Identification of the ambrosia beetle Anisandrus dispar (Fabricius) (Coleoptera Curculionidae Scolytinae) using TaqMan™ probe assay on biological samples
iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry, Volume 16, Issue 3, Pages 182-187 (2023)
doi: https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor4287-016
Published: Jun 30, 2023 - Copyright © 2023 SISEF
Research Articles
Abstract
The European shot-hole borer Anisandrus dispar (Fabricius) (Coleoptera Curculionidae Scolytinae) is a well-known ambrosia beetle living on shrubs and several ornamental and fruiting trees where it can cause heavy damages. Like other harmful xyleborine species, A. dispar can represent a potential threat outside its native region. Molecular diagnostic tools can lead to accurate identification of xylophagous species hidden in wooden matrix in phytosanitary surveys at entry points. A molecular assay based on qPCR TaqMan™ Probes was developed for the identification of A. dispar from different matrices. To setup and perform the test, DNA extraction was carried out from adults, larvae, and artificial samples of wood chips from oak healthy plants whose lysates were contaminated with a known amount of DNA of A. dispar adults. The assay has proven inclusive for A. dispar, and exclusive towards the non-target organisms, showing 100% analytical specificity. The limit of detection was 0.32 pg µL-1 for the samples of insect adult DNA of A. dispar, and at 0.8 pg µL-1 for the samples containing lysates of Quercus spp. and 0.1 ng µL-1 of A. dispar adult DNA. Repeatability and reproducibility showed low values independently from the matrix used for DNA extraction, confirming the possible use in diagnostics of biological samples even if not directly related to the presence of A. dispar developmental stages. The presented approach may be adjusted and applied for phytosanitary purposes to other quarantine pests and rapidly detect possible infestations in vegetal matrices globally traded.
Keywords
European Shot-hole Borer, Xyleborini, Quarantine Species, Molecular Diagnostics, Biological Traces
Introduction
Increasing threats to forest and fruiting trees around the world is driven by the introduction and establishment of exotic Ambrosia and bark beetles (Curculionidae: Scolytinae and Platypodinae) outside native territories. The Ambrosia beetle Anisandrus dispar (Coleoptera Curculionidae Scolytinae) is a Palaearctic species widely distributed in Europe and Asia ([33]) and established across North America, where it should be considered a high-risk invasive quarantine species ([23], [13]). The host plant range include many species of deciduous trees and conifers ([10], [39], [32], [11]). Although A. dispar usually attacks decaying trees, this beetle can colonize and severely infest wounded, injured or apparent healthy plants ([37]). Infestations may be particularly serious on hazelnut crops ([5], [34], [31]) and damages have been recorded in pear orchards ([37]). Like other harmful xyleborine species, A. dispar can represent a potential threat outside its native range ([12]).
The identification of xylophagous species in phytosanitary practice is generally rather complicated. Traditionally adult identification is time consuming with continuous comparison among similar morphological characters to distinguish a genus from a subfamily or a species from cogeneric ones ([6], [33]). Today the use of molecular diagnostic tools lead to accurate and ease identification and time savings. In all those cases where only signs of damage (empty galleries or with traces of frass) are available or juveniles hidden inside woody tissues with the issue to extract the intact bodies from galleries, traditional approaches show their limits. The molecular diagnosis becomes particularly useful if this tool can be applied to obtain results from indirect evidence. In fact, the identification of xylophagous species from frass has already been developed for several species ([14], [15], [26], [27], [36]). Moreover, the use of biological traces (exuviae, incomplete bodies, frass or faeces) for the identification at species level can be decisive, especially when fast, reliable and unambiguous diagnosis are needed to identify the presence of quarantine or invasive species in time ([26], [29]). From a phytosanitary point of view the setup of molecular protocols ready to use may support early pest detection carried out by any Plant Protection and Inspection Service ([40]).
