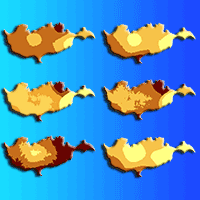
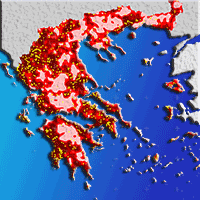
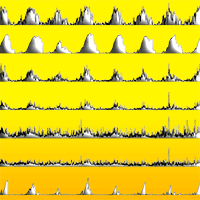
The prediction of wildfire occurrence is an important component of fire management. We have developed probabilistic daily fire prediction models for a Mediterranean region of Europe (Cyprus) at the mesoscale, based on Poisson regression. The models use only readily available spatio-temporal data, which enables their use in an operational setting. Influencing factors included in the models are weather conditions, land cover and human presence. We found that the influence of weather conditions on fire danger in the studied area can be expressed through the FWI component of the Canadian Forest Fire Weather Index System. However, the prediction ability of FWI alone was limited. A model that additionally includes land cover types, population density and road density was found to provide significantly improved predictions. We validated the probabilistic prediction provided by the model with a test data set and illustrate it with maps for selected days.
Keywords
, , ,
Citation
Papakosta P, Straub D (2016). Probabilistic prediction of daily fire occurrence in the Mediterranean with readily available spatio-temporal data. iForest 10: 32-40. - doi: 10.3832/ifor1686-009
Academic Editor
Davide Ascoli
Paper history
Received: Apr 24, 2015
Accepted: Jul 07, 2016
First online: Oct 06, 2016
Publication Date: Feb 28, 2017
Publication Time: 3.03 months
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2016
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.

Breakdown by View Type
(Waiting for server response...)
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 51046
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 41383
Abstract Page Views: 3569
PDF Downloads: 4584
Citation/Reference Downloads: 69
XML Downloads: 1441
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 3417
Overall contacts: 51046
Avg. contacts per week: 104.57
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2017): 9
Average cites per year: 1.00
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
(1)
Ager AA, Preisler HK, Arca B, Spano D, Salis M (2014)Wildfire risk estimation in the Mediterranean area. Environmetrics 25 (6): 384-396.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(2)
Akaike H (1974)A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 19 (6): 716-723.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(3)
Amatulli G, Rodrigues MJ, Trombetti M, Lovreglio R (2006)Assessing long-term fire risk at local scale by means of decision tree technique. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences 111: G04S05.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(4)
Arndt N, Vacik H, Koch V, Arpaci A, Gossow H (2013)Modeling human-caused forest fire ignition for assessing forest fire danger in Austria. iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry 6 (5): 315-325.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(5)
Bayraktarli YY, Ulfkjaer J, Yazgan U, Faber MH (2005)On the application of Bayesian probabilistic networks for earthquake risk management. In: Proceedings of the “9th International Conference on Structural Safety and Reliability - ICOSSAR” (Augusti et al. eds). Rome (Italy) 19-23 Jun 2005. Millpress, Rome, Italy, pp. 20-23.
Online |
Gscholar
(6)
Bensi M, Kiureghian AD, Straub D (2014)Framework for post-earthquake risk assessment and decision making for infrastructure systems. ASCE-ASME Journal of Risk and Uncertainty in Engineering Systems, Part A: Civil Engineering 1 (1): 04014003.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(7)
Blaser L, Ohrnberger M, Riggelsen C, Scherbaum F (2009)Bayesian belief network for tsunami warning decision support. In: Proceedings of the 10th European Conference “ECSQARU 2009”. Verona (Italy) 1-3 Jul 2009 (Sossai C, Chemello G eds). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, pp. 757-786.
