast Asia under predicted climate change. GECCO 20: e00800.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(4)
Barve N, Barve V, Jimenez-Valverde A, Lira-Noriega A, Maher SP, Peterson A, Soberon J, Villalobos F (2011)The crucial role of the accessible area in ecological niche modeling and species distribution modeling. Ecological Modelling 222: 1810e1819.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(5)
Benesperi R, Nascimbene J, Lazzaro L, Bianchi E, Tepsich A, Longinotti S, Giordani P (2018)Successful conservation of the endangered forest lichen
Lobaria pulmonaria requires knowledge of fine-scale population structure. Fungal Ecology 33: 65-71.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(6)
Blonder B, Lamanna Ch Violle C, Enquist BJ (2014)The n-dimensional hypervolume. Global Ecology and Biogeography 23 (5): 595-609.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(7)
Bowen AKM, Stevens MHH (2020)Temperature, topography, soil characteristics, and NDVI drive habitat preferences of a shade-tolerant invasive grass. Ecology and Evolution 10: 10785-10797.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(8)
Boyce MS, Vernier PR, Nielsen SE, Schmiegelow FKA (2002)Evaluating resource selection functions. Ecological Modelling 157 (2-3): 281-300.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(9)
Brooker RW, Callaway RM, Cavieres LA, Kikvidze Z, Lortie CJ, Michalet R, Pugnaire FI, Valiente-Banuet A, Whitham TG (2009)Don’t diss integration: a comment on Ricklefs’ disintegrating communities. The American Naturalist 174: 919-927.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(10)
Brunialti G, Frati L, Ravera S (2015)Ecology and conservation of the sensitive lichen
Lobaria pulmonaria in Mediterranean old-growth forests. In: “Old-growth Forests and Coniferous Forests. Ecology, Habitat and Conservation” (Weber RP ed). Nova Science Publishers, New York, USA, pp. 12-28.
Gscholar
(11)
Buhl-Mortensen L, Burgos J, Steingrund P, Buhl-Mortensen P, Olafsdottir S, Ragnarsson SA (2019)Vulnerable marine ecosystems (VMEs): coral and sponge VMEs in Arctic and sub-Arctic waters - Distribution and threats. Nordisk Ministerråd, Copenhagen, Denmark, pp. 145.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(12)
Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2002)Model selection and multimodal inference: a practical information-theoretic approach (2nd edn). Springer-Verlag, New York, USA, pp. 355.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(13)
Carlsson R, Nilsson K (2009)Status of the red-listed lichen
Lobaria pulmonaria on the land Islands, SW Finland. Annales Botanici Fennici 46 (6): 549-554.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(14)
Daget P, Ahdali L, David P (1988)Mediterranean bioclimate and its variation in the palaearctic region. In: “Mediterranean-type Ecosystems” (Lieth H, Mooney HA, Specht RL eds). Tasks for Vegetation Science, vol. 19, Springer, Dordrecht, Netherlands, pp. 139-148.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(15)
Di Nuzzo L, Giordani P, Benesperi R, Brunialti G, Fačkovcová Z, Frati L, Nascimbene J, Ravera S, Vallese C, Paoli L, Bianchi E (2022)Microclimatic alteration after logging affects the growth of the endangered lichen
Lobaria pulmonaria. Plants 11 (3): 295.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(16)
Dodgson NA (1992)Image resampling. University of Cambridge Computer Laboratory, Cambridge, UK, pp. 264.
Gscholar
(17)
Eaton S, Ellis C (2012)Local experimental growth rates respond to macroclimate for the lichen epiphyte
Lobaria pulmonaria. Plant Ecology and Diversity 5 (3): 365-372.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(18)
Eaton S, Ellis C, Genney D, Thompson R, Yahr R, Haydon DT (2018)Adding small species to the big picture: species distribution modelling in an age of landscape scale conservation. Biological Conservation 217: 251-258.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(19)
Ellis C (2019)Climate change, bioclimatic models and the risk to lichen diversity. Diversity 11 (4): 54.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(20)
Ellis C, Eaton S (2021)Climate change refugia: Landscape, stand and tree-scale microclimates in epiphyte community composition. Lichenologist 53 (1): 135-148.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(21)
Emberger L (1955)A biogeograpic classification of climates. Researches and developments in Montpellier Botanical Laboratory, Montpellier 7: 3-43.
