Selection of optimal conversion path for willow biomass assisted by near infrared spectroscopy
Anna Sandak (1-2), Jakub Sandak (1-2) , Boguslawa Waliszewska (3), Magdalena Zborowska (3), Miroslaw Mleczek (4)
iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry, Volume 10, Issue 2, Pages 506-514 (2017)
doi: https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor1987-010
Published: Apr 20, 2017 - Copyright © 2017 SISEF
Research Articles
Abstract
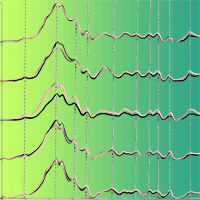
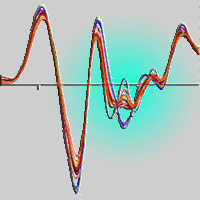
Willow (Salix sp.) is one of the most common hardwood species suitable for short-rotation coppice. It can be converted to different products, including chemicals, fuels, fibers or furniture. It may also be used in agriculture and environmental engineering. Molecular composition of biomass and its physical properties highly influence effectiveness of its chemical, thermo-chemical or mechanical-chemical conversion. Therefore, it is challenging to provide biomass feedstock with optimized properties, best suited for further downstream conversion. The goal of this research was to establish a procedure for determination of the willow biomass optimal use cultivated in four different plantations in Poland. A special attention has been paid to the application of the near infrared spectroscopy for evaluation of biomass chemical composition and its physical properties. Near infrared spectroscopy (NIR) could be an alternative to standard analytical methods supporting the research and development of biomass production technologies. Partial least squares regression models for quantitative prediction of wood chemical components (lignin, cellulose, holocellulose, hemicellulose and extractives) and high heating values were developed. The residual prediction deviation (RPD) values confirm the applicability of chemometric models for screening in breeding programmes (for lignin, cellulose and extractives content) and for research in the case of high heating value. The analysis of NIR spectra highlighted several peculiarities in the chemical composition of the investigated willow clones. Finally, a knowledge-based expert system and a prototype automatic NIR system allowing the computation of a “suitability index” based on PLS models and dedicated to selection of optimal biomass conversion path, was developed.
Keywords
Willows, NIR Spectroscopy, Optimal Conversion, Biomass Feedstock
Authors’ Info
Authors’ address
Jakub Sandak
CNR-IVALSA, Trees and Timber Institute, via Biasi 75, I-38010 San Michele all’Adige (Italy)
Jakub Sandak
University of Primorska, Faculty of Mathematics, Natural Sciences and Information Technology, Glagoljaška 8, 6000 Koper (Slovenia)
Magdalena Zborowska
Poznan University of Life Sciences, Institute of Chemical Wood Technology, ul. Wojska Polskiego 28, 60-637 Poznan (Poland)
Poznan University of Life Sciences, Department of Chemistry, ul. Wojska Polskiego 75, 60-625 Poznan (Poland)
Corresponding author
Paper Info
Citation
Sandak A, Sandak J, Waliszewska B, Zborowska M, Mleczek M (2017). Selection of optimal conversion path for willow biomass assisted by near infrared spectroscopy. iForest 10: 506-514. - doi: 10.3832/ifor1987-010
Academic Editor
Giorgio Alberti
Paper history
Received: Jan 18, 2016
Accepted: Feb 13, 2017
First online: Apr 20, 2017
Publication Date: Apr 30, 2017
Publication Time: 2.20 months
Copyright Information
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2017
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Web Metrics
Breakdown by View Type
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 49385
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 41663
Abstract Page Views: 2926
PDF Downloads: 3654
Citation/Reference Downloads: 26
XML Downloads: 1116
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 3214
Overall contacts: 49385
Avg. contacts per week: 107.56
Citation Metrics
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2017): 5
Average cites per year: 0.56
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
References
Paliwa stale Oznaczanie ciepla spalania i obliczanie wartosci opalowej [Solid fuels determination of gross calorific value and calculation of net calorific value]. Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny, Warsaw, Poland, pp. 11. [in Polish]
Gscholar
Changes in fiber properties during the growing season. In: “Paper and Composite from Agro-based Resources” (Rowell RM, Young RA, Rowell JK eds). Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton/New York/ London/Tokyo, pp. 23-37.
Gscholar
Modeling of pyrolysis in wood: a review. Journal of the Solar Energy Society of India 10 (1): 41-62.
Gscholar
Acid Insoluble lignin in wood and pulp. T 222 om-06. Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry, New York, USA, pp. 5.
Gscholar
Solvent extractives of wood and pulp. T 207 cm-08. Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry, New York, USA, pp 4.
Gscholar