Gscholar
(8)
Camia A, Amatulli G (2009)Weather factors and fire danger in the Mediterranean. In: “Earth Observation of Wildland Fires in Mediterranean Ecosystems” (Chuvieco E eds). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, pp. 71-82.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(9)
Cardille JA, Ventura SJ, Turner MG (2001)Environmental and social factors influencing wildfires in the Upper Midwest, United States. Ecological Applications 11 (1): 111-127.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(10)
Catry FX, Rego FC, Bação F, Moreira F (2010)Modeling and mapping wildfire ignition risk in Portugal. International Journal of Wildland Fire 18 (8): 921-931.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(11)
Chou YH, Chase RA (1993)Mapping probability of fire occurrence in San Jacinto Mountains, California, USA. Environmental Management 17 (1): 129-140.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(12)
Chuvieco E, González I, Verdú F, Aguado I, Yerba M (2009)Prediction of fire occurrence from live fuel moisture content measurements in a Mediterranean ecosystem. International Journal of Wildland Fire 18 (4): 430-441.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(13)
Cunningham AA, Martell DL (1973)A stochastic model for the occurrence of man-caused forest fires. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 3: 282-287.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(14)
Dimitrakopoulos AP, Bemmerzouk AM, Mitsopoulos ID (2011)Evaluation of the Canadian fire weather index system in an eastern Mediterranean environment. Meteorological Applications 18: 83-93.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(15)
Dlamini WM (2009)A Bayesian belief network analysis of factors influencing wildfire occurrence in Swaziland. Environmental Modelling and Software 25 (2): 199-208.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(16)
Giannakopoulos C, Karali A, Roussos A, Hatzaki M, Xanthopoulos G, Kaoukis K (2011)Evaluating present and future fire risk in Greece. Advances in Remote Sensing and GIS applications in Forest Fire Management. From local to global assessments. JRC Scientific and Technical Reports, European Commission, JRC-IES, Land Management and Natural Hazards Unit, Ispra, Italy, pp. 181.
Gscholar
(17)
Grêt-Regamey A, Straub D (2006)Spatially explicit avalanche risk assessment linking Bayesian networks to a GIS. Natural hazards and Earth System Sciences 6: 911-926.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(18)
Jensen FV, Nielsen TD (2007)Bayesian networks and decision graphs. Springer, Series Information Science and Statistics, NY, USA, pp. 447.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(19)
Joint Research Center/IES (2011)Forest fires in Europe 2010. Report no. 11, JRC Scientific and Technical Reports, European Commission, JRC-IES, Land Management and Natural Hazards Unit, Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg, pp. 92.
Gscholar
(20)
Kalabokidis KD, Koutsias N, Konstantinidis P, Vasilakos C (2007)Multivariate analysis of landscape wildfire dynamics in a Mediterranean ecosystem of Greece. Area 39 (3) pp. 392-402.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(21)
Kuehn NM, Riggelsen C, Scherbaum F (2011)Modeling the joint probability of earthquake, site, and ground-motion parameters using Bayesian Networks. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America 101 (1): 235-249.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(22)
Lawson BD, Armitage OB (2008)Weather guide for the Canadian forest fire danger rating system. Natural Resources Canada, Canadian Forest Service, Northern Forestry Centre. Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, pp. 73. -
Online |
Gscholar
(23)
Leemans R, Cramer WP (1991)The IIASA database for mean monthly values of temperature, precipitation and cloudiness on a global terrestrial grid. Report RR-91-18, International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis, Laxenburg, Austria, pp. 62.
Online |
Gscholar
(24)
Martell DL, Otukol S, Stocks BJ (1987)A logistic model for predicting daily people-caused forest fire occurrence in Ontario. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 17 (5): 394-401.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(25)
Martínez-Fernández J, Chuvieco E, Koutsias N (2013)Modelling long-term fire occurrence factors in Spain by accounting for local variations with geographically weighted regression. Natural Hazards and Earth System Science 13 (2): 311-327.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(26)
Miranda BR, Sturtevant BR, Stewart SI, Hammer RB (2012)Spatial and temporal drivers of wildfire occurrence in the context of rural development in northern Wisconsin, USA. International Journal of Wildland Fire 21 (2): 141-154.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(27)
Mandallaz D, Ye R (1997)Prediction of forest fires with Poisson models. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 27: 1685-1694.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(28)
Massada AB, Syphard DA, Stewart SI, Radeloff VC (2012)Wildfire ignition-distribution modelling: a comparative study in the Huron-Manistee national forest, Michigan, USA. International Journal of Wildland Fire 22 (2): 174-183.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(29)
Moriondo M, Good P, Durao R, Bindi M, Giannakopoulos C, Corte-Real J (2006)Potential impact of climate change on fire risk in the Mediterranean area. Climate Research 31: 85-95.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(30)
Oliveira S, Oehler F, San-Miguel-Ayanz J, Camia A, Pereira JMC (2012)Modeling spatial patterns of fire occurrence in Mediterranean Europe using multiple regression and Random Forest. Forest Ecology and Management 275: 117-129.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(31)
Padilla M, Vega-García C (2011)On the comparative importance of fire danger rating indices and their integration with spatial and temporal variables for predicting daily human-caused fire occurrences in Spain. International Journal of Wildland Fire 20 (1): 46-58.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(32)
Parisien MA, Moritz MA (2009)Environmental controls on the distribution of wildfire at multiple spatial scales. Ecological Monographs 79 (1): 127-154.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(33)
Pew KL, Larsen CPS (2001)GIS analysis of spatial and temporal patterns of human-caused wildfires in the temperate rain forest of Vancouver Island, Canada. Forest Ecology and Management 140 (1): 1-18.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(34)
Plucinski MP (2012)A review of wildfire occurrence research. CSIRO Ecosystem Sciences and CSIRO climate Adaptation Flagship, Bushfires Cooperative Research Center (CRC), Canberra, Australia, pp. 2-25.