Gscholar
(22)
ENVIREM (2023)ENVIronmental Rasters for Ecological Modeling. Web site.
Online |
Gscholar
(23)
Fielding AH, Bell JF (1997)A review of methods for the assessment of prediction errors in conservation presence/absence models. Environmental Conservation 24: 38-49.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(24)
Fos S, Gómez-Serrano M, Moreno M, Carles M (2017)Redescubrimiento del liquen
Lobaria pulmonaria, aparentemente extinto en la comunidad Valenciana [Rediscovery of the lichen
Lobaria pulmonaria, apparently extinct in the Valencian Community]. Flora Montiberica 67: 114-119. [In Spanish]
Online |
Gscholar
(25)
Gasparyan A, Sipman H (2020)The first record of Lobaria pulmonaria from Armenia. Herzogia 33: 554-558.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(26)
GBIF (2023)Global Biodiversity Information Facility. Web site.
Online |
Gscholar
(27)
Ginszt T, Laskowska-Ginszt A, Wolkowycki M (2022)The first observation of
Lobaria pulmonaria (L.) Hoffm. on Malus domestica Borkh. in the Bialowieza Forest. Sylwan 166: 297-308.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(28)
Guisan A, Thuiller W, Zimmermann N (2017)Habitat suitability and distribution models: with applications in R. University Printing House, Cambridge, UK, pp. 462.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(29)
Hijmans RJ, Phillips SJ, Leathwick J, Elith J (2017)dismo: species distribution modeling. R package version 1:3-3.
Online |
Gscholar
(30)
Hilmo O, Rocha L, Holien H, Gauslaa Y (2011)Establishment success of lichen diaspores in young and old boreal rainforests: a comparison between
Lobaria pulmonaria and
L. scrobiculata. Lichenologist 43: 241-255.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(31)
Holt EA, Bradford R, Garcia I (2015)Do lichens show latitudinal patterns of diversity? Fungal Ecology 15: 63-72.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(32)
Ignatenko R, Tarasova V (2018)The population structure of the lichen
Lobaria pulmonaria in the middle boreal forests depends on the time-since-disturbance. Folia Cryptogam Estonica 54: 83-94.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(33)
Istomina NB (2008)Lobaria pulmonaria (L.) Hoffm. In: “Red Data Book of Russian Federation (Plants and Fungi)” (Bardunov LV ed.). Tovarishchestvo Nauchnykh Izdaniy KMK, Moscow, Russia, pp. 885. [In Russian].
Gscholar
(34)
Ivanova N (2015)Factors limiting distribution of the rare lichen species
Lobaria pulmonaria (in forests of the Kologriv Forest Nature Reserve). Biology Bulletin 42: 187-96.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(35)
Jüriado I, Liira J, Csencsics D, Widmer I, Adolf C, Scheidegger C (2011)Dispersal ecology of the endangered woodland lichen
Lobaria pulmonaria in managed hemiboreal forest. Biodiversity and Conservation 20: 1803-1819.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(36)
Kassambara A, Mundt F (2019)Factoextra: extract and visualize the results of multivariate data analyses. R package version 1.0.7. Web site.