More than 30 species belong to the genus Anisandrus including forest threatening pests ([33]). Morphologically A. dispar could be confused with the smaller A. maiche Kurentzov ([13], [33]). Recently, this Asian species has been recovered in European Russia and Ukraine ([19]), Italy ([7], [30]) and Switzerland ([9]). Consequently, a precise molecular identification of A. dispar is considered to be of crucial importance to support its easy discrimination among congeneric exotic pests and avoid accidental introductions of non-native Anisandrus species across Europe.
Here we propose a molecular diagnostic test based on qPCR with TaqMan™ Probe technology developed for the identification of A. dispar using DNA extracted from samples of larvae, adults, and artificial sawdust obtained from healthy Quercus cerris branches, and subsequently contaminated with known amounts of A. dispar adult DNA. This approach could be shared and applied to several other organisms/insects for the development of standard identification methods.
Materials and methods
Biological samples
Adults and larvae of Anisandrus dispar were collected during routine monitoring inspections carried out by the Phytosanitary Service in Tuscany, or by other research institutions in the respective Regions (Tab. 1). Larvae and adults were stored in 70% ethanol solution at room temperature until use. Artificial sawdust samples to simulate the frass of A. dispar were obtained by holing healthy branches (5-10 cm diameter) from oak trees (Quercus cerris) with a manual drill. All samples were stored at room temperature in the lab until use, for a period ranging from 2 to 8 months to simulate the conditions in which natural samples could be collected.
Tab. 1 - List of samples of the target species Anisandrus dispar used for DNA extraction.
| Sample | Specimens in the sample |
Sample content |
|---|---|---|
| i | Anisandrus dispar | DNA from single adults and larvae |
| ii | A. dispar and Q. cerris | Mix at a ratio 1:5 of lysates from A. dispar adult and artificial sawdust, both of CTAB 2% |
| iii | A. dispar and Q. cerris | Mix of 0.1 ng/µL adult DNA and Q. cerris lysate in CTAB 2% |
The non-target insects (adults, larvae and/or frass in the case of xylophagous species) used for testing the analytical specificity of the assay, belonged to the biomolecular collection of the Phytopathological Lab of the Phytosanitary Service of the Tuscany Region, Italy. The non-target insects chosen were several other xylophagous beetles and moths, as specified in Tab. S1 (Supplementary material).
DNA extraction from target and non-target samples
Genomic DNA from all target samples was extracted using the modified protocol suggested by Li et al. ([18]), until the addition of chloroform and the subsequent centrifugation at 11.500 g for 5 min. Some 600 μL of the upper phase was purified using the Maxwell® RSC PureFood GMO and Authentication Kit in combination with the automated purificator MaxWell 16 (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Details of the purification have been previously described ([26], [27]). The DNA of non-target samples was extracted using the same procedure used for target samples, but in different times.
DNA extraction was carried out with the same methodology on different matrices as shown in Tab. 1: (i) single larvae and adults of A. dispar; (ii) lysate of CTAB 2% buffer of A. dispar adult added at lysate of CTAB 2% buffer from artificial sawdust at a ratio 1:5; (iii) A. dispar adult DNA (0.1 ng µL-1) mixed with artificial sawdust lysate in 2% CTAB buffer.
Serial dilutions 1:5 were made, and DNA extraction was carried out in duplicate for each dilution step, to verify the analytical sensibility of the extraction method. Extract dilutions were 5-1 - 5-7 for samples (ii) and 0.1 ng µL-1 - 0.24 fg µL-1 for samples (iii).
These different samples used for DNA extractions were chosen to test the sensibility of the method in discriminating A. dispar target specimens (DNA and lysate) from host plant lysate, simulating the indirect diagnosis of the woodborer from the natural frass (unavailable in our experiment).
The quality of the extracted DNA was assayed in qPCR after a dilution 1:20 of DNA in ddH2O; a dual-labeled probe (18S uni F/ -R) and a YakimaYellow-BHQ1 dual labeled probe (18S uni-P) targeting a highly conserved region of the 18S rDNA was used in the reaction ([36], [16]). The amplification tests of DNA samples were used as control and allowed to verify the presence of inhibitors in relation to both the Cq (quantification cycle) detected and the slope of the relative amplification curves.
