Nitrogen deposition and its impact on forest ecosystems in the Czech Republic - change in soil chemistry and ground vegetation
Radek Novotný (1) , Václav Buriánek (1), Vít Šrámek (1), Iva Hunová (2), Irena Skorepová (3), Miloš Zapletal (4-5), Bohumír Lomský (1)
iForest - Biogeosciences and Forestry, Volume 10, Issue 1, Pages 48-54 (2016)
doi: https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor1847-009
Published: Jun 29, 2016 - Copyright © 2016 SISEF
Research Articles
Collection/Special Issue: IUFRO RG7.01.00 - Nice (France 2015)
Global Challenges of Air Pollution and Climate Change to Forests
Guest Editors: Elena Paoletti, Pierre Sicard
Abstract
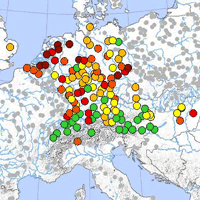
A repeated soil survey (1995 and 2006) on 66 ICP Forests pair plots in the Czech Republic revealed a significant relationship between modeled nitrogen deposition and nitrogen concentration in the soil. Nitrogen deposition was modeled for the years 1995, 2004 and 2006. We found a more significant relationship between deposition data in 2004 and soil data in 2006 than between deposition and soil data from the same year 2006. Concentration of total nitrogen in forest soil increased from 1995 to 2006. Forest soil showed effects of increased nitrogen input from the humus layer to around 20 cm depth of mineral soil. The occurrence and cover of nitrophilous species in the herb layer increased from 1995 to 2006 in 25% of the analyzed plots, which corresponds to the nitrogen increase in forest soil. The results suggest that nitrogen deposition still represents a threat for Czech forest ecosystems.
Keywords
Nitrogen Deposition, Soil Chemistry, Ground Vegetation, Ecosystem Changes, Norway Spruce
Authors’ Info
Authors’ address
Václav Buriánek
Vít Šrámek
Bohumír Lomský
Forestry and Game Management Research Institute, Strnady 136, 252 02 Jílovište (Czech Republic)
Czech Hydrometeorological Institute, Na Šabatce 2050/17, 143 06 Prague (Czech Republic)
Czech Geological Survey, Geologická 6, 152 00 Prague (Czech Republic)
Ekotoxa - Centre for Environment and Land Assessment, Otická 37, 746 01 Opava (Czech Republic)
Silesian University in Opava, Faculty of Philosophy and Science, Masarykova 37, 746 01 Opava (Czech Republic)
Corresponding author
Paper Info
Citation
Novotný R, Buriánek V, Šrámek V, Hunová I, Skorepová I, Zapletal M, Lomský B (2016). Nitrogen deposition and its impact on forest ecosystems in the Czech Republic - change in soil chemistry and ground vegetation. iForest 10: 48-54. - doi: 10.3832/ifor1847-009
Academic Editor
Elena Paoletti
Paper history
Received: Sep 01, 2015
Accepted: Mar 11, 2016
First online: Jun 29, 2016
Publication Date: Feb 28, 2017
Publication Time: 3.67 months
Copyright Information
© SISEF - The Italian Society of Silviculture and Forest Ecology 2016
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non Commercial 4.0 International (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Web Metrics
Breakdown by View Type
Article Usage
Total Article Views: 55874
(from publication date up to now)
Breakdown by View Type
HTML Page Views: 45162
Abstract Page Views: 3993
PDF Downloads: 4969
Citation/Reference Downloads: 52
XML Downloads: 1698
Web Metrics
Days since publication: 3532
Overall contacts: 55874
Avg. contacts per week: 110.74
Citation Metrics
Article Citations
Article citations are based on data periodically collected from the Clarivate Web of Science web site
(last update: Mar 2025)
Total number of cites (since 2017): 19
Average cites per year: 2.11
Publication Metrics
by Dimensions ©
Articles citing this article
List of the papers citing this article based on CrossRef Cited-by.
References
Plant sociology, the study of plants communities. Hafner, London, UK, pp. 439.
