Shrub encroachment alters topsoil C:N:P stoichiometric ratios in a high-altitude forest cutover
Defeng Feng (1-2), Weikai Bao (1)
iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry, Volume 11, Issue 5, Pages 594-599 (2018)
doi: https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor2803-011
Published: Sep 25, 2018 - Copyright © 2018 SISEF
Short Communications
Abstract
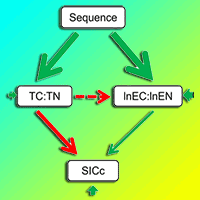
The effect of shrub encroachment on soil carbon (C): nitrogen (N): phosphorus (P) stoichiometric ratios are largely still unknown. We investigated this effect and the effect of shrub size in a high altitude forest cutover among four common shrub species: Cerasus trichostoma, Ribes glaciale, Rosa omeiensis and Salix sphaeronymphe. The difference in topsoil C:N ratio between meadows and shrub islands was greatly influenced by shrub species and plant sizes. Topsoil N:P and C:P ratios were always higher in shrub islands than in meadows, irrespective of shrub species and plant size. The expansion of shrubs merely increased the topsoil C:N ratio beneath Cerasus and Rosa, and increased the topsoil N:P and C:P ratios beneath the four shrub species. The increase in stoichiometric ratio followed an identical pattern among the four shrub species as shrub size increased. There were always higher topsoil C:P and N:P ratios beneath Ribes than under the other shrub species with the same plant size. This study clearly suggests that the effect of shrub islands on soil C:N:P stoichiometric ratios was dependent on shrub species and size. Our results are conducive to clarifying the currently confusion in secondary successional trends of soil C:N:P stoichiometry.
Keywords
Plant Species, Shrub Islands, Shrub Size, Soil Stoichiometry
Authors’ Info
Authors’ address
Weikai Bao
CAS Key Laboratory of Mountain Ecological Restoration and Bioresource Utilization & Ecological Restoration and Biodiversity Conservation Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, 610041 Sichuan (China)
Research Institute of Resource Insects, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Kunming, 650224 Yunnan (China)
Corresponding author
Paper Info
Citation
Feng D, Bao W (2018). Shrub encroachment alters topsoil C:N:P stoichiometric ratios in a high-altitude forest cutover. iForest 11: 594-599. - doi: 10.3832/ifor2803-011
Academic Editor
Francesco Ripullone
Paper history
Received: Mar 30, 2018
Accepted: Jul 03, 2018
First online: Sep 25, 2018
Publication Date: Oct 31, 2018
Publication Time: 2.80 months
Copyright Information
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2018
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Web Metrics
Breakdown by View Type
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 46651
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 39491
Abstract Page Views: 3140
PDF Downloads: 3056
Citation/Reference Downloads: 15
XML Downloads: 949
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 2716
Overall contacts: 46651
Avg. contacts per week: 120.23
Citation Metrics
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2018): 8
Average cites per year: 1.00
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
References
Soil C:N stoichiometry controls carbon sink partitioning between above-ground tree biomass and soil organic matter in high fertility forests. iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry 8: 195-206.
CrossRef | Gscholar