Effect of silver nanoparticles on hardness in medium-density fiberboard (MDF)
Hamid Reza Taghiyari (1) , Jack Norton (2)
iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry, Volume 8, Issue 5, Pages 677-680 (2014)
doi: https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor1188-007
Published: Dec 17, 2014 - Copyright © 2014 SISEF
Research Articles
Abstract
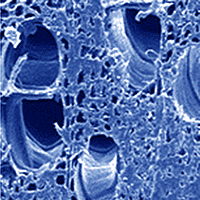
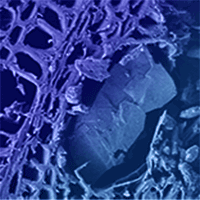
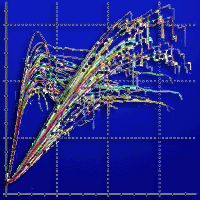
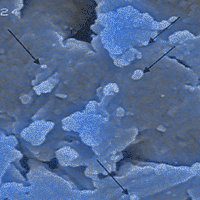
Effect of silver nanoparticles on hardness in medium-density fiberboard (MDF) was studied here. A 400 ppm aqueous nanosilver suspension was used at three consumption levels of 100, 150, and 200 mL kg-1, based on the dry weight of wood fibers; the results were then compared with the control panels. The size range of silver nanoparticles was 30-80 nm. Composite mats were hot-pressed for 6, 8, and 10 min. Results showed that the uniform and even dispersion of nanoparticles throughout the MDF-matrix significantly contributed to an increase in the hardness at lower hot-press time of 6 min. In the longer hot-press times, however, over-heating of the mat resulted in significant a decrease of hardness values. Significant high correlation was observed between water absorption and thickness swelling.
Keywords
Composite Board, Heat Transferring Property, Metal Nanoparticles, Nanosilver, Thermal Conductivity Coefficient, Wood Fiber
Authors’ Info
Authors’ address
Wood Science & Technology Department, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Shahid Rajaee Teacher Training University, Tehran (Iran)
Retired, Horticulture & Forestry Science, Queensland Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (Australia)
Corresponding author
Paper Info
Citation
Taghiyari HR, Norton J (2014). Effect of silver nanoparticles on hardness in medium-density fiberboard (MDF). iForest 8: 677-680. - doi: 10.3832/ifor1188-007
Academic Editor
Giacomo Goli
Paper history
Received: Nov 27, 2013
Accepted: Aug 07, 2014
First online: Dec 17, 2014
Publication Date: Oct 01, 2015
Publication Time: 4.40 months
Copyright Information
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2014
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Web Metrics
Breakdown by View Type
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 53106
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 44479
Abstract Page Views: 2900
PDF Downloads: 4152
Citation/Reference Downloads: 15
XML Downloads: 1560
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 4076
Overall contacts: 53106
Avg. contacts per week: 91.20
Citation Metrics
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2015): 9
Average cites per year: 0.82
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
References
Structural, electrical, and optical properties of molybdenum oxide thin films prepared by post-annealing of Mo thin films. International Journal of Bio-Inorganic Hybrid Nanomaterials 1 (3): 199-207.
Gscholar
Factors affecting particleboard pressing time: interaction with catalyst systems. Research Paper FPL 208, USDA Forest Service, Madison, Wisconsin, USA, pp. 22.
Gscholar
ELENA - a methodological approach for the long term monitoring of the natural regeneration of natural forest reserves dominated by Norway spruce (Vaccinio piceetea). Austrian Journal of Forest Science 129 (2): 67-105.
Gscholar
Effect of nanosilver on the rate of heat transfer to the core of the medium density fiberboard mat. International Journal of Bio-Inorganic Hybrid Nanomaterials 2 (1): 303-308.
Gscholar