Design of primers and probe and relative optimization
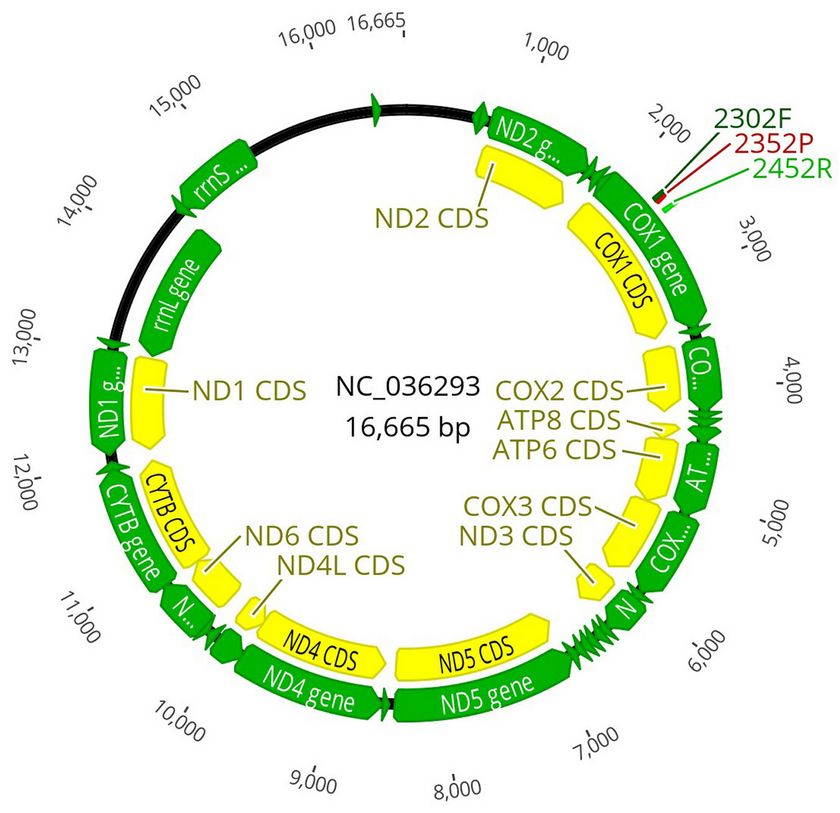
The software Oligo Architect Online® (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was used to design the primer pairs and probes, targeting the conserved sequences (voucher BMNH 1047383 mitochondrion, complete genome) of A. dispar genome (accession number KX035217.1) calculating the product size, the melting temperature and primer length. The absence of secondary structure was also considered when possible. For the development of the qPCR probe method, the sequences used are shown in Tab. 2.
Tab. 2 - List of the primers and probes designed for qPCR TaqMan protocol for Anisandrus dispar.
| Method | Primer/ Probe name |
Length (bp) |
Sequence 5′ - 3′ | Nucleotide position |
Product size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TaqMan Probe |
Xdisp_2302F | 21 | CCACCATTAGCTGCCAATATC | 2302 - 2323 | 151 |
| Xdisp_2452R | 21 | GTTCGGGCTTTATTCCTGTAG | 2452 - 2431 | ||
| Xdisp_2325P | 27 | HEX_CCACGAAGGAGCATCTGTTGACCTAGC_BHQ1 | 2325 - 2352 |
An in-silico test of the primer pairs was then performed with the BLAST® software (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool - ⇒ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST) to assess the specificity of the designed primer pairs and probe.
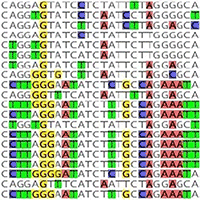
The in-silico specificity was further verified searching for the most related nucleotide sequences by means of the BLAST software, using as query the expected amplicons of the probe qPCR protocol. The sequences were aligned using the MAFFT program ([17]) implemented within the software Geneious® ver. 10.2.6 (Biomatters, Auckland, NZ - ⇒ http://www.geneious.com/). The results are shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2.
Fig. 1 - Alignments resulting from the in silico theoretical TaqMan amplicon and sequences of the related organisms present in GenBank.