Gscholar
Assessment of ground vegetation. Manual Part VII: 18. In: “Manual on methods and criteria for harmonized sampling, assessment, monitoring and analysis of the effects of air pollution on forests”. UNECE, ICP Forests Programme Co-ordinating Centre, Hamburg, Germany, pp. 1-15.
Gscholar
Intensive monitoring of forest ecosystems in Europe: 2000 technical report. EC, UN/ECE 2000, Brussels, Belgium and Geneva, Switzerland, pp. 191.
Gscholar
Forest floor vegetation response to nitrogen deposition in Europe. Global Change Biology 20 (2): 429-440.
CrossRef | Gscholar
Monitoring stavu lesa v Ä eské republice 1984-2003 [Forest condition monitoring in the Czech Republic 1984-2003]. Ministry of Agriculture of the Czech Republic, Forestry and Game Management Research Institute, Prague, Czech Republic, pp. 431. [in Czech]
Gscholar
The condition of forests in Europe: 2012 executive report. ICP Forests, Hamburg, Germany, pp. 24.
Online | Gscholar
Development of soil chemistry on FGMRI research plots during reduction of air pollution fallout. Zprávy lesnického výzkumu 51 (2): 106-120.
Gscholar
SO2-pollution and forests decline in the Ore Mountains. Forestry and Game Management Research Institute, Strnady, Czech Republic, pp. 342.
Gscholar
ZmÄ ny ve výživÄ fosforem v mladých smrkových porostech. [Changes in phosphorus supply in the young stands of Norway spruce]. Zprávy lesnického výzkumu [Reports of forestry research] 56 (2): 83-93. [in Czech]
Gscholar
The influence of pollution on the mineral nutrition of tree species. Lesnictví 32: 569-580.
Gscholar
Nitrogen saturation in Bavarian forests - results of the nitrate inventory. Forstarchiv 76 (2): 35-43.
Gscholar
Relationships between long-term trends of air temperature, precipitation, nitrogen nutrition and growth of coniferous stands in Central Europe and Finland. European Journal of Forest Research 127: 507-524.
CrossRef | Gscholar
Modelling and mapping of atmospherically-induced ecosystem impacts in Europe. CCE Status Report 2012, Coordination Centre for Effects, RIVM, Bilthoven, The Netherlands, pp. 141.
Gscholar
The condition of forests in Europe: 2013 executive report. ICP Forests, Eberswalde, pp. 36.
Online | Gscholar
Plant ecology. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, pp. 702.
Gscholar
Über Rauhreif und Duftbruch im Erzgebirge [About rime and rimebreak in Ore Mts.]. Centralblatt fürdas gesamteForstwesen 5/6: 161. [in German]
Gscholar
Analyses of the impact of changes in atmospheric deposition and climate on forest growth in European monitoring plots: a stand growth approach. Forest Ecology and Management 258 (8): 1735-1750.
CrossRef | Gscholar
Bechädigung de Vegetation durch Rauchgase und Fabriksexhalationen. [Damage to the vegetation by fumes and factory exhalations] Urban und Schwarzwenberg Verlag, Wien, Austria and Berlin, Germany, pp. 487. [in German]
Gscholar
Depozice dusíku v lesních porostech a jejich vliv na obsah nitrátu v odtékající vodÄ a na okyselování pudy. [Nitrogen deposition in the forest stands and the effect on nitrate amount in runoff water and on soil acidification]. Zprávy lesnického výzkumu 57 (4): 352-360. [in Czech]
Gscholar
Exceedance of critical loads and of critical limits impacts tree nutrition across Europe. Annals of Forest Science 72 (7): 929-939.
CrossRef | Gscholar
Historický vývoj atmosférické depozice síry a dusíku v Ä eské republice [Historical development of atmospheric deposition of sulphur and nitrogen in the Czech Republic]. Silesian University in Opava, Faculty of Philosophy and Science, Institute of Historical Sciences, Opava, Czech Republic, pp. 136. [in Czech]
Gscholar