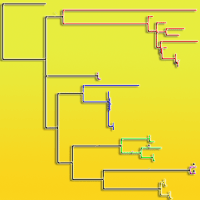
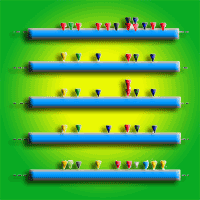
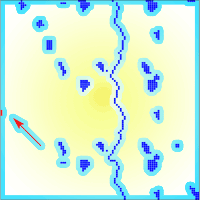
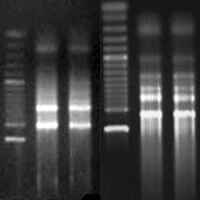
Western white pine (Pinus monticola Dougl.) is an important forest tree species, which is intensively plagued by the fungus Cronartium ribicola. Resistance gene analogs (RGAs) are the most highly abundant class of potential resistance (R) genes sharing greatly conserved domains and structures. Hence RGAs are crucial components for disease resistance breeding programs on P. monticola serving as useful functional markers. A total of 33 P. monticola RGAs gene homologues were mined from GenBank, encoding for R gene members of the TIR-NBS-LRR subfamily. The existence of positive selection acting upon RGAs was determined using a series of maximum likelihood analyses. Robust evidence of positive selection was showed to be acting widely in three clades across RGA gene phylogeny, both on terminal and ancestral lineages. Furthermore, our analysis revealed that the majority of positively selected residues sites are localized widely across these RGAs sequences, putatively affecting the structures of their ligand-binding domains and offering novel specificities. These results may find immediate application in ongoing disease resistance breeding programs.
Keywords
, , , , ,
Citation
Zambounis A, Avramidou E, Papadima A, Tsaftaris A, Arzimanoglou I, Barbas E, Madesis P, Aravanopoulos FA (2017). Adaptive response of Pinus monticola driven by positive selection upon resistance gene analogs (RGAs) of the TIR-NBS-LRR subfamily. iForest 10: 237-241. - doi: 10.3832/ifor2050-009
Academic Editor
Alberto Santini
Paper history
Received: Mar 09, 2016
Accepted: Sep 27, 2016
First online: Feb 02, 2017
Publication Date: Feb 28, 2017
Publication Time: 4.27 months
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2017
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.

Breakdown by View Type
(Waiting for server response...)
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 50349
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 42728
Abstract Page Views: 3139
PDF Downloads: 3235
Citation/Reference Downloads: 76
XML Downloads: 1171
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 3287
Overall contacts: 50349
Avg. contacts per week: 107.22
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
(No citations were found up to date. Please come back later)
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
(1)
Ameline-Torregrosa C, Wang B-B, O’Bleness MS, Deshpande S, Zhu H, Roe B, Young ND, Cannon SB (2008)Identification and characterization of nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat genes in the model plant
Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiology 146 (1): 5-21.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(2)
Aravanopoulos FA (2014)Genomics of trees. In: “Tree Biotechnology” (Ramawat KG, Merillon JM, Ahuja MR eds). CRC Press, Boca Raton, USA, pp. 514-557.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(3)
Chen Q, Han Z, Jiang H, Tian D, Yang S (2010)Strong positive selection drives rapid diversification of R-genes in
Arabidopsis relatives. Journal of Molecular Evolution 70 (2): 137-148.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(4)
Dangl JL, Horvath DM, Staskawicz BJ (2013)Pivoting the plant immune system from dissection to deployment. Science 341 (6147): 746-751.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(5)
Debener T, Byrne DH (2014)Disease resistance breeding in rose: current status and potential of biotechnological tools. Plant Science 228: 107-117.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(6)
Delph LF, Kelly JK (2014)On the importance of balancing selection in plants. New Phytologist 201 (1): 45-56.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(7)
Edgar RC (2004)MUSCLE: a multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinformatics 5: 1-19.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(8)
Friedman AR, Baker BJ (2007)The evolution of resistance genes in multi-protein plant resistance systems. Current Opinion in Genetics and Development 17 (6): 493-499.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(9)