Fig. 2 - Position of the primers used for Anisandrus dispar in the TaqMan probe protocol. The probe amplicon is yellow, from 2302 to 2452 bp. The probes were built on the same ribosomal DNA region using the sequence retrieved from GenBank (⇒ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/).
qPCR protocols
To determine the optimal annealing temperatures for the developed protocol, the temperature gradient from 52 to 62 °C were tested on 8 DNA samples extracted from two adults of A. dispar (4 samples of type (i) for each specimen - Tab. 1). Oligos and probes were used at different concentrations: 0.2 µM, 0.3 µM and 0.4 µM each. Samples were tested as technical duplicates. The amplification reactions in qPCR Probe were performed with a CFX96 (Biorad, Hercules, CA, USA) termocyclator in a final volume of 20 μL. Data obtained were analyzed with the software CFX Maestro ver. 2.0 (BioRad) using automatic thresholds and baselines for FAM (Fluorescein Amidite Dye). Samples were considered positive when the correspondent qPCR curves showed a clear inflection point and an increasing kinetics, and Cq values <32.
Validation of the method for the qPCR Probe
In view of the possibility to apply the test in routine diagnostics, performance criteria such as analytical sensitivity, analytical specificity, repeatability and reproducibility were determined. Validation was performed according to EPPO standard PM7/98 (5) updated in 2021 for insect samples (larvae and adults) and for the artificial sawdust. The parameters true positives, false negatives, false positives, and true negatives were considered according to the quoted EPPO standard ([8]).
Analytical sensitivity (limit of detection, LoD) of the test was estimated on 1:5 serial dilutions of samples (i), (ii) and (iii) previously described in Tab. 1.
DNA extracts were diluted to 5 ng µL-1 for DNA from A. dispar adults. Two µL of template were added to each sample and 3 replicates were set up for each sample. The evaluation range was included between 10 ng µL-1 up to 25.6 fg µL-1. All measurements were made using the QIAxpert® system (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany).