Online |
Gscholar
(37)
Khanov Z, Pshegusov R (2021)Modeling of population dynamics of the protected lichen
Lobaria pulmonaria (L.) Hoffm. in the Caucasus. BIO Web of Conferences 35: 00015.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(38)
Liu C, White M, Newell G (2013)Selecting thresholds for the prediction of species occurrence with presence-only data. Journal of Biogeography 40: 778-789.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(39)
Lê S, Josse J, Husson F (2008)FactoMineR: an R package for multivariate analysis. Journal of Statistical Software 25 (1): 1-18.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(40)
Matwiejuk A, Zbyryt A (2013)Nowe stanowisko
Lobaria pulmonaria (Stictaceae) z apotecjami w Polsce [New locality of Lobaria pulmonaria (Stictaceae) with apothecia in Poland]. Fragmenta Floristica et Geobotanica Polonica 20: 24-28. [In Polish]
Gscholar
(41)
Maus C, Rybacki S, Uhrmacher AM (2011)Rule-based multi-level modeling of cell biological systems. BMC Systems Biology 5 (1): 166.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(42)
Mikryukov V, Mikhailova I, Scheidegger C (2010)Reproductive parameters of
Lobaria pulmonaria (L.) Hoffm. in the Urals. Russian Journal of Ecology 41 (6): 475-479.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(43)
Muscarella R, Galante PJ, Soley-Guardia M, Boria RA, Kass JM, Uriarte M, Anderson RP (2014)ENMeval: an R package for conducting spatially independent evaluations and estimating optimal model complexity for MaxEnt ecological niche models. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 5 (11): 1198-1205.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(44)
Myers CE, Stigall AL, Lieberman BS (2015)PaleoENM: applying ecological niche modeling to the fossil record. Paleobiology 41 (2): 226-244.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(45)
Nadyeina O, Dymytrova L, Naumovych A, Postoyalkin S, Scheidegger C (2014)Distribution and dispersal ecology of
Lobaria pulmonaria in the largest primeval beech forest of Europe. Biodiversity and Conservation 23: 3241-3262.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(46)
Nascimbene J, Benesperi R, Casazza G, Chiarucci A, Giordani P (2020)Range shifts of native and invasive trees exacerbate the impact of climate change on epiphyte distribution: the case of lung lichen and black locust in Italy. Science of the Total Environment 735(9): 139537.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(47)
Ockinger E, Niklasson M, Nilsson S (2005)Is local distribution of the epiphytic lichen
Lobaria pulmonaria limited by dispersal capacity or habitat quality? Biodiversity and Conservation 14: 759-773.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(48)
Osorio-Olvera L, Lira-Noriega A, Soberón J, Peterson A, Falconi M, Contreras-Díaz RG, Martínez-Meyer E, Barve V, Barve N (2020)ntbox: an R package with graphical user interface for modelling and evaluating multidimensional ecological niches. Methods Ecology and Evolution 11 (10): 1199-1206.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(49)
PanoplyWin (2021)Panoply netCDF, HDF and GRIB Data Viewer. Web site.
Online |
Gscholar
(50)
Peterson A, Soberón J (2012)Species distribution modeling and ecological niche modeling: getting the concepts right. Natureza e Conservação 10 (2): 1-6.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(51)
Peterson A, Soberón J, Pearson R, Anderson R, Martínez-Meyer E, Nakamura M, Araújo M (2011)Ecological niches and geographic distributions. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ, USA, pp. 329.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(52)
Peterson A, Anamza T (2015)Ecological niches and present and historical geographic distributions of species: a 15-year review of frameworks, results, pitfalls, and promises. Folia Zoologica 64 (3): 207-217.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(53)
Phillips SJ, Anderson RP, Dudik M, Schapire RE, Blair ME (2017)Opening the black box: an open-source release of Maxent. Ecography 40 (7): 887-893.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(54)
Phillips SJ, Dudík M (2008)Modeling of species distributions with Maxent: new extensions and a comprehensive evaluation. Ecography 31 (2): 161-175.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(55)
Pshegusov R, Tembotova F, Chadaeva V, Sablirova Y, Mollaeva M, Akhomgotov A (2022)Ecological niche modeling of the main forest-forming species in the Caucasus. Forest ecosystems 9: 100019.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(56)
Qiao H, Escobar LE, Saupe EE, Ji L, Soberón J (2017)A cautionary note on the use of hypervolume kernel density estimators in ecological niche modelling. Global Ecology and Biogeography 26 (9): 1066-1070.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(57)
Riley S, Degloria SD, Elliot SD (1999)A terrain ruggedness index that quantifies topographic heterogeneity. IJS 5 (1-4): 23-27.
