Feasibility study of near infrared spectroscopy to detect yellow stain on cork granulate
David Pérez-Terrazas (1) , José Ramón González-Adrados (2), Mariola Sánchez-González (1)
iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry, Volume 11, Issue 1, Pages 111-117 (2018)
doi: https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor2563-010
Published: Jan 31, 2018 - Copyright © 2018 SISEF
Research Articles
Collection/Special Issue: INCOTW - Sassari, Italy (2017)
International Congress on Cork Oak Trees and Woodlands
Guest Editors: Piermaria Corona, Sandro Dettori
Abstract
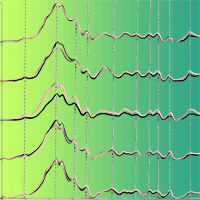
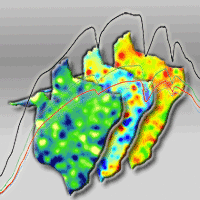
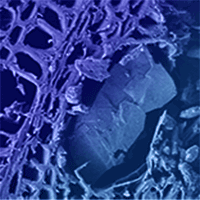
The aim of this study was to evaluate the viability of near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) to detect the anomaly known as yellow stain on cork granulate. Detecting this anomaly is crucial to the cork granulate stopper industry, since it is associated with the presence of 2.4.6-Trichloroanisole (TCA), this compound having been identified as the main agent responsible for cork off-flavours. Samples for the NIRS spectra were prepared by mixing in different proportions cork granulate with high visual quality and cork granulate with yellow stain, obtaining 120 samples with 8 different percentages of yellow stain (0, 5, 10, 15, 25, 35, 50 and 100%). Two spectra per sample were collected using a Bruker MPA spectrophotometer and the partial least squares (PLS) method was used to obtain numerous equations. The best equation was obtained by utilizing the standard normal variate (SNV) spectral preprocessing, making use of only one specific part of the near infrared spectral range: 9400-4250 cm-1. This equation shows a coefficient of determination (R²) of 99.42%, a root mean square error of cross validation (RMSECV) of 2.34%, and a residual prediction deviation (RPD) of 13.10. The critical level and the limit of detection are 3.8% and 7.6%, respectively. The calculated receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves show great discrimination capacity and the area under the ROC curve (AUC) is higher than 0.93 in any case. This study demonstrates that NIRS provides a viable technique for detecting yellow stain in cork granulate.
Keywords
Cork, Granulate, Yellow Stain, 2.4.6-Trichloroanisole, TCA, Near Infrared Spectroscopy, NIRS
Authors’ Info
Authors’ address
Mariola Sánchez-González
INIA-CIFOR, Ctra. de La Coruña km 7.5, E-28040 Madrid (Spain)
MONTES (School of Forest Engineering and Natural Environment), Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, C/ José Antonio Novais s/n, E-28040 Madrid (Spain)
Corresponding author
Paper Info
Citation
Pérez-Terrazas D, González-Adrados JR, Sánchez-González M (2018). Feasibility study of near infrared spectroscopy to detect yellow stain on cork granulate. iForest 11: 111-117. - doi: 10.3832/ifor2563-010
Academic Editor
Piermaria Corona
Paper history
Received: Jul 25, 2017
Accepted: Dec 12, 2017
First online: Jan 31, 2018
Publication Date: Feb 28, 2018
Publication Time: 1.67 months
Copyright Information
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2018
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Web Metrics
Breakdown by View Type
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 46893
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 39379
Abstract Page Views: 3050
PDF Downloads: 3407
Citation/Reference Downloads: 15
XML Downloads: 1042
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 2928
Overall contacts: 46893
Avg. contacts per week: 112.11
Citation Metrics
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2018): 1
Average cites per year: 0.13
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
References
El límite de detección de un método analítico [The limit of detection of an analytical method]. Técnicas de Laboratorio 296: 878-881. [in Spanish]
Gscholar
Sur la maladie de la tache jaune des lièges [In the disease of the yellow stain of cork]. Bulletin Académie Sciences 138 (15): 928-929. [in French]
Gscholar
Identification of fungal hyphae and conidia in samples of altered cork. Microbios 81 (326): 41-44.
Gscholar
Influencia de la mancha amarilla sobre la composición química del corcho y la presencia de TCA [Influence of the yellow stain on the chemical composition of the cork and the presence of TCA]. In: Proceedings of the III Spanish Forest Congress “Montes para la Sociedad del Nuevo Milenio” (SECF-Junta de Andalucía eds). Granada (Spain), 25-28 Sept 2001. Gráficas Coria, Sevilla, Spain, pp. 5. [in Spanish].
Gscholar
Cork stoppers. Determination of releasable 2.4.6-trichloroanisol (TCA). International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland, pp. 6.
Gscholar
Cork stoppers. Sensory analysis. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland, pp. 5.
Gscholar
Radiation detection and measurement: student solutions manual. John Wiley and Sons Ltd, USA, pp. 860.
Gscholar
Analysis of volatiles of corks affected by yellow stain and greening and corked wines using GC-sniffing and GC/MS techniques. Industrie delle Bevande 27 (158): 615-619.
Gscholar
Cork: biology, production and uses. Elsevier, Amsterdam, Netherlands, pp. 336.
Gscholar
Methodology for cork plank characterization (Quercus suber L.) by near-infrared spectroscopy and image analysis. Measurement Science and Technology 21 (6): 065602.
Gscholar
Interpretation of diagnostic tests. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, USA, pp. 1026.
Gscholar
Corcho. Vocabulario [Cork. Vocabulary]. Asociación Española de Normalización y Certificación, Madrid, Spain, pp. 31. [in Spanish]
Gscholar
How do we it: brief summary of the methods we use in developing near infrared calibration. In: “Near Infrared Spectroscopy: The Future Waves” (Davis AMC, Williams P eds). NIR Publications, Chichester, UK, pp. 185-188.
Gscholar
Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) plots: a fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clinical Chemistry 39 (4): 561-577.
Gscholar