The repeatability was tested on 8 DNA samples extracted from 2 adult (5 ng µL-1) samples (4 for each specimen) and on 8 samples of artificial sawdust lysate from healthy branches of Q. cerris in CTAB 2%, contaminated to 0.1 ng µL-1 DNA of A. dispar adult. The protocol of reproducibility followed was the same of the test on repeatability, but 2 different operators carried out the assays on different days.
Results
DNA extraction
The results of DNA extraction from adults, larvae and artificial sawdust are shown in Tab. 3. The data that have been obtained suggest a satisfactory performance of the DNA extraction method used in the experiment.
Tab. 3 - Qualitative and quantitative parameters of DNA extraction from different matrices (adults and larvae of Anisandrus dispar; artificial sawdust from healthy branches of Quercus cerris). (SD): standard deviation.
| Extraction matrix | DNA conc. ± SD (ng µL-1) |
A260/280 ratio |
Cq (18S rRNA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adults | 182.6 ± 23.2 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 18.2 ± 1.8 |
| Larvae | 202.4 ± 36.4 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 17.9 ± 2.1 |
| Artificial sawdust | 267.6 ± 38.5 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 23.2 ± 1.7 |
Optimization of the Probe qPCR assay conditions
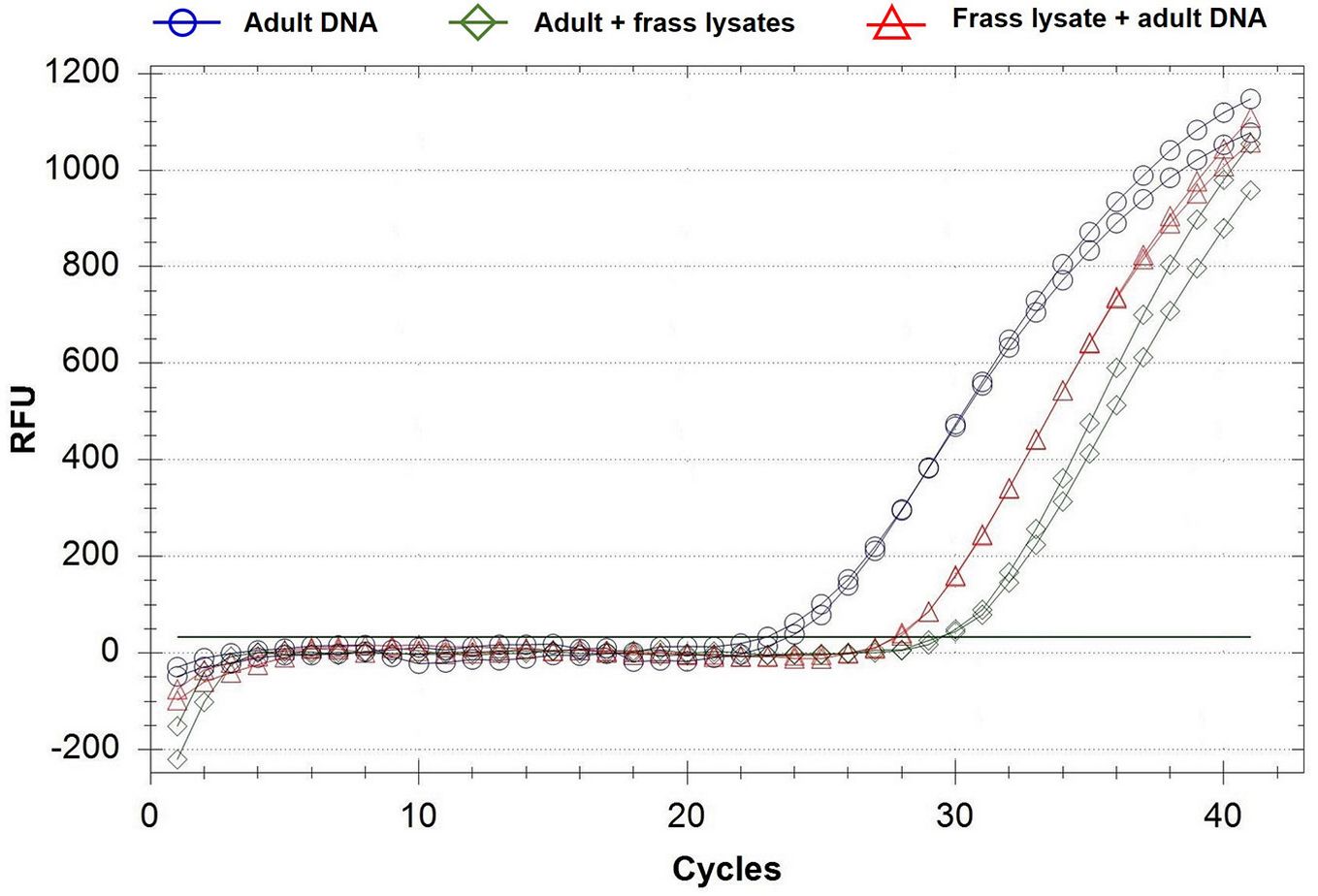
The optimal mix reaction for the protocol developed in this study on the targeted sequences of the mitochondrial genome of A. dispar, included 10 µL of 2× QuantiNova Probe PCR Master Mix® (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany) with 0.4 µM of primers and 0.2 µM probe concentration. The optimal annealing temperature was equal to 60 °C. The qPCR conditions consisted of an initial denaturation at 95 °C for 2 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 sec, and 60 °C for 40 sec (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3 - Amplification curves of Anisandrus dispar DNA from different matrices. Lines with blu circles: samples i) with 1 ng/µL of DNA from adult specimens; lines with green diamonds: sample ii) lysate from A. dispar adults added to lysate of Quercus cerris both in CTAB 2%; lines with red triangles: samples iii) lysate in CTAB 2% of Q. cerris contaminated to 0.1 ng/µL of DNA from A. dispar adults.