Jones P, Binns D, Chang HY, Fraser M, Li W, McAnulla C, McWilliam H, Maslen J, Mitchell A, Nuka G, Pesseat S, Quinn AF, Sangrador-Vegas A, Scheremetjew M, Yong SY, Lopez R, Hunter S (2014)InterProScan 5: genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 30 (9): 1236-1240.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(10)
Kearse M, Moir R, Wilson A, Stones-Havas S, Cheung M, Sturrock S, Buxton S, Cooper A, Markowitz S, Duran C, Thierer T, Ashton B, Mentjies P, Drummond A (2012)Geneious Basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 28 (12): 1647-1649.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(11)
Khan AM, Khan AA, Azhar MT, Amrao L, Cheema HM (2016)Comparative analysis of resistance gene analogues encoding NBS-LRR domains in cotton. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 96 (2): 530-538.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(12)
Kinloch BB, Sniezko RA, Barnes GD, Greathouse TE (1999)A major gene for resistance to white pine blister rust in western white pine from the western Cascade Range. Phytopathology 89: 861-867.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(13)
Kim J, Lim CJ, Lee BW, Choi JP, Oh SK, Ahmad R, Kwon SY, Ahn J, Hur CG (2012)A genome-wide comparison of NB-LRR type of resistance gene analogs (RGA) in the plant kingdom. Molecules and Cells 33 (4): 385-392.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(14)
Lalli DA, Decroocq V, Blenda AV, Schurdi-Levraud V, Garay L, Le Gall O, Damsteegt V, Reighard GL, Abbott AG (2005)Identification and mapping of resistance gene analogs (RGAs) in
Prunus: a resistance map for
Prunus. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 111 (8): 1504-1513.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(15)
Li J, Xu Y, Fei S, Li L (2006)Isolation, characterization and evolutionary analysis of resistance gene analogs in annual ryegrass, perennial ryegrass and their hybrid. Physiologia Plantarum 126 (4): 627-638.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(16)
Li J, Ding J, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Tang P, Chen J-Q, Tian D, Yang S (2010)Unique evolutionary pattern of numbers of Gramineous NBS-LRR genes. Molecular Genetics and Genomics 283 (5): 427-438.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(17)
Liu JJ, Ekramoddoullah AK (2003)Isolation, genetic variation and expression of TIR-NBS-LRR resistance gene analogs from western white pine (
Pinus monticola Dougl. ex. D. Don.). Molecular Genetics and Genomics 270: 432-441.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(18)
Liu JJ, Hunt R, Ekramoddoullah AK (2004)Recent insights into genetic resistance of western white pine to white pine blister rust. Recent Research Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering 6: 65-76.
Online |
Gscholar
(19)
Liu JJ, Ekramoddoullah AK, Hunt RS, Zamani A (2006)Identification and characterization of random amplified polymorphic DNA markers linked to a major gene (Cr2) for resistance to
Cronartium ribicola in
Pinus monticola. Phytopathology 4: 395-399.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(20)
Liu JJ, Ekramoddoullah AK (2007)The CC-NBS-LRR subfamily in
Pinus monticola: targeted identification, gene expression, and genetic linkage with resistance to
Cronartium ribicola. Phytopathology 97 (6): 728-736.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(21)
Loehman RA, Clark JA, Keane RE (2011)Modeling effects of climate change and fire management on western white pine (
Pinus monticola) in the northern Rocky Mountains, USA. Forests 2 (4): 832-860.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(22)
Lynn DJ, Higgs R, Gaines S, Tierney J, James T, Lloyd AT, Fares MA, Mulcahy G, Farrelly C (2004a)Bioinformatic discovery and initial characterisation of nine novel antimicrobial peptide genes in the chicken. Immunogenetics 56 (3): 170-177.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(23)
Lynn DJ, Lloyd AT, Fares MA, O’Farrelly C (2004b)Evidence of positively selected sites in mammalian α-defensins. Molecular Biology and Evolution 21 (5): 819-827.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(24)
Meyers BC, Kozik A, Griego A, Kuang H, Michelmore RW (2003)Genome-wide analysis of NBS-LRR-encoding genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15 (4): 809-834.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(25)