Online |
Gscholar
(35)
Preisler HK, Brillinger DR, Burgan RE, Benoit JW (2004)Probability based models for estimation of wildfire risk. International Journal of Wildland Fire 13: 133-142.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(36)
Romero-Calcerrada R, Novillo CJ, Millington JDA, Gomez-Jimenez I (2008)GIS analysis of spatial patterns of human-caused wildfire ignition risk in the SW of Madrid (Central Spain). Landscape Ecology 23 (3): 341-354.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(37)
Sebastián-López A, Salvador-Civil R, Gonzalo-Jiménez J, SanMiguel-Ayanz J (2008)Integration of socio-economic variables for modeling long-term fire danger in Southern Europe. European Journal of Forest Research 127: 149-163.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(38)
Shepard D (1968)A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data. In: Proceeding of the “23
rd ACM National Conference”. Las Vegas (NV, USA) 27-29 Aug 1968. ACM, New York, USA, pp. 517-524.
Online |
Gscholar
(39)
Straub D (2005)Natural hazards risk assessment using Bayesian networks. In: Proceedings of the “9th International Conference on Structural Safety and Reliability - ICOSSAR” (Augusti et al. eds). Rome (Italy) 19-23 Jun 2005. Millpress, Rome, Italy, pp. 2535-2542.
Online |
Gscholar
(40)
Syphard DA, Radeloff VC, Keuler NS, Taylor RS, Hawbaker TJ, Stewart SI, Clayton MK (2008)Predicting spatial patterns of fire on a southern California landscape. International Journal of Wildland Fire 17 (5): 602-613.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(41)
Taylor RS, Alexander ME (2006)Science, technology, and human factors in fire danger rating: the Canadian experience. International Journal of Wildland Fire 15: 121-135.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(42)
Van Wagner CE, Pickett TL (1985)Equations and FORTRAN program for the Canadian forest fire weather index system. Forestry Technical Report 33, Canadian Forestry Service, Government of Canada, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, pp. 33.
Online |
Gscholar
(43)
Van Wagner CE (1987)Development and structure of the Canadian forest fire weather index system. Forestry Technical Report 35, Canadian Forestry Service, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, pp. 44. -
Online |
Gscholar
(44)
Vasconcelos MJP, Silva S, Tomé M, Alvim M, Pereira JMC (2001)Spatial prediction of fire ignition probabilities: comparing logistic regression and neural networks. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing 67: 73-81.
Gscholar
(45)
Vasilakos C, Kalabokidis K, Hatzopoulos J, Matsinos I (2009)Identifying wildland fire ignition factors through sensitivity analysis of a neural network. Natural Hazards 50 (1): 125-143.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(46)
Venäläinen A, Korhonen N, Hyvärinen O, Koutsias N, Xystrakis F, Urbieta IR, Moreno JM (2014)Temporal variations and change in forest fire danger in Europe for 1960-2012. Natural Hazards and Earth System Science 14 (6): 1477-1490.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(47)
Viegas DX, Bovio G, Ferreira A, Nosenzo A, Sol B (1999)Comparative study of various methods of fire danger evaluation in Southern Europe. International Journal of Wildland Fire 9 (4): 235-246.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(48)
Vilar L, Woolford DG, Martell DL, Martín MP (2010)A model for predicting human-caused wildfire occurrence in the region of Madrid, Spain. International Journal of Wildland Fire 19 (3): 325-337.
CrossRef |
Gscholar
(49)
Wotton BM, Martell DL, Logan KA (2003)Climate change and people-caused forest fire occurrence in Ontario. Climatic Change 60 (3): 275-295.
CrossRef |
Gscholar