Validation method
The assay resulted inclusive for A. dispar, and exclusive towards the non-target organisms tested. All target specimens were correctly identified using the specific test and no false positive results were obtained for non-target organisms, resulting in a 100% analytical specificity and analytical sensitivity. The tests yielded the same qualitative results for all assayed samples and were not influenced by variation in assay conditions. The Cq values for the samples of adult DNA ranged between 23.55 ± 0.56 and 34.37 ± 0.45 and the LoD was 0.32 pg µL-1 (Tab. 4A).
Tab. 4 - LoD values of processed samples serially diluted 1:5. (A): Samples (i) 1 ng μL-1 of Anisandrus dispar adult DNA. (B): Samples (ii) 5-1 of lysate from A. dispar adults in artificial sawdust lysate of Q. cerris, both in CTAB 2%. (C) Samples (iii) mix of 0.1 ng μL-1 of adult DNA of A. dispar in lysate of artificial sawdust of Q. cerris in CTAB 2%.
| (A) Serial dilutions |
LoD (Avg Cq ± SD) |
(B) Serial dilutions |
LoD (Avg Cq ± SD) |
(C) Serial dilutions |
LoD (Avg Cq ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 ng μL-1 | 23.55 ± 0.56 | 5-1 | 26.73 ± 0.44 | 0.1 ng μL-1 | 24.01 ± 0.25 |
| 0.2 ng μL-1 | 27.40 ± 0.65 | 5-2 | 28.54 ± 0.33 | 0.02 ng μL-1 | 30.82 ± 0.39 |
| 0.04 ng μL-1 | 29.98 ± 0.24 | 5-3 | 30.72 ± 0.25 | 0.004 ng μL-1 | 33.20 ± 0.71 |
| 8 pg μL-1 | 31.29 ± 0.18 | 5-4 | 32.89 ± 0.37 | 0.8 pg μL-1 | 34.64 ± 0.12 |
| 1.6 pg μL-1 | 32.38 ± 1.07 | 5-5 | 35.45 ± 0.10 | 0.16 pg μL-1 | - |
| 0.32 pg μL-1 | 34.37 ± 0.45 | 5-6 | 36.59 ± 0.67 | 0.03 pg μL-1 | - |
| 0.06 pg μL-1 | - | 5-7 | - | 0.006 pg μL-1 | - |
| 12.8 fg μL-1 | - | 5-8 | - | 1.2 fg μL-1 | - |
| 2.56 fg μL-1 | - | - | - | 0.24 fg μL-1 | - |
For samples (ii), the Cq included values between 26.73 ± 0.44 and 36.59 ± 0.67, and the LoD was determined at a dilution factor of 5-6 (Tab. 4B).
The LoD of samples (iii) (dilution 1:5 of 0.1 ng µL-1 of A. dispar adult DNA added to lysate of Q. cerris artificial sawdust in CTAB 2%) was included in a range (Cq ± standard deviation, SD) of 24.01 ± 0.25 and 34.64 ± 0.12 and corresponded to a dilution of 0.8 pg µL-1 (Tab. 4C).
Repeatability and reproducibility were estimated on samples (i) and (ii), showing very low values of SD and averages in both types of samples (Tab. 5). Repeatability and reproducibility values measured as standard deviation ranged between 0.22 and 0.98.
Tab. 5 - Repeatability (inter-variability) and reproducibility (intra-variability) values of the qPCR assays were measured as standard deviation (SD) of the mean values of the replicates for each series.
| Kind | Assay | Samples | Replicate no. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |||
| Repeatability | Assay 1 | (i) adult DNA | 0.25 | 0.52 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.22 | 0.54 | 0.36 |
| (ii) artificial sawdust lysate | 0.88 | 0.76 | 0.98 | 0.67 | 0.95 | 0.36 | 0.22 | ||
| Assay 2 | (i) adult DNA | 0.39 | 0.37 | 0.31 | 0.98 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.30 | |
| (ii) artificial sawdust lysate | 0.79 | 0.85 | 0.34 | 0.46 | 0.87 | 0.98 | 0.36 | ||
| Reproducibility | Assay 1 | (i) adult DNA | 0.53 | 0.22 | 0.37 | 0.73 | 0.74 | 0.44 | 0.24 |
| (ii) artificial sawdust lysate | 0.67 | 0.07 | 0.43 | 0.46 | 0.96 | 0.39 | 0.18 | ||
| Assay 2 | (i) adult DNA | 0.36 | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.4 | 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.43 | |
| (ii) artificial sawdust lysate | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.77 | ||
Discussion
The global trade of living plants, timber and wood packaging material contribute to the increasing rate of accidental introduction of ambrosia beetles throughout the world, a phenomenon reported regularly for temperate climate zones ([25], [20]). The economic and ecological consequences of the establishment by invasive Scolytinae represent serious threats to agriculture and forestry; therefore, timely alien species detection and identification in import is crucial ([22], [6]).