Mondragón-Palomino M, Meyers BC, Michelmore RW, Gaut BS (2002)Patterns of positive selection in the complete NBS-LRR gene family of
Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Research 12 (9): 1305-1315.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(26)
Panetsos KP, Moulalis D, Mitsopoulos D, Skaltsoyiannes A (1983)Results of exotic and native forest species trials at the Aristotle University forests. Laboratory of Forest Genetics and Tree Breeding, Aristotle University, Publ. No. 6, Thessaloniki, Greece, pp. 30. [in Greek with English summary]
Gscholar
(27)
Panetsos KP, Alizoti PG, Moulalis D, Skaltsoyiannes A, Aravanopoulos FA (1996)Results of exotic forest species testing in Pertouli. In: Proceedings of the “6th Pan-Hellenic Conference of the Hellenic Scientific Society of Plant Genetics and Breeding”. Florina (Greece) 2-4 Oct 1996. Hellenic Scientific Society for Plant Genetics and Breeding , Thessaloniki, Greece, pp. 310-316. [in Greek with English summary]
Gscholar
(28)
Papadima A, Sotikopoulos N (1995)Results of exotic and native forest species trials at the Aristotle University forests. BSc Thesis, Faculty of Agriculture, Forestry and Natural Environment, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Aristotle University Publ., Thessaloniki, Greece, pp. 73. [in Greek with English summary]
Gscholar
(29)
Parniske M, Hammond-Kosack KE, Golstein C, Thomas CM, Jones DA, Harrison K, Wulff BBH, Jones JDG (1997)Novel disease resistance specificities result from sequence exchange between tandemly repeated genes at the Cf-4/9 locus of tomato. Cell 91 (6): 821-832.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(30)
Perazzolli M, Malacarne G, Baldo A, Righetti L, Bailey A, Fontana P, Velasco R, Malnoy M (2014)Characterization of resistance gene analogues (RGAs) in apple (
Malus x domestica Borkh.) and their evolutionary history of the Rosaceae family. PloS One 9 (2): e83844.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(31)
Sekhwal MK, Li P, Lam I, Wang X, Cloutier S, You FM (2015)Disease resistance gene analogs (RGAs) in plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16 (8): 19248-19290.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(32)
Stamatakis A (2014)RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30 (9): 1312-1313.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(33)
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011)MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molecular Biology and Evolution 28 (10): 2731-2739.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(34)
Wan H, Zhao Z, Malik AA, Qian C, Chen J (2010)Identification and characterization of potential NBS-encoding resistance genes and induction kinetics of a putative candidate gene associated with downy mildew resistance in
Cucumis. BMC Plant Biology 10 (1): 186.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(35)
Yang Z, Nielsen R (2000)Estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous substitution rates under realistic evolutionary models. Molecular Biology and Evolution 17 (1): 32-43.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(36)
Yang Z (2007)PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Molecular Biology and Evolution 24 (8): 1586-1591.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(37)
Yang S, Zhang X, Yue J-X, Tian D, Chen J-Q (2008)Recent duplications dominate NBS-encoding gene expansion in two woody species. Molecular Genetics and Genomics 280 (3): 187-198.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(38)
Yang S, Li J, Zhang X, Zhang Q, Huang J, Chen J-Q, Hartl DL, Tian D (2013)Rapidly evolving R genes in diverse grass species confer resistance to rice blast disease. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 110 (46): 18572-18577.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(39)
Zambounis A, Elias M, Sterck L, Maumus F, Gachon CMM (2012)Highly dynamic exon shuffling in candidate pathogen receptors… What if brown algae were capable of adaptive immunity? Molecular Biology and Evolution 29 (4): 1263-1276.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(40)
Zhou T, Wang Y, Chen JQ, Araki H, Jing Z, Jiang K, Shen J, Tian D (2004)Genome-wide identification of NBS genes in japonica rice reveals significant expansion of divergent non-TIR NBS-LRR genes. Molecular Genetics and Genomics 271 (4): 402-415.
CrossRef |
Gscholar