Gscholar
(58)
Rys A (2005)Granicznik plucnik
Lobaria pulmonaria w Lasach Panstwowych i jego ochrona [
Lobaria pulmonaria in state forests and its protection]. Wyd Studio Avalon, Olsztyn, Poland, pp. 135. [in Polish]
Gscholar
(59)
Shkhagapsoev S, Kurasheva L (2022)Forests of Kabardino-Balkaria: forest management, afforestation, composition, protection. Publishing house of M. and V. Kotlyarov, Nalchik, Russian Federation, pp. 340. [in Russian]
Gscholar
(60)
Sillero N, Arenas-Castro S, Enriquez-Urzela U, Vale CG, Sousa-Guedes D, Martínez-Freiría F, Real R, Barbosa AM (2021)Want to model a species niche? A step-by-step guideline on correlative ecological niche modelling. Ecological Modelling 456: 109671.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(61)
Soberón J, Peterson A (2005)Interpretation of models of fundamental ecological niches and species’ distributional areas. Biodiversity Informatics 2: 1-10.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(62)
Soberón J, Osorio-Olvera L (2023)A dynamic theory of the area of distribution. Journal of Biogeography 50 (6): 1037-1048.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(63)
SpatialEco (2023)Spatial analysis and modelling of ecological systems, version 1:3-7, Web site.
Online |
Gscholar
(64)
SRTM (2023)Shuttle radar topography mission. Web site.
Online |
Gscholar
(65)
Stoykov D (2015)Lobaria pulmonaria (Ascomycota, Lobariaceae) in Bulgaria. Trakya University Journal of Natural Sciences 13 (2): 109-114.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(66)
Sutton L, Anderson D, Franco M, McClure Ch, Miranda E, Vargas F, Vargas G, Puschendorf R (2023)Prey resources are equally important as climatic conditions for predicting the distribution of a broad-ranged apex predator. Diversity and Distributions 29: 613-628.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(67)
Tembotova F, Pshegusov R, Tlupova Y (2012)Forests of the northern macroslope of the Central Caucasus (Elbrus and Terek variants of zonation). In: “Biological Diversity of Forest Ecosystems” (Isayev AS ed). Tovarishchestvo Nauchnykh Izdaniy KMK, Moscow, Russia, pp. 242-259. [in Russian]
Gscholar
(68)
Title PO, Bemmels JB (2018)ENVIREM: an expanded set of bioclimatic and topographic variables increases flexibility and improves performance of ecological niche modeling. Ecography 41 (2): 291-307.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(69)
Tytar V (2021)Associations between habitat quality and body size in the Carpathian-Podolian land snail
Vestia turgida (Gastropoda, Clausiliidae): species distribution model selection and assessment of performance. Zoodiversity 55: 25-40.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(70)
Urbanavichene IN, Urbanavichus GP (2014)Contribution to the lichen flora of the Achipse River valley (SW Caucasus, Krasnodarsky Kray). Novosti Sistematiki Vysshikh Rastenii 48: 315-326. [In Russian]
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(71)
Wickham H (2009)ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. Springer-Verlag, New York, USA, pp. 260.
Gscholar
(72)
Wiens JJ (2011)The niche, biogeography and species interactions. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series 366 (1576): 2336-2350.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(73)
Wisz M, Pottier J, Kissling W, Pellissier L, Lenoir J, Damgaard C, Dormann C, Forchhammer M, Grytnes J, Guisan A, Heikkinen R, Hoye T, Kühn I, Luoto M, Maiorano L, Nilsson M-Ch Normand S, Ockinger E, Schmidt N, Svenning J-C (2013)The role of biotic interactions in shaping distributions and realised assemblages of species: Implications for species distribution modelling. Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society 88 (1): 15-30.
CrossRef |
Gscholar