The availability of easy-to-handle discrimination methods is crucial for the identification of invasive scolytine species. However, the traditional taxonomic keys essential to identify adults are reserved to experienced staff figures not always on hand ([38], [6]). Moreover, the problematic identification of intercepted juvenile stages of these pests is another open issue ([21], [40]).
Nowadays, the constant updating of still incomplete DNA sequence databases may facilitate accurate beetle identification with time ([4]) as well as the continuous developing/tuning of enhanced molecular protocols may better support the inspection efforts at points of entry where a rapid identification is required ([24], [3]).
Different DNA extraction methods have been compared and proposed by authors to suggest less expensive, reliable and not time-consuming methods providing highest purity of extracts needed for accurate bark beetle identification ([1], [2]).
The test developed for the molecular identification of Anisandrus dispar in this study showed good performance in terms of inclusivity and exclusivity, analytical sensibility, repeatability, and reproducibility. Although the test is not economic, its reliability and rapidity make it a possible candidate as official standard identification method for A. dispar from different matrices. In a previous paper ([29]), a molecular diagnostic test based on qPCR with TaqMan probe technology has been developed for three species belonging to the genus Xylosandrus (Coleoptera Curculionidae Scolytinae). The results obtained for these Ambrosia beetles were comparable, in terms of analytical sensibility, to those obtained for A. dispar.
For the identification of A. dispar, an artificial frass created in the lab has been used to simulate the natural one. This choice has been supported by previous experiments where both types of frass were processed ([28]). The comparison of the obtained experimental data related to DNA extraction showed excellent results. This further evidence supports the idea that the artificial sawdust can be used to finalize the molecular identification test, since the artificial samples are not subjected to the degradation by environmental factors (temperature, humidity) as well as by enzyme activity that can denature part of insect DNA ([35]). The obtained results confirm the soundness of this approach and underlines the need to proceed with the fine-tuning of other easy to arrange DNA extraction protocols for phytosanitary purposes. These new tools might be certainly applied in all those cases where a possible presence of quarantine pests in different plant matrices is suspected (e.g., at ports of entry).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the colleagues of the Plant Protection Phytosanitary Service of Tuscany supporting the field collection of insect samples and frass. Thanks are due also to prof. Tiziana Panzavolta of DAGRI, University of Florence, for providing Anisandrus dispar samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization of the research approach, detailed laboratory methodologies, experimental designs for this study were developed and conducted by DR (principal investigator) with the assistance of ADA, LB, CR, AM, IS, and DDL. All sample preparations, data collection and statistical analyses of data collected from DNA extracts were completed by DR, ADA, DDL, and LB. DR, APG, FP and ER wrote the manuscript and formatted the draft. Revisions of the manuscript were completed by all authors.
References
CrossRef | Gscholar
CrossRef | Gscholar
Gscholar
CrossRef | Gscholar
CrossRef | Gscholar
CrossRef | Gscholar
CrossRef | Gscholar
CrossRef | Gscholar
Gscholar
CrossRef | Gscholar
Authors’ Info
Authors’ Affiliation
Linda Bartolini
Laboratory of Phytopathological Diagnostics and Molecular Biology, Plant Protection Service of Tuscany, v. Ciliegiole 99, I-51100 Pistoia (Italy)
Igor Stabile
Chiara Ranaldi
Andrea Marrucci
Claudia Gabriela Zubieta
Daniele Da Lio 0000-0002-9222-9501
Elisabetta Rossi 0000-0002-6073-1046
Department of Agricultural, Food and Agro-Environmental Sciences, University of Pisa, v. del Borghetto 80, I-56124 Pisa (Italy)
CREA - Research Centre for Plant Protection and Certification, v. Lanciola 12/A, I-50125 Florence (Italy)
Department of Agricultural Sciences, University of Naples “Federico II”, v. Università 100, I-80055 Portici (Italy)
Corresponding author
Paper Info
Citation
Rizzo D, D’Agostino A, Stabile I, Ranaldi C, Marrucci A, Zubieta CG, Da Lio D, Bartolini L, Pennacchio F, Rossi E, Garonna AP (2023). Identification of the ambrosia beetle Anisandrus dispar (Fabricius) (Coleoptera Curculionidae Scolytinae) using TaqMan™ probe assay on biological samples. iForest 16: 182-187. - doi: 10.3832/ifor4287-016
Academic Editor
Matteo Marchioro
Paper history
Received: Dec 09, 2022
Accepted: Mar 28, 2023
First online: Jun 30, 2023
Publication Date: Jun 30, 2023
Publication Time: 3.13 months
Copyright Information
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2023
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Web Metrics
Breakdown by View Type
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 20911
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 16022
Abstract Page Views: 2909
PDF Downloads: 1629
Citation/Reference Downloads: 3
XML Downloads: 348
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 954
Overall contacts: 20911
Avg. contacts per week: 153.44
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
(No citations were found up to date. Please come back later)
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
Related Contents
iForest Similar Articles
Research Articles
Evaluating short term simulations of a forest stand invaded by emerald ash borer
vol. 8, pp. 19-24 (online: 26 May 2014)
Review Papers
Linking deadwood traits with saproxylic invertebrates and fungi in European forests - a review
vol. 11, pp. 423-436 (online: 18 June 2018)
Research Articles
Distribution and habitat suitability of two rare saproxylic beetles in Croatia - a piece of puzzle missing for South-Eastern Europe
vol. 11, pp. 765-774 (online: 28 November 2018)
Research Articles
The spread of the non-native pine tortoise scale Toumeyella parvicornis (Hemiptera: Coccidae) in Europe: a major threat to Pinus pinea in Southern Italy
vol. 11, pp. 628-634 (online: 04 October 2018)
Research Articles
Spruce budworm biological and nutritional performance responses to varying levels of monoterpenes
vol. 6, pp. 310-314 (online: 16 July 2013)
Research Articles
Distribution and abundance of the alien Xylosandrus germanus and other ambrosia beetles (Coleoptera: Curculionidae, Scolytinae) in different forest stands in central Slovenia
vol. 12, pp. 451-458 (online: 29 September 2019)
Research Articles
Discovering interaction between oaks and carabid beetles on a local scale by point pattern analysis
vol. 9, pp. 618-625 (online: 06 May 2016)
Research Articles
Exposure elevation and forest structure predict the abundance of saproxylic beetles’ communities in mountain managed beech forests
vol. 16, pp. 155-164 (online: 08 June 2023)
Research Articles
Diversity of saproxylic beetle communities in chestnut agroforestry systems
vol. 13, pp. 456-465 (online: 07 October 2020)
Research Articles
Sensitivity of European beech trees to unfavorable environmental factors on the edge and outside of their distribution range in northeastern Europe
vol. 9, pp. 259-269 (online: 16 October 2015)
iForest Database Search
Google Scholar Search
Citing Articles
Search By Author
- D Rizzo
- A D’Agostino
- I Stabile
- C Ranaldi
- A Marrucci
- CG Zubieta
- D Da Lio
- L Bartolini
- F Pennacchio
- E Rossi
- AP Garonna
Search By Keywords
PubMed Search
Search By Author
- D Rizzo
- A D’Agostino
- I Stabile
- C Ranaldi
- A Marrucci
- CG Zubieta
- D Da Lio
- L Bartolini
- F Pennacchio
- E Rossi
- AP Garonna
Search By Keyword